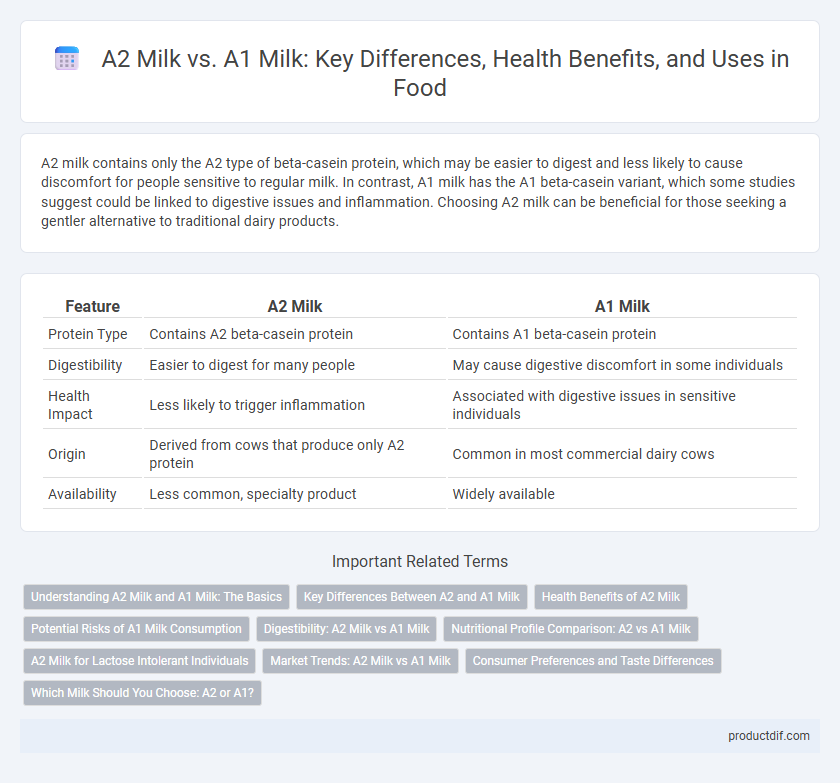
A2 milk contains only the A2 type of beta-casein protein, which may be easier to digest and less likely to cause discomfort for people sensitive to regular milk. In contrast, A1 milk has the A1 beta-casein variant, which some studies suggest could be linked to digestive issues and inflammation. Choosing A2 milk can be beneficial for those seeking a gentler alternative to traditional dairy products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | A2 Milk | A1 Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Type | Contains A2 beta-casein protein | Contains A1 beta-casein protein |
| Digestibility | Easier to digest for many people | May cause digestive discomfort in some individuals |
| Health Impact | Less likely to trigger inflammation | Associated with digestive issues in sensitive individuals |
| Origin | Derived from cows that produce only A2 protein | Common in most commercial dairy cows |
| Availability | Less common, specialty product | Widely available |
Understanding A2 Milk and A1 Milk: The Basics
A2 milk contains the A2 beta-casein protein, which differs from the A1 beta-casein found in regular milk and is believed to be easier to digest for some individuals. Research suggests that A1 beta-casein may be linked to digestive discomfort, whereas A2 milk is often marketed as a natural alternative for people sensitive to regular milk. Understanding the genetic differences between cow breeds that produce A1 or A2 proteins is essential for consumers seeking potential digestive benefits.
Key Differences Between A2 and A1 Milk
A2 milk contains the A2 beta-casein protein, which is considered easier to digest and less likely to cause digestive discomfort compared to the A1 beta-casein protein found in regular A1 milk. Studies suggest that A1 beta-casein may be linked to inflammation and digestive issues in some individuals, while A2 milk eliminates this concern by lacking the A1 protein variant. Nutritionally, both A2 and A1 milk provide similar levels of calcium, protein, and essential vitamins, but A2 milk is preferred by those with milk intolerance related to A1 proteins.
Health Benefits of A2 Milk
A2 milk contains the A2 beta-casein protein, which is associated with easier digestion and reduced risk of digestive discomfort compared to A1 milk. Studies show A2 milk may lower inflammation and improve gut health for individuals sensitive to A1 beta-casein. Its natural composition supports better nutrient absorption and may help reduce symptoms of lactose intolerance.
Potential Risks of A1 Milk Consumption
A1 milk contains a protein called beta-casein A1, which during digestion can release beta-casomorphin-7 (BCM-7), a peptide linked to potential inflammatory responses and digestive discomfort. Studies suggest that BCM-7 may contribute to increased risks of type 1 diabetes, heart disease, and neurological disorders in susceptible individuals. Consumers with lactose intolerance or milk sensitivity might experience exacerbated symptoms when consuming A1 milk compared to A2 milk, which lacks the A1 beta-casein variant.
Digestibility: A2 Milk vs A1 Milk
A2 milk contains the A2 beta-casein protein, which is believed to enhance digestibility by reducing gastrointestinal discomfort compared to A1 milk that contains A1 beta-casein. Studies indicate that A1 beta-casein can produce beta-casomorphin-7 (BCM-7) during digestion, potentially causing inflammation and digestive issues. Consumers with lactose intolerance or milk sensitivity often report better tolerance to A2 milk, suggesting improved digestive outcomes linked to protein composition.
Nutritional Profile Comparison: A2 vs A1 Milk
A2 milk contains the A2 beta-casein protein, which may be easier to digest compared to the A1 beta-casein found in regular milk, potentially reducing digestive discomfort. Both A2 and A1 milk provide similar levels of essential nutrients, including calcium, vitamin D, and protein, vital for bone health and muscle repair. Studies suggest that A2 milk might cause fewer gastrointestinal symptoms in sensitive individuals, although its overall macronutrient and micronutrient profile closely resembles that of A1 milk.
A2 Milk for Lactose Intolerant Individuals
A2 milk contains a type of beta-casein protein that is easier to digest for many lactose intolerant individuals compared to A1 milk, which can cause digestive discomfort. Studies suggest that A2 milk may reduce symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea often experienced by those with lactose intolerance. This milk is sourced from specific breeds of cows like Guernsey and Jersey, making it a suitable alternative for people sensitive to A1 protein digestion.
Market Trends: A2 Milk vs A1 Milk
The market for A2 milk is experiencing significant growth due to increasing consumer demand for dairy products perceived as easier to digest and linked to fewer health concerns compared to A1 milk. Retail data from 2023 indicates a rising market share for A2 milk in regions such as North America, Europe, and Australia, driven by health-conscious consumers and expanding product lines from major dairy brands. Forecasts predict that the A2 milk segment will continue to outperform A1 milk in sales growth, fueled by targeted marketing and growing awareness of the genetic differences between A1 and A2 beta-casein proteins.
Consumer Preferences and Taste Differences
Consumers often prefer A2 milk due to its purported easier digestibility and reduced likelihood of causing discomfort compared to A1 milk. Taste preferences vary, with some individuals describing A2 milk as creamier and milder, while A1 milk can have a slightly sharper flavor. Market trends indicate a growing demand for A2 milk driven by health-conscious consumers seeking natural alternatives.
Which Milk Should You Choose: A2 or A1?
A2 milk contains the A2 beta-casein protein, which may be easier to digest and less likely to cause gastrointestinal discomfort compared to A1 milk, which has the A1 beta-casein variant linked to digestive issues in some individuals. Scientific studies suggest A2 milk could benefit people with milk intolerance symptoms without lactose intolerance, as it reduces inflammation and bloating. Choosing A2 milk over A1 milk depends on personal digestive tolerance and potential health benefits related to beta-casein protein types.
A2 Milk vs A1 Milk Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com