Zero sugar beverages contain no added sugars or calories, making them an appealing choice for those seeking to reduce calorie intake without sacrificing sweetness. Diet drinks typically use artificial or natural sweeteners to mimic the taste of sugar while maintaining a low or zero-calorie profile. Both options cater to health-conscious consumers but differ in ingredient composition and taste preferences.
Table of Comparison
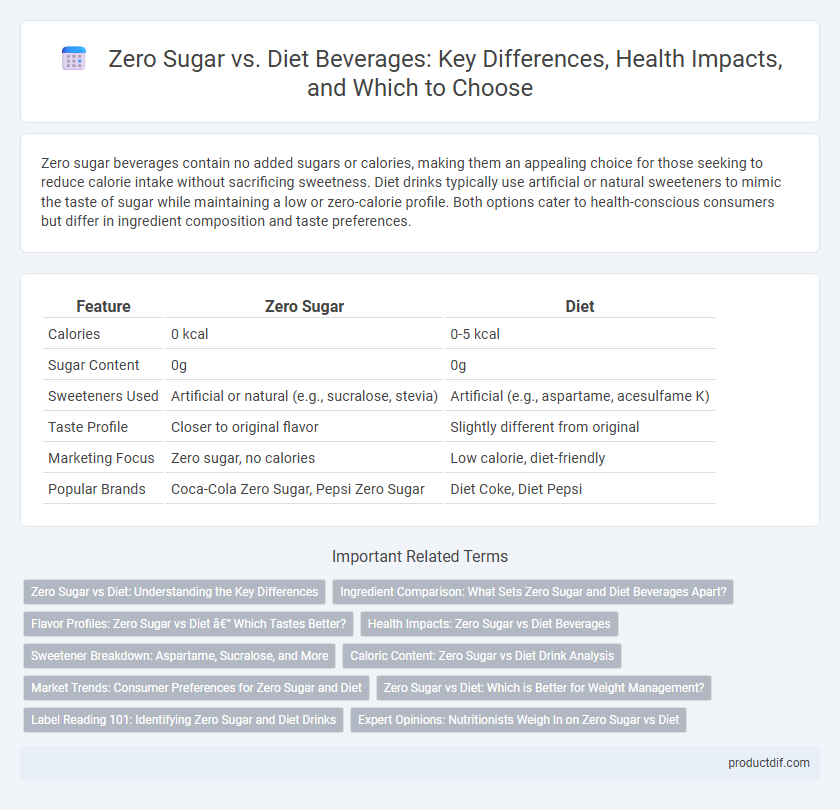
| Feature | Zero Sugar | Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 0 kcal | 0-5 kcal |
| Sugar Content | 0g | 0g |
| Sweeteners Used | Artificial or natural (e.g., sucralose, stevia) | Artificial (e.g., aspartame, acesulfame K) |
| Taste Profile | Closer to original flavor | Slightly different from original |
| Marketing Focus | Zero sugar, no calories | Low calorie, diet-friendly |
| Popular Brands | Coca-Cola Zero Sugar, Pepsi Zero Sugar | Diet Coke, Diet Pepsi |
Zero Sugar vs Diet: Understanding the Key Differences
Zero Sugar beverages contain no sugar and often use alternative sweeteners to provide sweetness without calories, appealing to consumers seeking to reduce sugar intake. Diet drinks typically use artificial sweeteners and focus on reducing calories while maintaining flavor, but may still contain small amounts of carbohydrates or additives. Understanding these key differences helps consumers make informed choices based on health goals and taste preferences.
Ingredient Comparison: What Sets Zero Sugar and Diet Beverages Apart?
Zero Sugar beverages typically use artificial sweeteners like sucralose or acesulfame potassium to achieve sweetness without any calories, while Diet beverages primarily rely on aspartame as their main sweetening agent. Both options contain minimal to no sugar, but ingredient formulations vary to influence taste and aftertaste profiles. Flavor enhancers and preservatives may differ between Zero Sugar and Diet drinks, affecting overall sensory experience and consumer preference.
