Open-pollinated seeds offer gardeners the advantage of saving seeds that retain their parent plant's traits, promoting biodiversity and traditional varieties. Hybrid seeds result from crossing two different parent plants to combine specific benefits like disease resistance and higher yields, but seeds saved from hybrids often do not produce true-to-type plants. Choosing between open-pollinated and hybrid seeds depends on whether long-term seed saving or maximizing immediate garden performance is the priority.
Table of Comparison
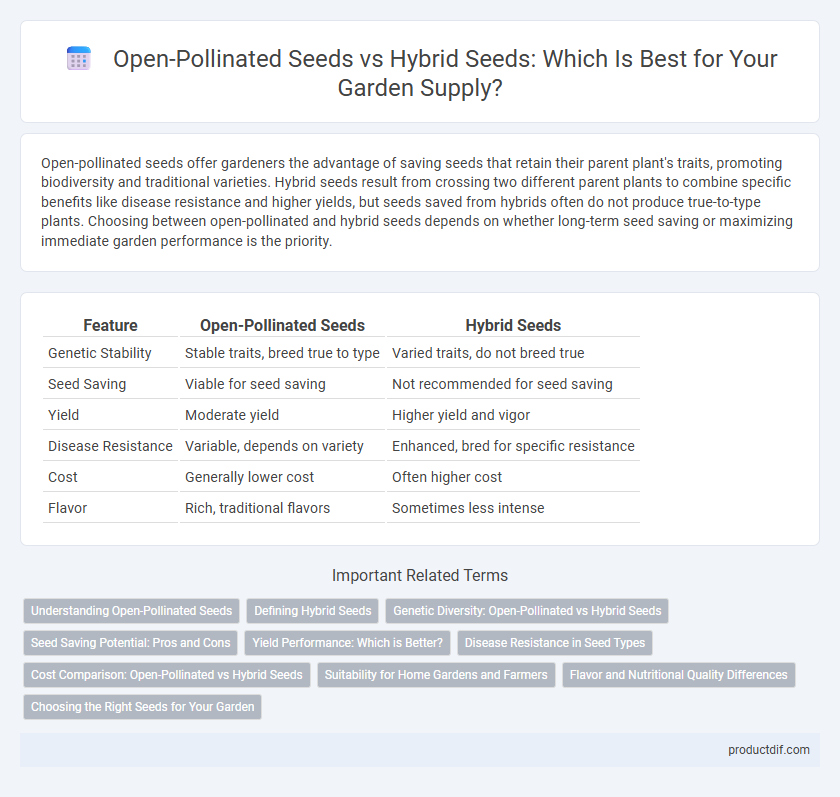
| Feature | Open-Pollinated Seeds | Hybrid Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Stability | Stable traits, breed true to type | Varied traits, do not breed true |
| Seed Saving | Viable for seed saving | Not recommended for seed saving |
| Yield | Moderate yield | Higher yield and vigor |
| Disease Resistance | Variable, depends on variety | Enhanced, bred for specific resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Often higher cost |
| Flavor | Rich, traditional flavors | Sometimes less intense |
Understanding Open-Pollinated Seeds
Open-pollinated seeds come from plants that are naturally pollinated by wind, insects, or birds, preserving true-to-type genetic traits across generations. These seeds allow gardeners to save and replant harvests, ensuring consistent plant characteristics such as flavor, growth habits, and resilience. Unlike hybrid seeds, open-pollinated varieties contribute to biodiversity and adapt well to local growing conditions, making them a preferred choice for sustainable gardening and seed saving.
Defining Hybrid Seeds
Hybrid seeds result from the controlled cross-pollination of two genetically distinct parent plants, combining specific traits to enhance yield, disease resistance, and uniformity. These seeds do not breed true to type, meaning their offspring may exhibit varied characteristics, unlike open-pollinated seeds that maintain genetic consistency across generations. Gardeners often choose hybrid seeds for predictable performance and improved productivity in specific growing conditions.
