Enzymatic cleaners use natural enzymes to break down organic stains and debris, making them highly effective for removing protein-based messes like food, blood, and pet stains. Chemical cleaners rely on synthetic compounds that can quickly dissolve grease, dirt, and grime but may contain harsh ingredients that irritate skin or damage surfaces. Choosing between enzymatic and chemical cleaners depends on the cleaning task, desired safety, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
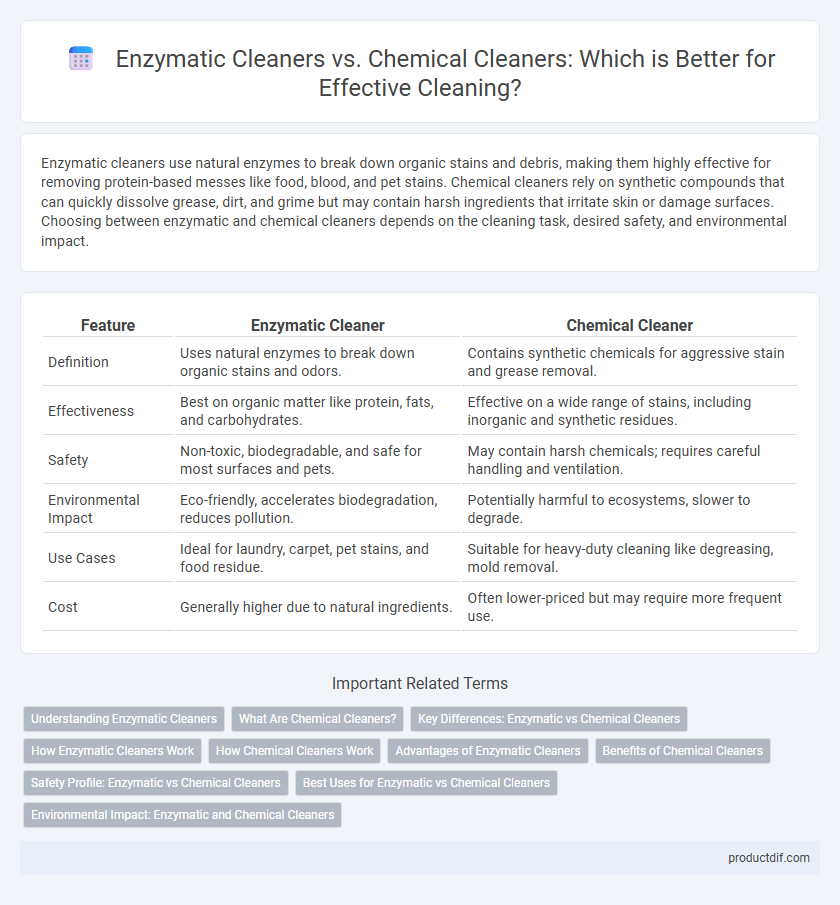
| Feature | Enzymatic Cleaner | Chemical Cleaner |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses natural enzymes to break down organic stains and odors. | Contains synthetic chemicals for aggressive stain and grease removal. |
| Effectiveness | Best on organic matter like protein, fats, and carbohydrates. | Effective on a wide range of stains, including inorganic and synthetic residues. |
| Safety | Non-toxic, biodegradable, and safe for most surfaces and pets. | May contain harsh chemicals; requires careful handling and ventilation. |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, accelerates biodegradation, reduces pollution. | Potentially harmful to ecosystems, slower to degrade. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for laundry, carpet, pet stains, and food residue. | Suitable for heavy-duty cleaning like degreasing, mold removal. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to natural ingredients. | Often lower-priced but may require more frequent use. |
Understanding Enzymatic Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners utilize natural enzymes like protease, amylase, and lipase to break down organic stains such as proteins, starches, and fats at a molecular level, making them highly effective for bio-based messes. Unlike chemical cleaners that rely on harsh solvents and detergents, enzymatic cleaners are biodegradable, non-toxic, and eco-friendly, reducing environmental impact and health risks. Their specific action targets complex stains with precision, promoting safer, deeper cleaning in medical, food, and household applications.
