Ceramic cookware offers excellent heat retention and non-stick properties, making it ideal for low to medium heat cooking, while porcelain cookware is known for its durability and resistance to chipping, often used for elegant serving dishes. Ceramic cookware is typically made from natural clay and is more porous, which may require seasoning or care to prevent staining, whereas porcelain is a type of ceramic fired at higher temperatures resulting in a denser, glass-like finish. Choosing between ceramic and porcelain cookware depends on whether you prioritize cooking performance or aesthetic appeal and longevity.
Table of Comparison
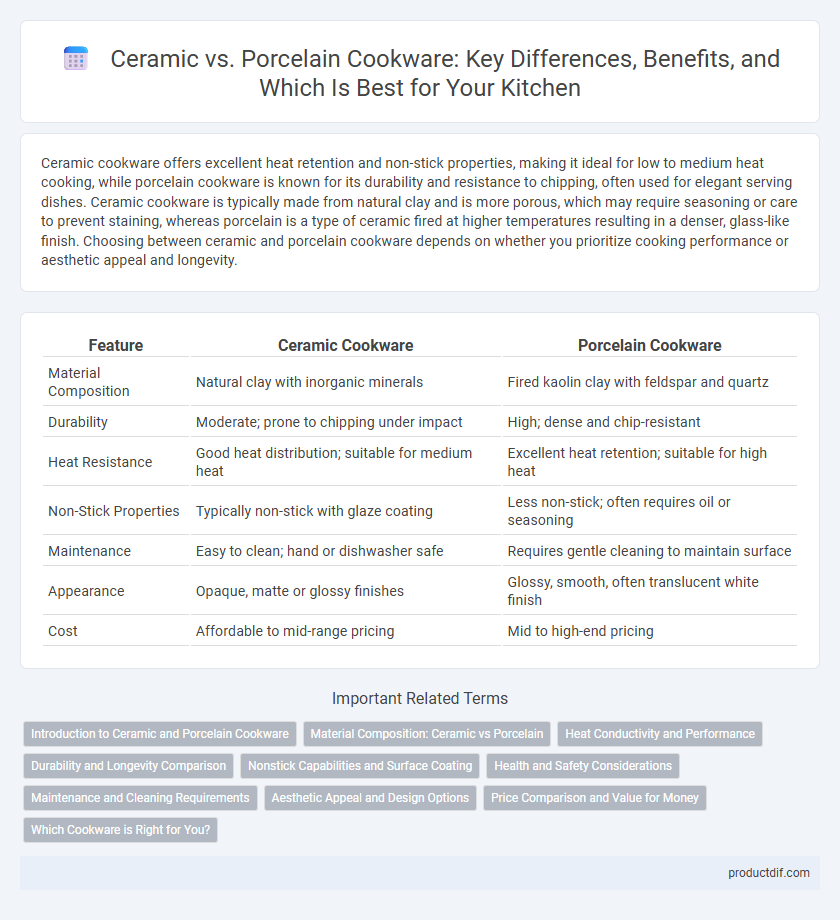
| Feature | Ceramic Cookware | Porcelain Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural clay with inorganic minerals | Fired kaolin clay with feldspar and quartz |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chipping under impact | High; dense and chip-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Good heat distribution; suitable for medium heat | Excellent heat retention; suitable for high heat |
| Non-Stick Properties | Typically non-stick with glaze coating | Less non-stick; often requires oil or seasoning |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean; hand or dishwasher safe | Requires gentle cleaning to maintain surface |
| Appearance | Opaque, matte or glossy finishes | Glossy, smooth, often translucent white finish |
| Cost | Affordable to mid-range pricing | Mid to high-end pricing |
Introduction to Ceramic and Porcelain Cookware
Ceramic cookware features a non-stick, heat-resistant glaze made from natural clay and minerals, offering excellent heat retention and even cooking performance. Porcelain cookware is crafted from fine, dense clay fired at high temperatures, resulting in a smooth, durable surface that resists chipping and scratching. Both materials provide chemical-free, eco-friendly options for safer cooking but differ in texture, weight, and temperature tolerance.