Genetic Diversity: Open-Pollinated vs Hybrid Seeds
Open-pollinated seeds preserve genetic diversity by enabling plants to naturally cross-pollinate, resulting in offspring that maintain the traits of the parent plants over generations. Hybrid seeds, created through controlled crossbreeding of specific parent varieties, often exhibit uniform characteristics but lack genetic variability, limiting adaptability to changing environmental conditions. Gardeners seeking resilience and seed-saving potential prioritize open-pollinated seeds for their contribution to long-term genetic diversity in crop populations.
Seed Saving Potential: Pros and Cons
Open-pollinated seeds offer significant seed saving potential since they breed true to type, allowing gardeners to harvest and replant seeds with consistent plant traits year after year. Hybrid seeds, created by crossing two distinct parent lines, often cannot reliably reproduce their desirable characteristics in saved seeds, leading to unpredictable plant performance in subsequent generations. While seed saving from open-pollinated varieties supports genetic diversity and cost savings, hybrid seeds typically require annual purchase for guaranteed crop uniformity and vigor.
Yield Performance: Which is Better?
Open-pollinated seeds typically produce plants with consistent traits, promoting genetic diversity but often yielding less than hybrids, which are bred for maximum productivity and disease resistance. Hybrid seeds are engineered for higher yield performance, uniformity, and vigor, making them suitable for commercial gardeners prioritizing crop quantity. While open-pollinated varieties support seed saving and adaptability, hybrid seeds deliver superior yield in intensive gardening systems.
Disease Resistance in Seed Types
Open-pollinated seeds often exhibit greater genetic diversity, which can enhance natural disease resistance across plant generations, making them favorable for organic and sustainable gardening. Hybrid seeds are selectively bred to combine specific traits from parent plants, frequently providing improved resistance to particular diseases but sometimes at the cost of reduced genetic variability. Gardeners prioritizing long-term adaptability and resilience may prefer open-pollinated seeds, while those seeking targeted disease resistance and higher yields might opt for hybrid varieties.
Cost Comparison: Open-Pollinated vs Hybrid Seeds
Open-pollinated seeds generally cost less than hybrid seeds due to their traditional breeding methods and seed saving potential, allowing gardeners to reuse seeds season after season. Hybrid seeds often come at a higher price because of the advanced breeding techniques used to enhance traits like disease resistance and yield, which increases production costs. Choosing open-pollinated seeds can reduce long-term seed expenses, while hybrids typically represent a higher upfront investment with potential benefits in crop performance.
Suitability for Home Gardens and Farmers
Open-pollinated seeds are ideal for home gardens and small-scale farmers seeking seed-saving capabilities and genetic diversity, as they produce plants true to type with stable traits across generations. Hybrid seeds, favored by commercial farmers, offer higher yields and disease resistance but do not breed true, making them less suitable for seed saving in home gardening. Selecting open-pollinated seeds supports sustainable practices and biodiversity, while hybrids cater to efficiency and uniformity in large-scale agricultural production.
Flavor and Nutritional Quality Differences
Open-pollinated seeds often produce fruits and vegetables with richer flavor profiles and higher nutritional content compared to hybrid seeds, which are typically bred for yield and uniformity rather than taste. Heirloom varieties grown from open-pollinated seeds tend to retain complex antioxidants and vitamins, enhancing both flavor depth and health benefits. Hybrid seeds may sacrifice some of these qualities due to selective breeding aimed at disease resistance and shelf life.
Choosing the Right Seeds for Your Garden
Open-pollinated seeds produce plants that grow true to type, ensuring reliable fruit and flower characteristics in subsequent generations, making them ideal for gardeners interested in seed saving and biodiversity. Hybrid seeds offer higher yields, disease resistance, and uniformity, which benefit gardeners seeking consistent, vigorous plants suited for specific growing conditions. Selecting the right seeds depends on your garden goals, whether prioritizing sustainability and preservation with open-pollinated varieties or optimizing performance and productivity through hybrids.
Open-Pollinated Seeds vs Hybrid Seeds Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com