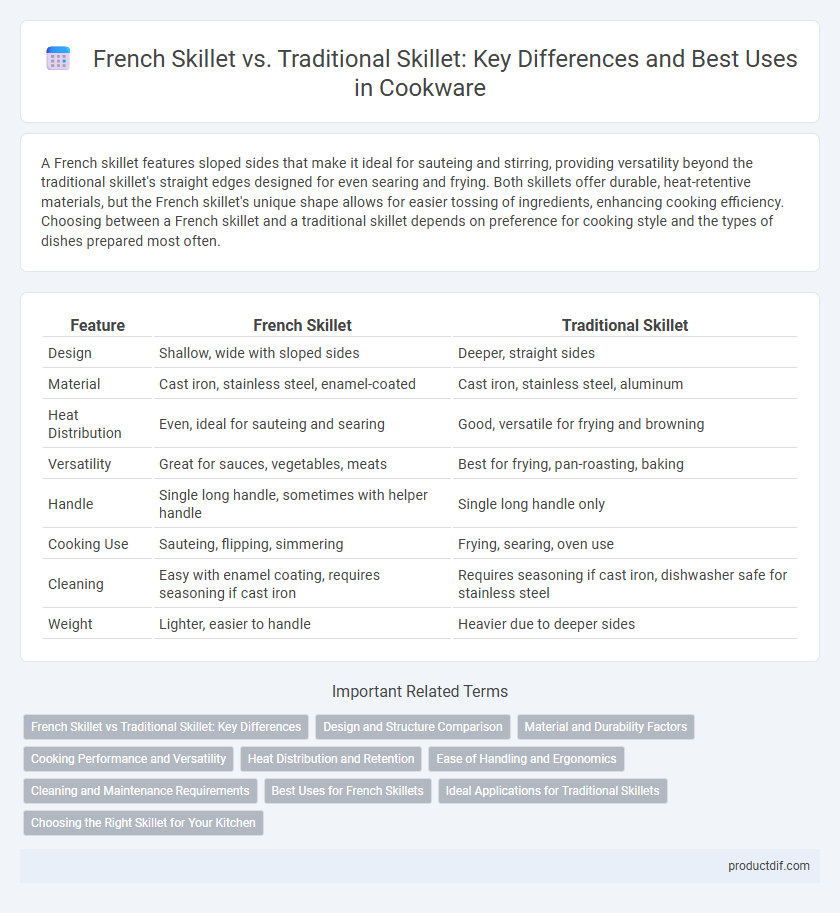
A French skillet features sloped sides that make it ideal for sauteing and stirring, providing versatility beyond the traditional skillet's straight edges designed for even searing and frying. Both skillets offer durable, heat-retentive materials, but the French skillet's unique shape allows for easier tossing of ingredients, enhancing cooking efficiency. Choosing between a French skillet and a traditional skillet depends on preference for cooking style and the types of dishes prepared most often.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | French Skillet | Traditional Skillet |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Shallow, wide with sloped sides | Deeper, straight sides |
| Material | Cast iron, stainless steel, enamel-coated | Cast iron, stainless steel, aluminum |
| Heat Distribution | Even, ideal for sauteing and searing | Good, versatile for frying and browning |
| Versatility | Great for sauces, vegetables, meats | Best for frying, pan-roasting, baking |
| Handle | Single long handle, sometimes with helper handle | Single long handle only |
| Cooking Use | Sauteing, flipping, simmering | Frying, searing, oven use |
| Cleaning | Easy with enamel coating, requires seasoning if cast iron | Requires seasoning if cast iron, dishwasher safe for stainless steel |
| Weight | Lighter, easier to handle | Heavier due to deeper sides |
French Skillet vs Traditional Skillet: Key Differences
French skillets feature sloped sides that facilitate easy stirring and flipping, while traditional skillets have straight, vertical sides ideal for searing and retaining moisture. The design of French skillets makes them versatile for sauteing vegetables and cooking sauces, whereas traditional skillets excel in frying and browning meats. Material composition often overlaps, but French skillets are typically lighter and preferred for delicate tasks, contrasting with the heavier, sturdier build of traditional skillets suited for high-heat cooking.
