A saute pan features straight, tall sides and a wide surface, making it ideal for searing, frying, and reducing sauces with ease. A braiser has a wider, shallower shape with sloped sides and a tight-fitting lid, perfect for slow-cooking and braising tougher cuts of meat to tender perfection. Choosing between saute pans and braisers depends on cooking method and the desired texture of your dish.
Table of Comparison
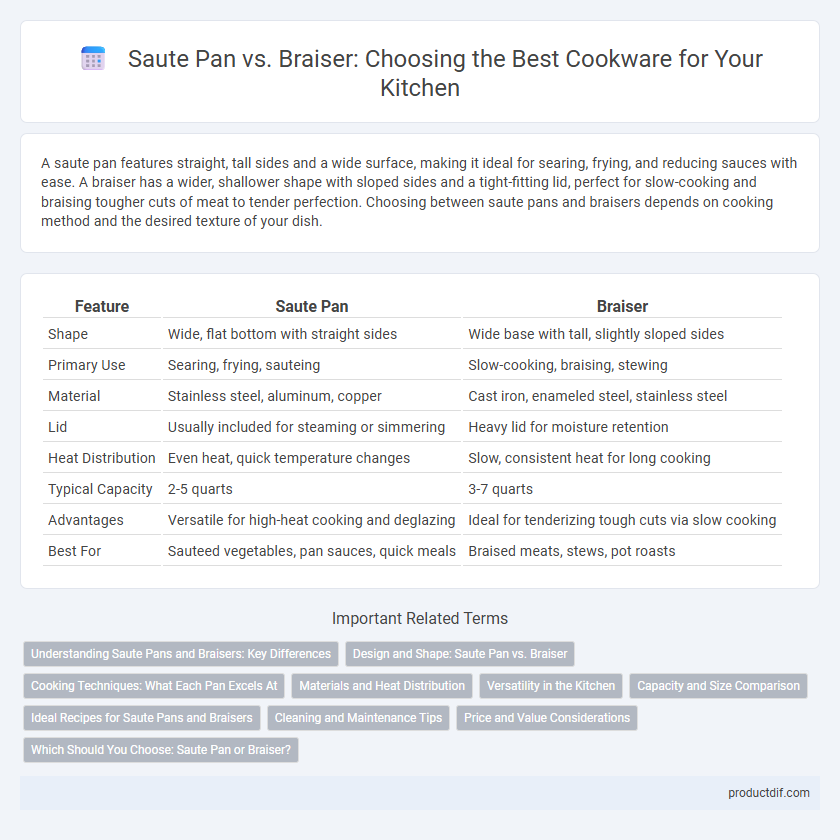
| Feature | Saute Pan | Braiser |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Wide, flat bottom with straight sides | Wide base with tall, slightly sloped sides |
| Primary Use | Searing, frying, sauteing | Slow-cooking, braising, stewing |
| Material | Stainless steel, aluminum, copper | Cast iron, enameled steel, stainless steel |
| Lid | Usually included for steaming or simmering | Heavy lid for moisture retention |
| Heat Distribution | Even heat, quick temperature changes | Slow, consistent heat for long cooking |
| Typical Capacity | 2-5 quarts | 3-7 quarts |
| Advantages | Versatile for high-heat cooking and deglazing | Ideal for tenderizing tough cuts via slow cooking |
| Best For | Sauteed vegetables, pan sauces, quick meals | Braised meats, stews, pot roasts |
Understanding Saute Pans and Braisers: Key Differences
Saute pans feature straight sides and a wide flat bottom, ideal for quick cooking methods such as searing and frying with easy stirring and flipping. Braisers have deeper, slightly sloped sides and a tight-fitting lid, designed for slow cooking techniques like braising and stewing that require moisture retention and even heat distribution. Understanding these key differences helps choose the right cookware for recipes that demand either high-heat sauteing or gentle, prolonged cooking.
