A saucier features sloped sides that facilitate whisking and reducing sauces, making it ideal for emulsions and delicate preparations, while a saucepan typically has straight sides designed for boiling and simmering liquids. The saucier's rounded design prevents ingredients from getting trapped in corners, enhancing stirring efficiency. Choosing between the two depends on your cooking style and the types of sauce or dish you frequently prepare.
Table of Comparison
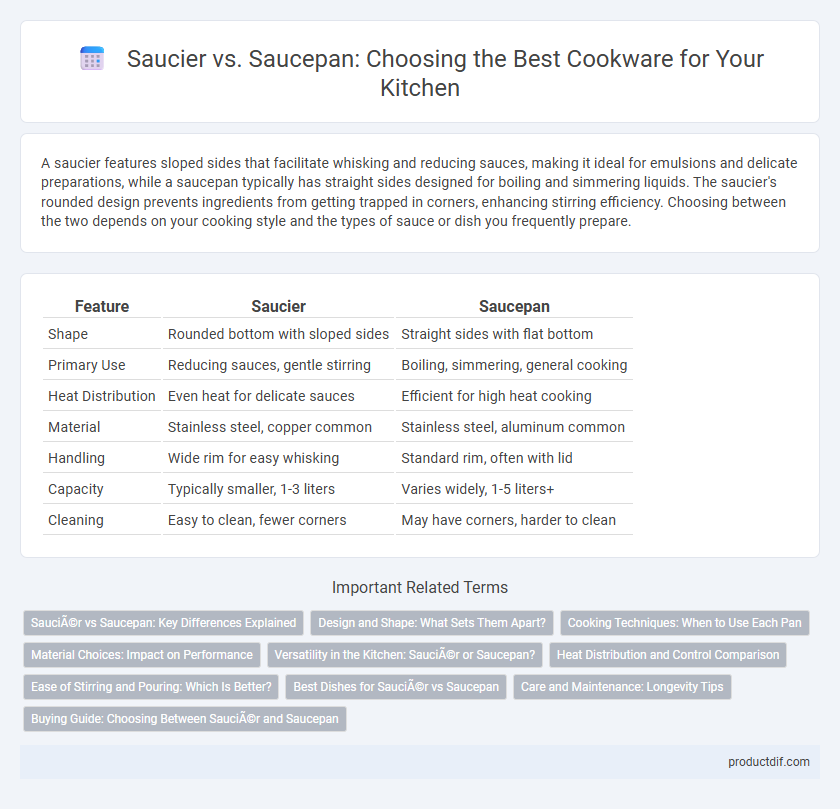
| Feature | Saucier | Saucepan |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Rounded bottom with sloped sides | Straight sides with flat bottom |
| Primary Use | Reducing sauces, gentle stirring | Boiling, simmering, general cooking |
| Heat Distribution | Even heat for delicate sauces | Efficient for high heat cooking |
| Material | Stainless steel, copper common | Stainless steel, aluminum common |
| Handling | Wide rim for easy whisking | Standard rim, often with lid |
| Capacity | Typically smaller, 1-3 liters | Varies widely, 1-5 liters+ |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean, fewer corners | May have corners, harder to clean |
Sauciér vs Saucepan: Key Differences Explained
A saucier features sloped sides that facilitate whisking and reducing sauces by preventing ingredients from sticking in corners, while a saucepan has straight sides designed for boiling and simmering liquids efficiently. The saucier's curved interior enhances stirring and makes it ideal for delicate sauces, whereas the saucepan's shape provides greater surface area for heat transfer and cooking larger quantities. Material construction for both often includes stainless steel or copper for precise temperature control, but the design distinction directly impacts usability in sauce preparation.
Design and Shape: What Sets Them Apart?
Saucier features rounded, sloping sides that facilitate easy stirring and whisking, ideal for preparing sauces and reductions, while saucepans have straight, high sides that maximize liquid capacity and even heat distribution. The wide base and curved edges of a saucier prevent ingredients from getting stuck in corners, enhancing smooth sauce preparation, whereas the saucepan's more vertical shape suits boiling or simmering tasks. These distinct design elements cater to specific cooking techniques, making each essential for different culinary needs.
Cooking Techniques: When to Use Each Pan
Saucier pans feature rounded sides, promoting even heat distribution and making them ideal for reducing sauces and stirring continuously to prevent burning. Saucepan pans have straight sides, providing greater volume and making them better suited for boiling, simmering, and cooking liquids that require minimal stirring. Choose a saucier for delicate sauce preparations and a saucepan for general-purpose boiling and simmering tasks.
Material Choices: Impact on Performance
Choosing between a saucier and a saucepan heavily depends on material selection, as each impacts heat conductivity and cooking efficiency. Sauciers often feature copper or stainless steel with a copper core, providing precise temperature control for delicate sauces, while saucepans commonly use aluminum or stainless steel, offering even heat distribution and durability. The material's thermal properties directly influence cooking performance, with copper excelling in responsiveness and aluminum delivering consistent heat for everyday use.
Versatility in the Kitchen: Sauciér or Saucepan?
Saucier pots feature rounded interiors and sloping sides, ideal for stirring and reducing sauces without scraping, offering superior control for delicate tasks like emulsifying and glazing. Saucepan designs typically have straight sides and a flat bottom, making them versatile for boiling, simmering, and general cooking, but less efficient for sauce-specific techniques. Home cooks seeking precision in sauce preparation may prefer sauciers, while saucepans remain a practical all-purpose choice for everyday kitchen use.
Heat Distribution and Control Comparison
Saucier features rounded sides that promote even heat distribution, minimizing hotspots and enabling smooth stirring, which is ideal for delicate sauces. Saucepan typically has straight sides that can create uneven heat zones but offer better control for simmering and boiling with its precise temperature management. The saucier's design enhances gentle heat control for delicate cooking, whereas the saucepan allows for more straightforward heat adjustments during various cooking processes.
Ease of Stirring and Pouring: Which Is Better?
Sauciers feature sloped sides that facilitate effortless stirring and prevent ingredients from sticking, making them superior for tasks requiring constant agitation. Saucepan designs typically have straight sides and a narrower base, which can hinder easy stirring but improve heat distribution for boiling. For pouring, sauciers often come with wide lips and rounded edges, enabling smoother, drip-free pouring compared to the more angular spouts of saucepans.
Best Dishes for Sauciér vs Saucepan
Saucier excels in preparing delicate sauces, risottos, and reductions due to its rounded sides and wide base, which facilitate easy stirring and prevent burning. Saucepan is ideal for boiling, simmering, and reheating liquids like soups, stews, and custards thanks to its straight sides and deeper design that minimizes evaporation. Selecting the right cookware enhances cooking precision and texture, making saucier perfect for creamy dishes while saucepans suit more liquid-focused recipes.
Care and Maintenance: Longevity Tips
Saucier and saucepan cookware require proper cleaning to maintain their non-stick surfaces and prevent warping. Use gentle dish soap with a soft sponge, avoiding abrasive materials to preserve the cookware's finish and ensure even heat distribution. Regular seasoning of carbon steel sauciers and immediate drying after washing prolong their lifespan and reduce rust risks.
Buying Guide: Choosing Between Sauciér and Saucepan
When choosing between a saucier and a saucepan, consider the saucier's rounded sides for effortless stirring and reduced food sticking, ideal for delicate sauces and reductions. A saucepan's straight sides and higher walls are better suited for boiling, simmering, and cooking larger quantities of liquids or soups. Assess cooking habits and recipe requirements to select the cookware that optimizes heat distribution, ease of use, and cleaning efficiency.
Sauciér vs Saucepan Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com