Wearables primarily track health and fitness metrics through sensors embedded in devices like smartwatches and fitness bands, offering real-time monitoring of heart rate, steps, and sleep patterns. Hearables, on the other hand, focus on audio experiences, combining advanced sound technology with connectivity features such as noise cancellation, voice assistants, and biometric sensing within earbuds or hearing aids. Both categories enhance user interaction with technology but address distinctly different needs in the electronics ecosystem.
Table of Comparison
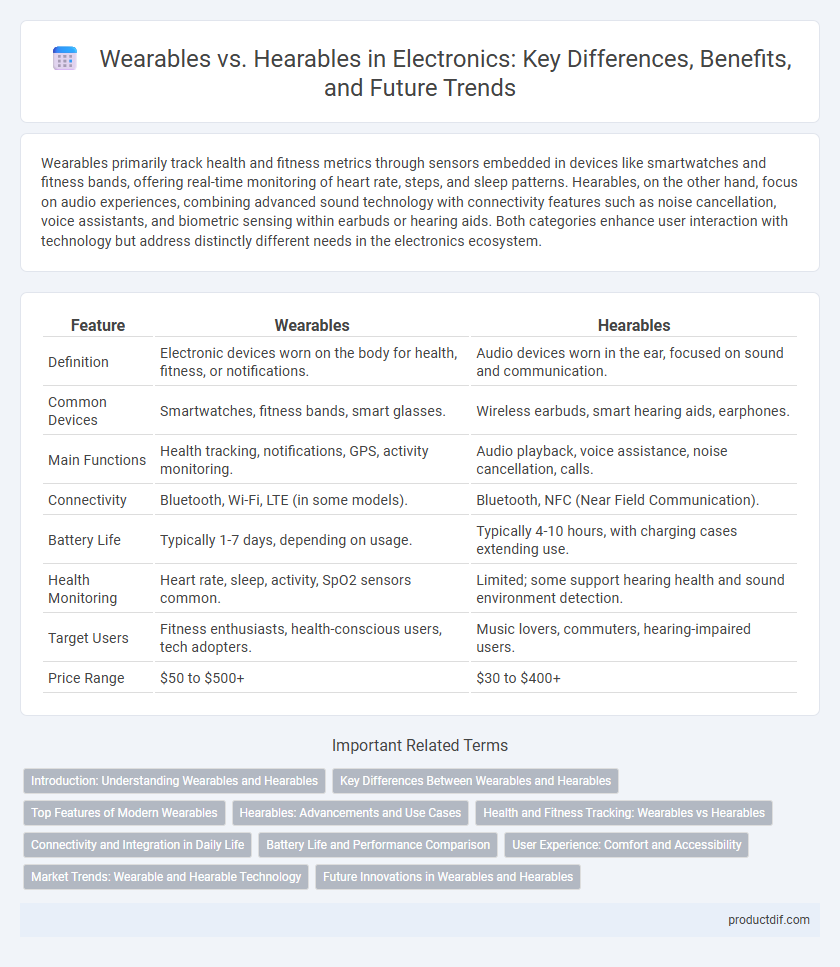
| Feature | Wearables | Hearables |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronic devices worn on the body for health, fitness, or notifications. | Audio devices worn in the ear, focused on sound and communication. |
| Common Devices | Smartwatches, fitness bands, smart glasses. | Wireless earbuds, smart hearing aids, earphones. |
| Main Functions | Health tracking, notifications, GPS, activity monitoring. | Audio playback, voice assistance, noise cancellation, calls. |
| Connectivity | Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, LTE (in some models). | Bluetooth, NFC (Near Field Communication). |
| Battery Life | Typically 1-7 days, depending on usage. | Typically 4-10 hours, with charging cases extending use. |
| Health Monitoring | Heart rate, sleep, activity, SpO2 sensors common. | Limited; some support hearing health and sound environment detection. |
| Target Users | Fitness enthusiasts, health-conscious users, tech adopters. | Music lovers, commuters, hearing-impaired users. |
| Price Range | $50 to $500+ | $30 to $400+ |
Introduction: Understanding Wearables and Hearables
Wearables are electronic devices worn on the body that monitor health metrics, fitness, and activity levels, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers. Hearables refer to advanced ear-based devices like wireless earbuds or smart hearing aids that provide audio functions alongside health and biometric monitoring. Both categories integrate sensors and connectivity features, but wearables offer broader body tracking while hearables specialize in immersive audio experiences combined with health data.
