Forged aluminum cookware offers superior durability and heat distribution due to its manufacturing process, where solid aluminum is heated and shaped under high pressure. Stamped aluminum, made by pressing thin sheets into shape, tends to be lighter and less expensive but may warp more easily and have uneven heat conduction. Choosing forged aluminum enhances cooking performance and longevity, making it a preferred option for serious home cooks and professionals alike.
Table of Comparison
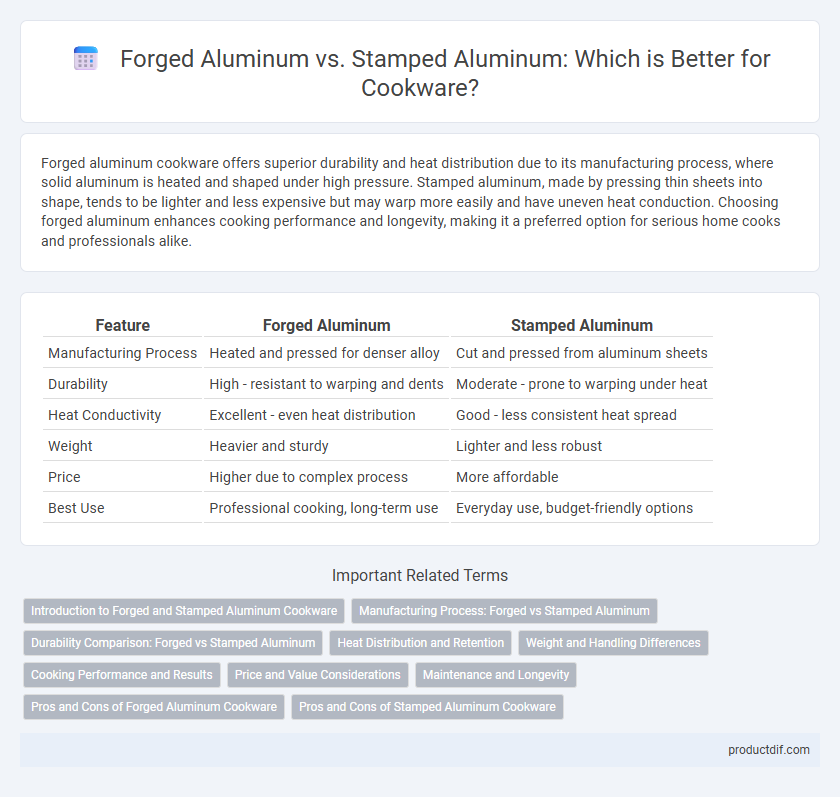
| Feature | Forged Aluminum | Stamped Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Heated and pressed for denser alloy | Cut and pressed from aluminum sheets |
| Durability | High - resistant to warping and dents | Moderate - prone to warping under heat |
| Heat Conductivity | Excellent - even heat distribution | Good - less consistent heat spread |
| Weight | Heavier and sturdy | Lighter and less robust |
| Price | Higher due to complex process | More affordable |
| Best Use | Professional cooking, long-term use | Everyday use, budget-friendly options |
Introduction to Forged and Stamped Aluminum Cookware
Forged aluminum cookware is created by shaping an aluminum billet under high pressure, resulting in a dense and durable material that offers superior heat distribution and resistance to warping. Stamped aluminum cookware is produced by pressing thin aluminum sheets into shape, leading to lightweight pans that heat quickly but may be less durable and prone to denting. Choosing between forged and stamped aluminum cookware depends on the desired balance of durability, heat performance, and weight for specific cooking needs.
Manufacturing Process: Forged vs Stamped Aluminum
Forged aluminum cookware is crafted by shaping solid aluminum billets under extreme heat and pressure, resulting in denser, stronger, and more durable pans with enhanced heat conduction. Stamped aluminum cookware is produced by pressing thin aluminum sheets into molds, enabling faster, cost-effective mass production but often leading to thinner, less resilient cookware with uneven heat distribution. Manufacturers prefer forged aluminum for premium performance and longevity, while stamped aluminum suits budget-friendly and lightweight options.
Durability Comparison: Forged vs Stamped Aluminum
Forged aluminum cookware exhibits superior durability compared to stamped aluminum due to its denser, more uniform metal structure created through high-pressure forging processes. This manufacturing technique enhances resistance to warping, scratching, and corrosion, making forged aluminum ideal for heavy-duty cooking applications. In contrast, stamped aluminum is thinner and more prone to dents and deformation, resulting in a shorter lifespan under frequent or intense use.
Heat Distribution and Retention
Forged aluminum cookware offers superior heat distribution and retention due to its denser, thicker construction, providing even cooking temperatures. Stamped aluminum pans are thinner and lighter, which can cause hot spots and faster heat loss. For consistent heat performance and efficient energy use, forged aluminum is generally preferred.
Weight and Handling Differences
Forged aluminum cookware is denser and heavier than stamped aluminum, providing superior durability and heat retention for consistent cooking performance. Stamped aluminum is lighter and thinner, making it easier to handle and ideal for quick, everyday use but less resistant to warping under high heat. The weight difference directly impacts maneuverability and comfort, with forged aluminum favored by professional chefs for its robust build and stability.
Cooking Performance and Results
Forged aluminum cookware delivers superior heat distribution and retention due to its denser, thicker construction, ensuring even cooking and precise temperature control. Stamped aluminum pans, being thinner and lighter, heat up quickly but may develop hot spots, leading to uneven cooking results. Professional chefs often prefer forged aluminum for its durability and consistent performance in achieving perfectly cooked meals.
Price and Value Considerations
Forged aluminum cookware typically commands a higher price due to its dense, durable construction that ensures even heat distribution and long-lasting performance. Stamped aluminum is more budget-friendly but often sacrifices thickness and durability, potentially leading to warping and uneven cooking over time. Evaluating initial cost against longevity and cooking efficiency helps determine the best value for your cookware investment.
Maintenance and Longevity
Forged aluminum cookware offers superior durability and resists warping or denting over time compared to stamped aluminum, which tends to be thinner and more prone to damage. Maintenance for forged aluminum typically involves gentle hand washing and avoiding abrasive scrubbers to preserve its nonstick properties and finish. Stamped aluminum requires more careful handling to prevent surface scratches and often has a shorter lifespan due to its susceptibility to wear and tear.
Pros and Cons of Forged Aluminum Cookware
Forged aluminum cookware offers superior durability and excellent heat retention due to its thicker, denser construction, making it ideal for high-heat cooking and even heat distribution. Its robust build resists warping and provides a longer lifespan compared to stamped aluminum, but this comes with increased weight and typically higher cost. However, forged aluminum may require more maintenance to prevent surface damage and is often less affordable for budget-conscious cooks.
Pros and Cons of Stamped Aluminum Cookware
Stamped aluminum cookware offers excellent heat conduction and affordability, making it ideal for everyday cooking and budget-conscious buyers. However, it is generally thinner and less durable than forged aluminum, leading to potential warping and uneven heating over time. While lightweight and easy to handle, stamped aluminum may lack the structural strength and long-term performance demanded by professional chefs.
Forged Aluminum vs Stamped Aluminum Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com