Stevia-sweetened beverages offer a low-calorie alternative to traditional sugar-sweetened drinks, making them ideal for those managing weight or blood sugar levels. Unlike sugar-sweetened beverages, stevia does not contribute to tooth decay or blood glucose spikes. Choosing stevia-sweetened drinks helps reduce overall sugar intake while maintaining a sweet taste.
Table of Comparison
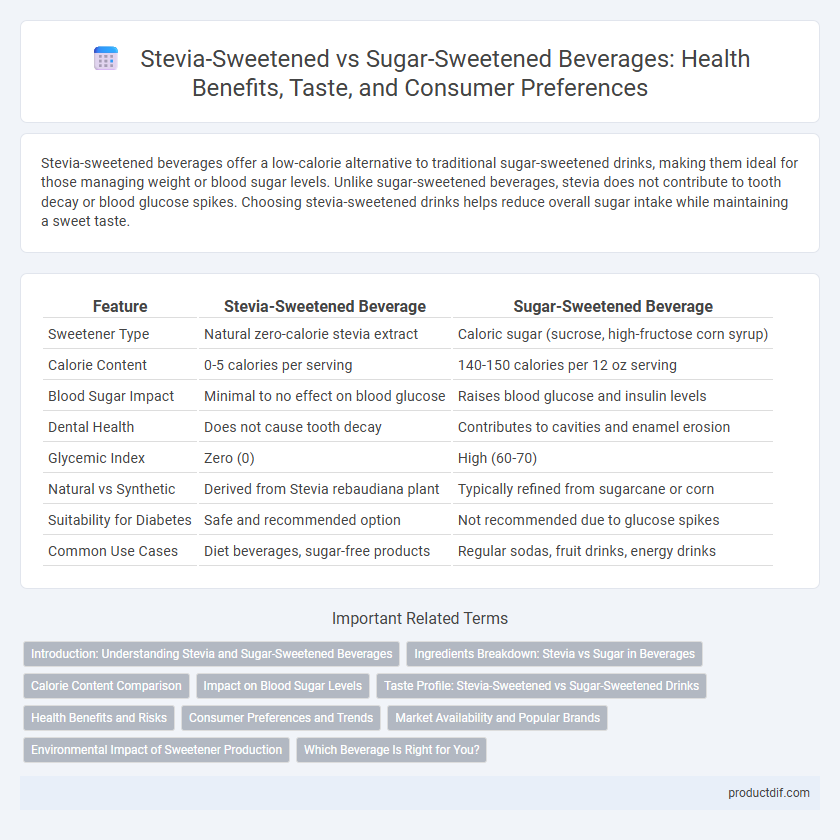
| Feature | Stevia-Sweetened Beverage | Sugar-Sweetened Beverage |
|---|---|---|
| Sweetener Type | Natural zero-calorie stevia extract | Caloric sugar (sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup) |
| Calorie Content | 0-5 calories per serving | 140-150 calories per 12 oz serving |
| Blood Sugar Impact | Minimal to no effect on blood glucose | Raises blood glucose and insulin levels |
| Dental Health | Does not cause tooth decay | Contributes to cavities and enamel erosion |
| Glycemic Index | Zero (0) | High (60-70) |
| Natural vs Synthetic | Derived from Stevia rebaudiana plant | Typically refined from sugarcane or corn |
| Suitability for Diabetes | Safe and recommended option | Not recommended due to glucose spikes |
| Common Use Cases | Diet beverages, sugar-free products | Regular sodas, fruit drinks, energy drinks |
Introduction: Understanding Stevia and Sugar-Sweetened Beverages
Stevia-sweetened beverages use natural zero-calorie sweeteners derived from the Stevia rebaudiana plant, providing a healthier alternative to traditional sugar-sweetened beverages that contain high levels of sucrose or high-fructose corn syrup. Sugar-sweetened beverages contribute significantly to calorie intake and are linked to increased risks of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the distinct metabolic and glycemic effects of stevia versus sugar helps consumers make informed choices for better health outcomes.