Key Differences Between Wearables and Hearables
Wearables are multifunctional electronic devices worn on the body, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, designed primarily for health monitoring, navigation, and communication. Hearables, a subset of wearables, specialize in audio-related functions like wireless earbuds and smart hearing aids, integrating features such as voice assistants, noise cancellation, and biometric sensors. The key differences lie in their form factor, primary use cases, and sensor integration, with hearables focusing more on auditory experiences and wearables offering broader usability across physical and digital health domains.
Top Features of Modern Wearables
Modern wearables boast advanced health sensors that monitor heart rate, blood oxygen levels, and sleep patterns with precise accuracy. Integration with AI-driven fitness coaching and personalized activity tracking enhances user experience and motivation. Long battery life combined with water resistance and seamless smartphone connectivity are key features defining today's wearable technology.
Hearables: Advancements and Use Cases
Hearables have advanced significantly with integrations of AI-powered noise cancellation, biometric sensors, and real-time language translation, enhancing both communication and health monitoring. These devices are widely used in fitness tracking, hearing assistance, and immersive audio experiences, offering hands-free convenience and personalized sound environments. Emerging applications also include virtual assistants and augmented reality audio, making hearables essential in smart ecosystems.
Health and Fitness Tracking: Wearables vs Hearables
Wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness bands, provide comprehensive health and fitness tracking with sensors that monitor heart rate, sleep patterns, step count, and calorie burn, offering detailed user insights. Hearables, including true wireless earbuds with embedded biosensors, focus primarily on real-time heart rate monitoring, oxygen saturation (SpO2), and VO2 max estimation, enhancing workout performance through audio feedback. Both devices leverage advanced algorithms and AI to analyze biometric data, but wearables deliver broader health metrics while hearables excel in audio-integrated fitness guidance.
Connectivity and Integration in Daily Life
Wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, offer seamless connectivity through Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, enabling real-time health monitoring and smartphone notifications. Hearables, including wireless earbuds and smart hearing aids, integrate advanced voice assistants and adaptive sound technologies to enhance communication and audio experiences. Both categories prioritize low-latency connections and synchronization with mobile devices, ensuring smooth integration into daily routines and smart ecosystems.
Battery Life and Performance Comparison
Wearables typically offer longer battery life, ranging from 4 to 7 days on a single charge due to lower power consumption designed for continuous health monitoring and activity tracking. Hearables prioritize audio performance and real-time communication features, resulting in shorter battery life usually between 4 to 8 hours but enhanced by fast-charging technologies and efficient DSP chips. Performance in wearables emphasizes sensor accuracy and connectivity stability, whereas hearables focus on high-fidelity sound quality, noise cancellation, and voice assistant integration.
User Experience: Comfort and Accessibility
Wearables prioritize user comfort with ergonomic designs that ensure seamless integration into daily activities, featuring adjustable straps and breathable materials to reduce fatigue. Hearables enhance accessibility by offering voice-controlled commands and real-time audio feedback, facilitating hands-free interaction for users. Both technologies leverage lightweight construction and intuitive interfaces to maximize prolonged use and ease of access.
Market Trends: Wearable and Hearable Technology
Wearable and hearable technology markets are experiencing rapid growth driven by advancements in sensor integration and AI capabilities. Fitness trackers and smartwatches dominate wearables with expanding health monitoring features, while hearables such as wireless earbuds incorporate voice assistants and biometric sensors for improved user interaction. Market forecasts predict the global wearable device market to reach over $60 billion by 2027, with hearables accounting for a significant share due to increasing consumer demand for multifunctional audio devices.
Future Innovations in Wearables and Hearables
Future innovations in wearables and hearables are driven by advanced sensor technology, AI integration, and improved battery efficiency, enabling more accurate health monitoring and personalized user experiences. Wearables are evolving with flexible displays and enhanced biometric data collection, while hearables incorporate spatial audio and voice recognition for seamless communication. Emerging developments in wireless charging and material science will continue to enhance comfort and functionality in both device categories.
Wearables vs Hearables Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com