Material Composition: Ceramic vs Porcelain
Ceramic cookware is primarily made from clay that is fired at lower temperatures and coated with a glaze, resulting in a more porous and less dense material. Porcelain cookware, crafted from a refined clay mixture fired at higher temperatures, boasts a denser, non-porous surface with superior durability and resistance to chipping. The difference in material composition directly impacts heat retention, surface hardness, and longevity in cookware performance.
Heat Conductivity and Performance
Ceramic cookware offers excellent heat conductivity, allowing for even heat distribution and consistent cooking results, while porcelain cookware generally has lower thermal conductivity, which can result in slower heating and less efficient cooking. The performance of ceramic cookware excels in maintaining steady temperatures, making it ideal for frying, sauteing, and simmering. Porcelain cookware, often used for baking and serving, performs best in oven applications due to its heat retention but is less responsive to rapid temperature changes.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Ceramic cookware is renowned for its resistance to chipping and cracking, offering moderate durability suited for everyday cooking, while porcelain cookware, typically denser and harder, provides superior toughness and longer lifespan under regular use. Porcelain's non-porous surface enhances resistance to stains and thermal shock, contributing to its extended longevity compared to ceramic options. Both materials require careful handling, but porcelain cookware generally outperforms ceramic in maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal over time.
Nonstick Capabilities and Surface Coating
Ceramic cookware features a nonstick surface derived from a silica-based coating that resists high temperatures and chemical release, enhancing safe cooking and easy cleaning. Porcelain cookware, commonly found as an enamel coating over metal, offers a smooth, non-porous surface but typically lacks inherent nonstick properties, requiring oil or butter for cooking. The ceramic coating excels in natural nonstick capabilities without synthetic chemicals, while porcelain relies more on surface smoothness and heat retention for food release.
Health and Safety Considerations
Ceramic cookware is prized for its non-toxic, PTFE- and PFOA-free composition, ensuring no harmful chemicals leach into food during cooking. Porcelain cookware, often glazed with lead-free finishes, is safe for food preparation but can chip, potentially exposing underlying materials. Both types offer heat-resistant properties, but ceramic's natural, non-porous surface reduces the risk of bacterial contamination, making it a safer option for frequent use.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Ceramic cookware requires gentle hand washing with mild detergent to preserve its non-stick surface and prevent chipping, while porcelain cookware is more durable and often dishwasher-safe, making cleaning more convenient. Both materials avoid the use of abrasive scrubbers to maintain their smooth, non-porous surfaces that resist staining and odor retention. Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of ceramic and porcelain cookware by preventing surface damage and ensuring optimal performance during cooking.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Ceramic cookware offers a wide range of vibrant colors and handcrafted finishes that enhance kitchen aesthetics with unique, artisanal designs. Porcelain cookware features a smooth, glossy surface with elegant, classic patterns often found in traditional and formal table settings. Both materials provide distinct design options, but ceramic stands out for its versatility in bold and modern styles, while porcelain excels in timeless sophistication.
Price Comparison and Value for Money
Ceramic cookware typically offers a more affordable price point compared to porcelain cookware, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious consumers. Porcelain cookware often features enhanced durability and a refined finish, which can justify its higher cost for those seeking long-term investment. When evaluating value for money, ceramic cookware suits everyday cooking needs, while porcelain cookware provides superior heat retention and aesthetic appeal for premium kitchen setups.
Which Cookware is Right for You?
Ceramic cookware offers excellent heat retention and non-stick properties, making it ideal for low-fat cooking and easy cleaning, while porcelain cookware provides superior durability and resistance to chipping, suitable for frequent oven use and elegant table presentation. Consider ceramic cookware if you prioritize lightweight and eco-friendly materials with non-toxic coatings, whereas porcelain is better if you seek versatile cookware that transitions seamlessly from stovetop to oven with a glossy, aesthetic finish. Your choice depends on cooking style, maintenance preferences, and desired durability in cookware performance.
Ceramic Cookware vs Porcelain Cookware Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com