Flavor Profiles: Zero Sugar vs Diet – Which Tastes Better?
Zero Sugar beverages typically offer a crisper, more balanced flavor profile with fewer artificial aftertastes compared to traditional diet options, which often rely on older sweeteners like aspartame. Diet drinks tend to have a sweeter initial impact but can leave a more pronounced chemical aftertaste, affecting overall palatability. Consumer preference often favors Zero Sugar for a cleaner, more natural taste experience in the beverage market.
Health Impacts: Zero Sugar vs Diet Beverages
Zero Sugar beverages typically contain artificial sweeteners without added caloric sugars, aiming to reduce calorie intake while maintaining sweetness. Diet beverages also use low or no-calorie sweeteners but may include additional ingredients like caffeine or preservatives, influencing overall health effects differently. Studies suggest both types can impact metabolism and gut microbiota, so choosing between zero sugar and diet options depends on individual health goals and sensitivities.
Sweetener Breakdown: Aspartame, Sucralose, and More
Zero sugar beverages primarily use alternative sweeteners like stevia, erythritol, or monk fruit extract to achieve sweetness without calories, while diet beverages often rely on artificial sweeteners such as aspartame and sucralose for a low-calorie profile. Aspartame, known for its sugar-like taste, metabolizes into amino acids and methanol, whereas sucralose passes through the body largely undigested, making it non-caloric. Understanding the sweetener breakdown is crucial for consumers managing health concerns, taste preferences, and potential sensitivities related to artificial additives.
Caloric Content: Zero Sugar vs Diet Drink Analysis
Zero Sugar beverages contain zero calories due to the absence of sugars and often use artificial sweeteners, providing a calorie-free alternative to traditional drinks. Diet drinks also aim to reduce caloric intake by substituting sugar with non-nutritive sweeteners, typically maintaining low or zero-calorie content. Both options support calorie-conscious consumers but vary in ingredient profiles and flavor formulations.
Market Trends: Consumer Preferences for Zero Sugar and Diet
Consumer preference for zero sugar beverages has surged due to increasing health consciousness and demand for natural alternatives without artificial sweeteners. Market trends indicate that zero sugar drinks outperform traditional diet sodas, driven by younger demographics seeking cleaner labels and authentic flavors. Data from 2023 shows a 25% year-over-year growth in zero sugar beverage sales, compared to a 10% growth in diet soda segments.
Zero Sugar vs Diet: Which is Better for Weight Management?
Zero sugar beverages contain no sugar or calories, making them ideal for weight management by minimizing calorie intake. Diet drinks often use artificial sweeteners, which help reduce calories but may trigger cravings in some individuals, potentially hindering weight loss efforts. Choosing zero sugar over diet options can better support sustained weight management by preventing insulin spikes and excessive calorie consumption.
Label Reading 101: Identifying Zero Sugar and Diet Drinks
Zero Sugar beverages are labeled to highlight the absence of added sugars and often use alternative sweeteners like stevia or erythritol, making them a clear choice for sugar-conscious consumers. Diet drinks typically indicate reduced or no calories on their labels and may contain artificial sweeteners such as aspartame or sucralose, which differ from zero sugar options in formulation. Understanding ingredient lists and nutritional facts panels helps consumers accurately distinguish between zero sugar and diet drinks for informed choices aligned with health goals.
Expert Opinions: Nutritionists Weigh In on Zero Sugar vs Diet
Nutritionists emphasize that zero sugar beverages often use non-nutritive sweeteners like sucralose, which do not affect blood glucose levels, making them suitable for diabetics. Diet drinks may contain artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, which have been extensively studied and deemed safe but remain controversial among some experts. Both options provide calorie-free alternatives to sugary drinks, with health impacts largely depending on individual consumption patterns and overall diet quality.
Zero Sugar vs Diet Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com