What Are Chemical Cleaners?
Chemical cleaners are formulated using synthetic substances designed to break down dirt, grease, and stains through chemical reactions. These cleaners often contain acids, alkalis, surfactants, and solvents that target specific types of contaminants for effective surface cleaning. Unlike enzymatic cleaners, chemical cleaners act quickly but may produce harsher residues and require careful handling to avoid damage or health risks.
Key Differences: Enzymatic vs Chemical Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners utilize natural enzymes like protease, lipase, and amylase to break down organic stains by targeting proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, making them highly effective for biological messes such as pet stains and food residues. Chemical cleaners rely on synthetic compounds, such as surfactants and solvents, to dissolve grease, dirt, and inorganic grime through chemical reactions, offering faster action but potentially harsher effects on surfaces and the environment. While enzymatic cleaners provide eco-friendly, biodegradable solutions with specificity for organic matter, chemical cleaners often deliver broader-spectrum cleaning power suitable for industrial and heavy-duty applications.
How Enzymatic Cleaners Work
Enzymatic cleaners break down organic stains and soils by using natural enzymes that target proteins, fats, and carbohydrates at a molecular level. These enzymes catalyze the breakdown of complex substances into simpler particles, making it easier to remove dirt and grime effectively. Unlike chemical cleaners that rely on harsh ingredients, enzymatic cleaners are biodegradable and safer for sensitive surfaces and the environment.
How Chemical Cleaners Work
Chemical cleaners work by using strong acids, alkalis, or solvents to break down and dissolve dirt, grease, and stains at a molecular level. They often contain surfactants that lower surface tension, allowing the cleaner to penetrate and lift away contaminants from surfaces effectively. Unlike enzymatic cleaners that biologically digest organic matter, chemical cleaners rely on reactive compounds to achieve rapid and thorough removal of a wide range of soils.
Advantages of Enzymatic Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners offer superior stain removal by breaking down organic matter such as proteins, fats, and starches at a molecular level, making them highly effective for biohazard cleaning and pet stains. These cleaners are environmentally friendly, biodegradable, and non-toxic, reducing harmful chemical residues in homes and workplaces. Enzymatic cleaners also promote safer use around children and pets, providing a sustainable alternative to harsh chemical cleaners.
Benefits of Chemical Cleaners
Chemical cleaners provide powerful and fast-acting solutions for removing tough stains, grease, and bacteria from various surfaces. Their strong chemical compounds are effective in disinfecting and sanitizing, ensuring a hygienic environment in homes and commercial spaces. Unlike enzymatic cleaners, chemical cleaners offer immediate results without relying on biological processes, making them ideal for quick and intensive cleaning tasks.
Safety Profile: Enzymatic vs Chemical Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners offer a safer profile by using natural enzymes that break down organic stains without harsh chemicals, reducing the risk of skin irritation and respiratory issues. Chemical cleaners often contain strong acids, alkalis, or solvents that can cause burns, toxic fumes, and environmental harm if not handled properly. Choosing enzymatic cleaners improves safety for users and minimizes ecological impact.
Best Uses for Enzymatic vs Chemical Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners excel at breaking down organic stains such as food, pet waste, and blood by using natural enzymes that target proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, making them ideal for household and pet-related messes. Chemical cleaners, containing strong solvents and surfactants, are more effective for removing grease, oils, and inorganic residues in industrial settings or heavy-duty cleaning tasks. Choosing between enzymatic and chemical cleaners depends on the specific stain type and cleaning environment, optimizing stain removal efficiency and surface safety.
Environmental Impact: Enzymatic and Chemical Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners break down organic stains using natural enzymes, resulting in lower toxicity and reduced environmental pollution compared to chemical cleaners, which often contain harsh synthetic compounds and volatile organic chemicals (VOCs) that can harm ecosystems. Enzymatic cleaners are biodegradable and pose minimal risks to aquatic life, while many chemical cleaners contribute to water contamination and bioaccumulation of harmful substances. Choosing enzymatic cleaners supports sustainable cleaning practices by minimizing hazardous waste and promoting safer biodegradation processes.
Enzymatic cleaner vs Chemical cleaner Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com