Enzymatic cleaners break down organic stains and debris using natural enzymes, making them highly effective for removing food, blood, and other protein-based messes without harsh chemicals. Solvent-based cleaners rely on chemical solvents to dissolve grease, oil, and synthetic residues, offering powerful cleaning for industrial and heavy-duty applications but often requiring careful ventilation. Choosing between enzymatic and solvent-based cleaners depends on the type of stain and the cleaning environment, balancing effectiveness with safety and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
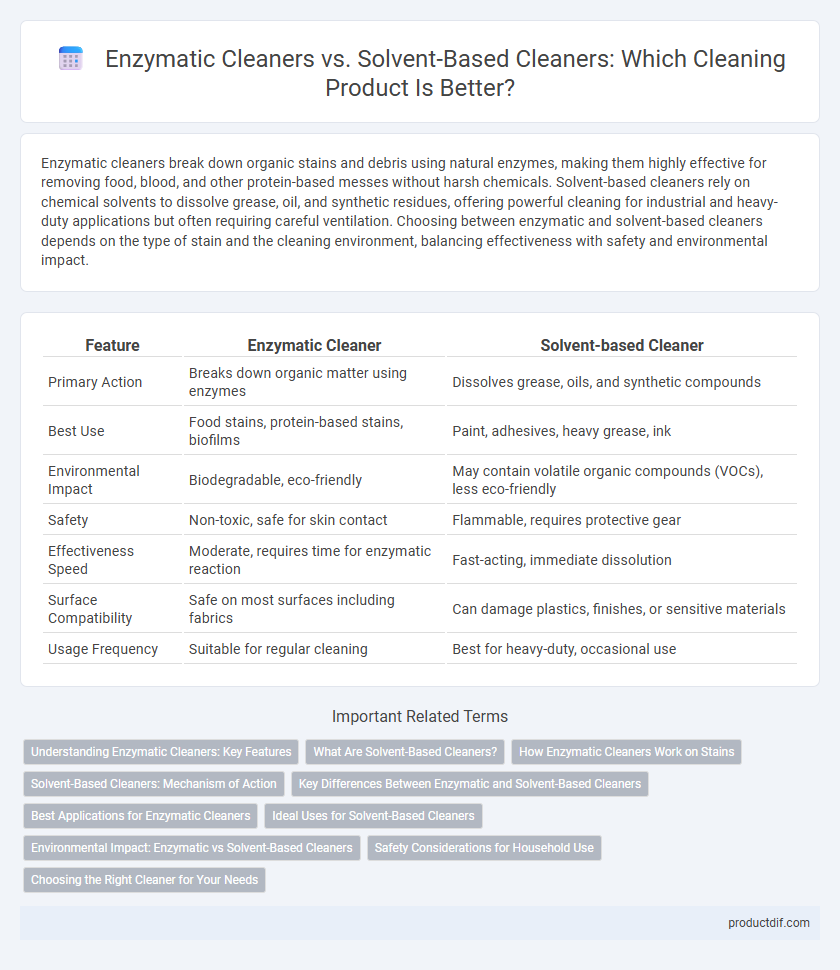
| Feature | Enzymatic Cleaner | Solvent-based Cleaner |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Action | Breaks down organic matter using enzymes | Dissolves grease, oils, and synthetic compounds |
| Best Use | Food stains, protein-based stains, biofilms | Paint, adhesives, heavy grease, ink |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | May contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs), less eco-friendly |
| Safety | Non-toxic, safe for skin contact | Flammable, requires protective gear |
| Effectiveness Speed | Moderate, requires time for enzymatic reaction | Fast-acting, immediate dissolution |
| Surface Compatibility | Safe on most surfaces including fabrics | Can damage plastics, finishes, or sensitive materials |
| Usage Frequency | Suitable for regular cleaning | Best for heavy-duty, occasional use |
Understanding Enzymatic Cleaners: Key Features
Enzymatic cleaners utilize natural enzymes like protease, lipase, and amylase to break down organic stains such as proteins, fats, and starches, promoting efficient and eco-friendly cleaning. These cleaners excel in removing bio-based soils without harsh chemicals, making them ideal for sensitive environments like hospitals and food processing areas. Unlike solvent-based cleaners that rely on chemical dissolution, enzymatic formulas offer biodegradability and reduced toxicity, enhancing safety during use and disposal.
