Induction cookware requires magnetic materials like cast iron or stainless steel to work efficiently, while gas-compatible cookware can be made from a wider range of materials including aluminum and copper. Induction cooking offers faster heating and precise temperature control, whereas gas provides visual flame control and versatility for different cooking techniques. Choosing between induction and gas-compatible cookware depends on your stovetop type and cooking preferences.
Table of Comparison
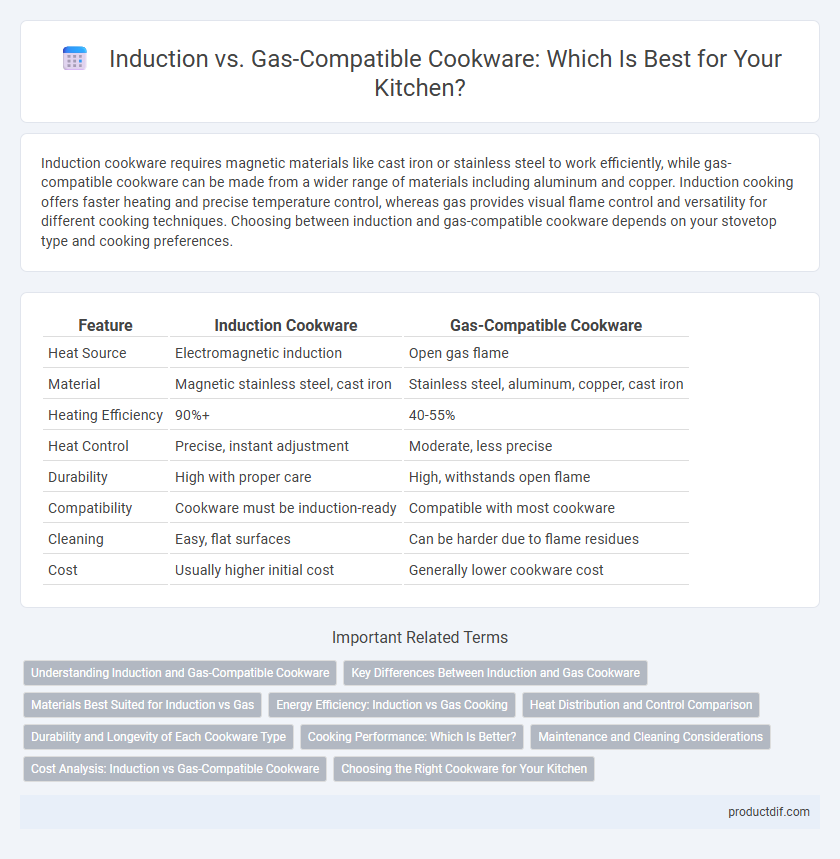
| Feature | Induction Cookware | Gas-Compatible Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Electromagnetic induction | Open gas flame |
| Material | Magnetic stainless steel, cast iron | Stainless steel, aluminum, copper, cast iron |
| Heating Efficiency | 90%+ | 40-55% |
| Heat Control | Precise, instant adjustment | Moderate, less precise |
| Durability | High with proper care | High, withstands open flame |
| Compatibility | Cookware must be induction-ready | Compatible with most cookware |
| Cleaning | Easy, flat surfaces | Can be harder due to flame residues |
| Cost | Usually higher initial cost | Generally lower cookware cost |
Understanding Induction and Gas-Compatible Cookware
Induction cookware features ferromagnetic materials like stainless steel or cast iron, allowing efficient heat transfer through electromagnetic currents on induction cooktops. Gas-compatible cookware is typically made from materials such as copper, aluminum, or stainless steel with a flat bottom to ensure even heat distribution on open flames. Understanding these differences helps select pots and pans that optimize cooking performance for each stovetop type.
