Induction cookware requires a magnetic base to work efficiently with induction cooktops, while gas-compatible cookware must withstand direct flame and distribute heat evenly. Stainless steel and cast iron are ideal for both induction and gas stoves due to their durability and magnetic properties. Choosing cookware that supports both cooking methods ensures versatility and optimal cooking performance in any kitchen setup.
Table of Comparison
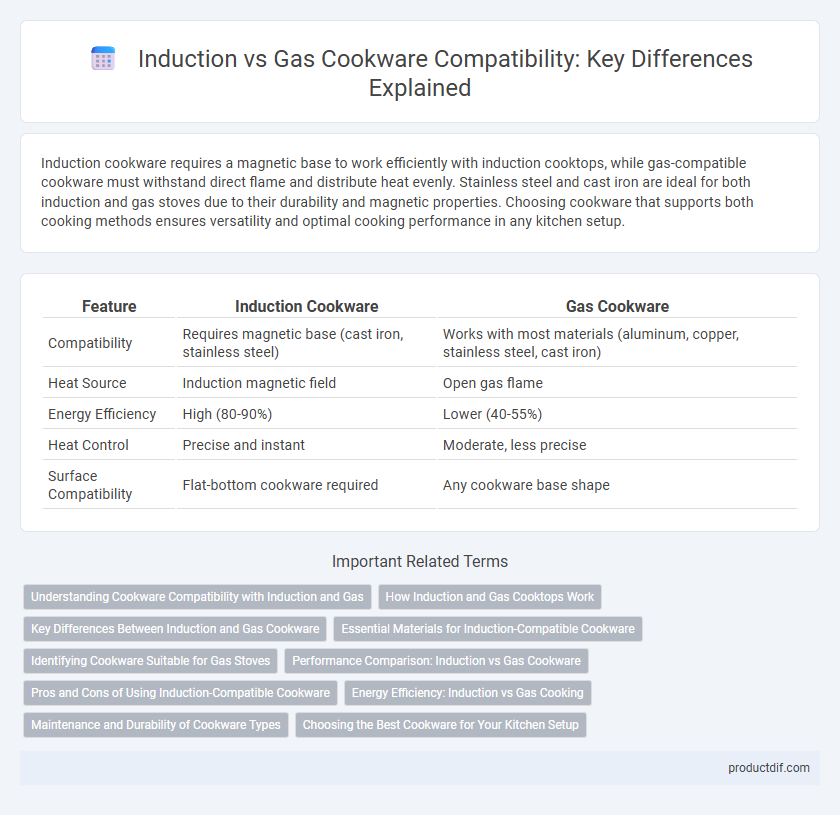
| Feature | Induction Cookware | Gas Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | Requires magnetic base (cast iron, stainless steel) | Works with most materials (aluminum, copper, stainless steel, cast iron) |
| Heat Source | Induction magnetic field | Open gas flame |
| Energy Efficiency | High (80-90%) | Lower (40-55%) |
| Heat Control | Precise and instant | Moderate, less precise |
| Surface Compatibility | Flat-bottom cookware required | Any cookware base shape |
Understanding Cookware Compatibility with Induction and Gas
Cookware compatibility with induction and gas cooktops depends on the material's magnetic properties and heat conductivity. Induction cooktops require magnetic materials like cast iron or stainless steel with a magnetic base to generate heat through electromagnetic fields. Gas stoves work with almost any cookware material, but those with heavy, flat bottoms provide optimal heat distribution and efficiency.
How Induction and Gas Cooktops Work
Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to directly heat compatible cookware through magnetic induction, ensuring rapid and precise temperature control. Gas cooktops generate an open flame fueled by natural gas or propane, providing immediate heat that can be visually adjusted. While induction requires ferromagnetic materials for optimal performance, gas cooktops work with virtually any type of cookware, offering broader compatibility.
Key Differences Between Induction and Gas Cookware
Induction cookware requires magnetic materials such as stainless steel or cast iron to generate heat through electromagnetic fields, while gas cookware works with any material by direct flame contact. Induction offers precise temperature control and faster heating times, whereas gas provides more visual heat adjustment and versatility with different cookware types. Compatibility with induction stoves depends on the cookware's magnetic properties, whereas gas cooktops accommodate a broader range of pots and pans.
Essential Materials for Induction-Compatible Cookware
Essential materials for induction-compatible cookware include ferromagnetic metals such as cast iron, stainless steel with a magnetic base, and enameled steel, which allow efficient electromagnetic induction heating. Cookware must have a magnetic bottom to trigger induction cooktops, as non-magnetic materials like aluminum, copper, or glass are generally incompatible unless layered with a magnetic plate. Choosing cookware with high-quality ferromagnetic properties ensures optimal energy transfer, faster heating, and enhanced cooking performance on induction stoves.
Identifying Cookware Suitable for Gas Stoves
Cookware suitable for gas stoves typically features materials like stainless steel, cast iron, and copper due to their excellent heat conductivity and durability under direct flame. Unlike induction-compatible cookware, gas stove pots and pans do not require magnetic properties, allowing a broader variety of metals and styles. Selecting cookware with a flat bottom and sturdy construction ensures even heat distribution and stability atop gas burners, enhancing cooking performance.
Performance Comparison: Induction vs Gas Cookware
Induction cookware offers faster heating and precise temperature control by using electromagnetic energy directly on magnetic cookware, resulting in higher energy efficiency compared to gas. Gas cookware provides more visual heat cues and instant flame adjustment but often leads to uneven heating and greater energy loss. Performance-wise, induction excels in speed and efficiency, while gas remains favored for traditional cooking techniques requiring tactile heat management.
Pros and Cons of Using Induction-Compatible Cookware
Induction-compatible cookware offers precise temperature control and energy efficiency due to its magnetic base, which rapidly heats only the pan without wasting energy on the surrounding stovetop. However, it requires ferromagnetic materials like cast iron or stainless steel, limiting compatibility compared to gas cookware that works with virtually any pot or pan. The non-reactive surface of many induction pans reduces food sticking and rust, yet they can be more expensive upfront and less versatile on non-induction cooktops.
Energy Efficiency: Induction vs Gas Cooking
Induction cookware offers superior energy efficiency by directly heating the pan through electromagnetic fields, minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment. Gas cooking systems waste more energy as heat dissipates around the burner and cookware, often requiring higher energy input for the same cooking results. Studies indicate induction cooktops can be up to 84% energy-efficient, whereas gas ranges typically operate around 40-55% efficiency, making induction a more sustainable choice for energy-conscious kitchens.
Maintenance and Durability of Cookware Types
Induction cookware requires magnetic materials like cast iron or stainless steel for optimal performance, offering high durability and resistance to warping when maintained properly. Gas cookware, often made from aluminum or copper, provides excellent heat conductivity but may experience quicker wear and require more frequent polishing and maintenance. Proper cleaning and avoidance of abrasive materials extend the lifespan of both types, ensuring sustained cooking efficiency and surface integrity.
Choosing the Best Cookware for Your Kitchen Setup
When selecting cookware, consider your kitchen's heat source to ensure compatibility. Induction cookware requires magnetic materials such as cast iron or stainless steel with a ferrous base, whereas gas cookware offers more flexibility across various materials like copper, aluminum, and non-magnetic stainless steel. Prioritize cookware that maximizes heat efficiency and durability for your induction or gas stove to optimize cooking performance and energy use.
Induction vs Gas Compatibility Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com