What Are Solvent-Based Cleaners?
Solvent-based cleaners are powerful cleaning agents primarily composed of organic solvents such as alcohols, hydrocarbons, or ketones, designed to dissolve oils, greases, and heavy-duty contaminants. They effectively break down stubborn residues through chemical action rather than enzymatic breakdown, making them ideal for industrial and automotive applications. Common solvents include acetone, mineral spirits, and toluene, which provide rapid evaporation and strong lipid dissolution properties.
How Enzymatic Cleaners Work on Stains
Enzymatic cleaners break down stains by using specific enzymes that target organic materials such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, effectively dissolving dirt and grime at a molecular level. These enzymes, including protease, lipase, and amylase, catalyze the breakdown of complex stain components, making them easier to rinse away and preventing residue buildup. Unlike solvent-based cleaners that rely on chemical dissolution, enzymatic cleaners provide a biodegradable and non-toxic solution ideal for removing biological stains like blood, food, and grease.
Solvent-Based Cleaners: Mechanism of Action
Solvent-based cleaners operate by dissolving oils, greases, and non-polar substances through their chemical affinity, breaking down stubborn residues that water-based cleaners cannot effectively remove. These cleaners utilize organic solvents such as kerosene, acetone, or ethanol, which penetrate and emulsify contaminants for easy removal. Their rapid evaporation rate leaves surfaces dry and residue-free, making them ideal for degreasing metals and electronic components.
Key Differences Between Enzymatic and Solvent-Based Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners use biological catalysts to break down organic stains and residues, making them ideal for bio-based messes like food, blood, and grease. Solvent-based cleaners rely on chemical solvents to dissolve oils, paints, and synthetic substances, offering rapid removal of tough contaminants but potentially posing greater health and environmental risks. Their key differences lie in composition, mechanism of action, target soils, safety profiles, and environmental impact.
Best Applications for Enzymatic Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners excel in breaking down organic stains, making them ideal for removing protein-based soils such as blood, food residue, and pet stains. Their use is especially effective in healthcare facilities, food processing plants, and households where deep cleaning of organic matter is essential. Unlike solvent-based cleaners that dissolve grease and oils, enzymatic cleaners target specific substrates without harsh chemicals, ensuring safer and environmentally friendly cleaning.
Ideal Uses for Solvent-Based Cleaners
Solvent-based cleaners excel at dissolving oils, greases, and adhesives, making them ideal for heavy-duty cleaning tasks in automotive, industrial, and mechanical maintenance. Their fast-acting formula effectively removes stubborn residues from metal surfaces, machinery parts, and tools without requiring extensive scrubbing. These cleaners are preferred for degreasing engines, cleaning paint brushes, and eliminating sticky substances that enzymatic cleaners cannot break down.
Environmental Impact: Enzymatic vs Solvent-Based Cleaners
Enzymatic cleaners utilize natural enzymes to break down organic stains and residues, resulting in a biodegradable and eco-friendly solution with minimal toxicity. In contrast, solvent-based cleaners often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that contribute to air pollution and pose risks to aquatic ecosystems during disposal. Choosing enzymatic cleaners significantly reduces environmental impact by promoting safer biodegradation and lowering chemical emissions.
Safety Considerations for Household Use
Enzymatic cleaners are generally safer for household use as they contain biodegradable enzymes that break down organic stains without harsh chemicals or strong fumes, reducing the risk of respiratory irritation and skin sensitivity. Solvent-based cleaners often involve volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can pose health hazards such as toxicity, flammability, and environmental harm, requiring proper ventilation and careful handling. Choosing enzymatic cleaners minimizes exposure to harmful substances, making them preferable for homes with children, pets, or individuals with allergies.
Choosing the Right Cleaner for Your Needs
Enzymatic cleaners excel at breaking down organic stains like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, making them ideal for food-related messes and biological spills. Solvent-based cleaners effectively dissolve grease, oils, and synthetic substances, suitable for tough industrial grime and heavy-duty degreasing tasks. Choosing the right cleaner depends on the specific type of stain, surface compatibility, and environmental safety considerations to ensure optimal cleaning performance and material preservation.
Enzymatic cleaner vs Solvent-based cleaner Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com