Design and Structure Comparison
French skillets typically feature sloped sides and a wide flat base, facilitating easy stirring and flipping of ingredients, while traditional skillets often have straighter sides and a more compact shape that retains heat effectively. The design of French skillets caters to sauteing and browning with quick evaporation, whereas traditional skillets are versatile for searing and frying with better heat distribution. Both skillets usually include long handles for maneuverability, but French skillets may lack a lid compared to some traditional skillet models which come with fitted covers.
Material and Durability Factors
French skillets, often crafted from high-quality stainless steel or heavy-gauge aluminum, provide excellent heat conductivity and resistance to warping, enhancing durability for frequent use. Traditional skillets, typically made from cast iron or carbon steel, excel in heat retention and develop a natural non-stick seasoning over time, offering long-lasting performance with proper care. The choice between these materials impacts the skillet's weight, maintenance, and longevity, with French skillets favoring lightweight durability and traditional skillets emphasizing robust, enduring construction.
Cooking Performance and Versatility
French skillets, characterized by their sloped sides and lightweight design, offer superior heat distribution and quick temperature adjustments, making them ideal for sauteing and delicate cooking tasks. Traditional skillets feature straight sides and a heavier build, providing excellent heat retention suitable for frying, searing, and versatile oven use. The choice between a French skillet and a traditional skillet hinges on cooking performance preferences and the need for versatility in various culinary techniques.
Heat Distribution and Retention
French skillets, often made from heavier materials like cast iron or carbon steel, provide superior heat retention, enabling more consistent cooking temperatures compared to traditional skillets, which are typically lighter and may lose heat more quickly. The thicker construction of French skillets ensures even heat distribution across the cooking surface, reducing hotspots and promoting uniform browning. Traditional skillets, while versatile, may require more active heat management to prevent uneven cooking due to their thinner metal composition.
Ease of Handling and Ergonomics
French skillets feature a sloped side design and a long handle, facilitating easier stirring and flipping, which enhances ease of handling during cooking. Traditional skillets typically have straight sides and a shorter handle, providing stable heat retention but requiring more effort to maneuver. Ergonomically, the French skillet's lightweight construction and balanced grip reduce wrist strain, making it preferable for prolonged cooking tasks.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
French skillets typically have sloped sides that make them easier to stir and clean, while traditional skillets with straight sides can trap more food residue. Cast iron French skillets require seasoning and careful drying to prevent rust, whereas non-stick traditional skillets demand gentle cleaning to preserve their coating. Both types benefit from hand washing and avoiding abrasive scrubbers to maintain their cooking surfaces and extend lifespan.
Best Uses for French Skillets
French skillets, characterized by their straight sides and wide surface area, excel in searing, sauteing, and deglazing due to their ability to contain liquids and facilitate even heat distribution. They are ideal for cooking dishes that require simmering sauces or frying with minimal oil, such as chicken piccata or pan-fried vegetables. Their design makes them perfect for recipes needing both stovetop and oven finishing, enhancing versatility in meal preparation.
Ideal Applications for Traditional Skillets
Traditional skillets excel in high-heat cooking methods such as frying, searing, and browning due to their flat, shallow surface and sloped sides that facilitate easy flipping and stirring. They are ideal for preparing foods that require quick, even heat distribution like sauteed vegetables, pancakes, and grilled sandwiches. Their versatile design suits everyday tasks where efficient moisture evaporation and fast cooking are essential.
Choosing the Right Skillet for Your Kitchen
A French skillet, with its straight sides and larger surface area, is ideal for sauteing and searing, offering better heat distribution for precise cooking. Traditional skillets typically feature sloped sides, which make flipping and stirring easier, perfect for tasks like frying and scrambling. Choosing the right skillet depends on your cooking style and the types of dishes you prepare most often, ensuring optimal performance and versatility in your kitchen.
French Skillet vs Traditional Skillet Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com