Design and Shape: Saute Pan vs. Braiser
A saute pan features straight, tall sides and a wide, flat bottom designed for high-heat searing and quick, even cooking of ingredients with minimal stirring. In contrast, a braiser combines a wide, heavy base with sloped sides and a tight-fitting lid, optimized for slow cooking and braising, allowing moisture to circulate and tenderize tougher cuts of meat. The saute pan's design facilitates easy flipping and sauteing, while the braiser's shape supports long, low-temperature cooking and moisture retention.
Cooking Techniques: What Each Pan Excels At
Saute pans feature wide, flat bottoms and tall, straight sides ideal for high-heat techniques like searing, frying, and sauteing, allowing quick evaporation and browning. Braisers combine a wide, shallow design with a tight-fitting lid, excelling at slow-cooking methods like braising and simmering, which require even heat distribution and moisture retention. Each pan's structural design optimizes cooking performance for specific methods, enhancing flavor development and texture in dishes.
Materials and Heat Distribution
Saute pans are commonly made from stainless steel or aluminum with copper or aluminum cores to enhance heat conductivity and ensure quick, even heat distribution ideal for searing and frying. Braisers typically feature heavy-gauge carbon steel or enameled cast iron, materials that retain heat longer and distribute it slowly, perfect for low-and-slow cooking and braising. The choice between these materials directly affects cooking performance: saute pans excel in rapid heat response, while braisers provide consistent, gentle heat over extended periods.
Versatility in the Kitchen
A saute pan's high, straight sides and wide surface area make it ideal for searing, sauteing, and frying a variety of foods, offering excellent versatility for everyday cooking tasks. In contrast, a braiser combines the features of a saute pan and a Dutch oven, featuring a heavy lid and thicker base designed for slow-cooking, braising, and roasting, which adds depth to its multifunctional use. Choosing between a saute pan and a braiser depends on the cooking methods you prioritize, with the saute pan excelling in quick, high-heat techniques, while the braiser is better suited for long, slow simmering and one-pot meals.
Capacity and Size Comparison
Saute pans typically offer a wide range of capacities from 3 to 5 quarts, featuring a straight, tall sidewall design that provides ample cooking surface and even heat distribution, ideal for browning and searing. Braisers generally have larger capacities, often between 4 to 7 quarts, with a wider base and lower sides, designed to accommodate braising large cuts of meat or slow-cooking vegetables with liquid. When comparing size, saute pans are more versatile for everyday stovetop cooking while braisers provide more volume and surface area for slow, moist heat cooking in bulk quantities.
Ideal Recipes for Saute Pans and Braisers
Saute pans excel at cooking dishes that require quick browning and tossing, such as stir-fries, seared vegetables, and pan-fried meats. Braisers are ideal for slow-cooked recipes like braised short ribs, pot roasts, and stews that benefit from even heat distribution and moisture retention. Choosing between a saute pan and a braiser depends on the cooking technique and the recipe's demand for either fast searing or slow braising.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Saute pans feature straight sides and non-stick surfaces that simplify cleaning by preventing food from sticking, while braisers often have wider bases and lower sides requiring careful scrubbing to avoid residue buildup. Both cookware types benefit from hand washing with mild detergent and avoiding abrasive scrubbers to preserve non-stick coatings and prevent damage. Regular seasoning of carbon steel or cast iron braisers ensures longevity and enhances non-stick properties, whereas stainless steel saute pans typically require less maintenance.
Price and Value Considerations
Saute pans typically offer a lower price point compared to braisers, making them accessible for everyday cooking needs without compromising on quality. Braisers, with their heavier construction and versatility for slow-cooking and searing, provide greater long-term value for chefs focused on hearty, slow-cooked meals. Investing in a braiser may involve a higher initial cost but delivers enhanced durability and multifunctional use, maximizing value over time.
Which Should You Choose: Saute Pan or Braiser?
Choosing between a saute pan and a braiser depends on cooking techniques and dish requirements. A saute pan features straight sides and a wide, flat base ideal for searing, frying, and quick-cooking vegetables or meats with minimal liquid. A braiser has deeper sides and a tight-fitting lid, perfect for slow-cooking, braising tougher cuts of meat, and retaining moisture during long cooking processes.
Saute Pan vs Braiser Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com