Ingredients Breakdown: Stevia vs Sugar in Beverages
Stevia-sweetened beverages contain steviol glycosides derived from the Stevia rebaudiana plant, offering zero calories and a minimally processed natural sweetener alternative. Sugar-sweetened beverages primarily use sucrose or high-fructose corn syrup, which contribute significant calories and impact blood glucose levels. The Ingredient breakdown highlights stevia's non-nutritive sweetness compared to sugar's carbohydrate-based energy content, influencing product formulation and consumer health choices.
Calorie Content Comparison
Stevia-sweetened beverages contain zero or negligible calories, making them an ideal low-calorie alternative to sugar-sweetened beverages, which typically provide 140-150 calories per 12-ounce serving. This significant calorie reduction helps in weight management and lowering the risk of obesity-related diseases. Choosing stevia as a sweetener supports calorie control without compromising sweetness in beverages.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Stevia-sweetened beverages significantly reduce blood sugar spikes compared to sugar-sweetened beverages, making them a preferred choice for individuals managing diabetes or insulin resistance. Clinical studies show that stevia has a negligible effect on glucose and insulin levels, while sugar-sweetened beverages cause rapid increases in blood glucose, leading to increased risk of metabolic disorders. Substituting sugar with stevia in beverages helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and supports overall glycemic control.
Taste Profile: Stevia-Sweetened vs Sugar-Sweetened Drinks
Stevia-sweetened beverages often exhibit a distinct taste profile characterized by a clean sweetness with subtle herbal or licorice notes, which can be perceived as slightly bitter or metallic by some consumers. In contrast, sugar-sweetened drinks provide a familiar, rounded sweetness with a smooth mouthfeel and no aftertaste, making them widely preferred for traditional flavor experiences. Taste perception varies based on formulation, individual sensitivity to steviol glycosides, and the type of beverage, influencing overall consumer acceptance.
Health Benefits and Risks
Stevia-sweetened beverages offer a low-calorie alternative to sugar-sweetened drinks, helping reduce the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and dental cavities by minimizing sugar intake. Unlike sugar-sweetened beverages, stevia does not cause rapid blood glucose spikes, making it suitable for individuals managing insulin sensitivity and metabolic disorders. However, excessive consumption of stevia-sweetened products may lead to digestive discomfort in some individuals, while sugar-sweetened beverages are linked to higher calorie consumption and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Stevia-sweetened beverages are rapidly gaining consumer preference due to increased health awareness and demand for natural, low-calorie alternatives to sugar-sweetened beverages. Market trends indicate a significant rise in stevia's market share as consumers seek products with reduced sugar content to combat obesity and diabetes. Major beverage brands are expanding their stevia-sweetened product lines to cater to this growing health-conscious demographic.
Market Availability and Popular Brands
Stevia-sweetened beverages have gained significant market availability due to increased consumer demand for natural, low-calorie sweeteners, with popular brands like Bai, Zevia, and Sprite Green leading the segment. In contrast, sugar-sweetened beverages remain widely available across global markets, dominated by industry giants such as Coca-Cola, PepsiCo, and Nestle. Retail presence of stevia beverages is expanding rapidly in health-conscious and specialty stores, while sugar-sweetened beverages maintain strong distribution in mainstream supermarkets and convenience outlets.
Environmental Impact of Sweetener Production
Stevia-sweetened beverages exhibit a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to sugar-sweetened beverages due to reduced water usage and land requirements during cultivation. Sugar production involves extensive use of pesticides and fertilizers, leading to soil degradation and high greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, stevia cultivation demands less intensive agricultural inputs, contributing to more sustainable beverage production practices.
Which Beverage Is Right for You?
Choosing between stevia-sweetened and sugar-sweetened beverages depends on dietary goals and health considerations. Stevia-sweetened beverages offer zero calories and a lower glycemic impact, making them suitable for weight management and blood sugar control. Sugar-sweetened beverages provide natural energy but contribute to higher calorie intake and increased risk of metabolic diseases.
Stevia-Sweetened Beverage vs Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com