Key Differences Between Induction and Gas Cookware
Induction cookware requires a magnetic base, typically made of stainless steel or cast iron, to generate heat through electromagnetic fields, whereas gas cookware can be made from a wider variety of materials since it relies on an open flame. Induction cookware offers faster heating and more precise temperature control, while gas cookware provides visible flame and instant heat adjustment favored by professional chefs. Compatibility also differs: induction needs flat, ferromagnetic surfaces, but gas burners accommodate non-magnetic materials like aluminum or copper, allowing greater versatility in cookware choice.
Materials Best Suited for Induction vs Gas
Cookware materials best suited for induction cooking include magnetic stainless steel, cast iron, and enameled iron, as they effectively conduct magnetic fields needed for induction heating. In contrast, gas-compatible cookware often features materials such as copper, aluminum, and non-magnetic stainless steel, which provide excellent heat distribution and durability over open flames. Choosing the right material ensures optimal performance: induction requires magnetism for heat generation, while gas relies on direct flame contact and heat conductivity.
Energy Efficiency: Induction vs Gas Cooking
Induction cookware offers superior energy efficiency by directly heating the pan through electromagnetic fields, minimizing heat loss compared to gas stoves that convert energy into flame and heat the surrounding air. Induction cooking typically achieves an energy efficiency of 80-90%, whereas gas cooking generally operates at 40-55% efficiency due to heat dispersion. Choosing induction cookware reduces energy consumption and shortens cooking times, making it an eco-friendly and cost-effective option for modern kitchens.
Heat Distribution and Control Comparison
Induction cookware offers superior heat distribution through electromagnetic energy, providing rapid and uniform heating that minimizes hot spots. Gas-compatible cookware relies on flame heat, which can create uneven temperatures and slower response times when adjusting heat levels. Precision and energy efficiency make induction cookware ideal for delicate cooking, while gas-compatible pots offer versatile control favored by experienced chefs.
Durability and Longevity of Each Cookware Type
Induction-compatible cookware features magnetic stainless steel or cast iron construction, offering exceptional durability and resistance to warping over extended use. Gas-compatible cookware, often made from materials like copper, aluminum, or non-magnetic stainless steel, provides excellent heat distribution but may experience faster wear due to direct flame exposure and higher risk of warping. The longevity of induction cookware tends to surpass gas-compatible options, driven by its sturdy build and ability to maintain performance without degrading under intense heat fluctuations.
Cooking Performance: Which Is Better?
Induction cookware offers superior cooking performance with rapid, even heat distribution and precise temperature control, reducing cooking times and energy consumption. Gas-compatible cookware performs well with instant heat adjustments and works on all stovetops but may have uneven heat distribution causing hot spots. For consistent results and energy efficiency, induction-compatible cookware is generally considered better.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Induction cookware typically features a smooth, flat magnetic base that resists food sticking and allows for easy cleaning with a soft cloth, while gas-compatible cookware may develop soot and grease buildup on the exterior, requiring more frequent scrubbing. Stainless steel induction pots and pans often withstand abrasive cleaners better than non-stick gas-compatible options, which can degrade with harsh cleaning methods. Proper maintenance for induction cookware involves avoiding metal utensils that can scratch the surface, whereas gas-compatible cookware demands regular inspection of flame exposure spots to prevent discoloration and damage.
Cost Analysis: Induction vs Gas-Compatible Cookware
Induction cookware typically costs more upfront due to specialized magnetic materials, while gas-compatible cookware is generally less expensive and widely available. Energy efficiency in induction cooking reduces long-term utility expenses, offsetting initial higher costs compared to gas stoves with open flames, which consume more energy. Maintenance and replacement frequency further influence overall cost, with induction cookware often lasting longer due to even heating and less wear.
Choosing the Right Cookware for Your Kitchen
Selecting cookware compatible with your cooking surface is essential for efficient meal preparation and energy use. Induction cookware requires magnetic materials like stainless steel or cast iron to generate heat, while gas-compatible cookware can be made from various materials, including copper, aluminum, and cast iron, offering direct flame contact for versatility. Understanding the compatibility ensures optimal heat distribution and prolongs the lifespan of your cookware set.
Induction vs Gas-Compatible Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com