Analog control systems in appliances offer smooth, continuous adjustment through dials and knobs, providing intuitive user interaction. Digital control systems utilize microprocessors and digital interfaces for precise settings, enhanced functionality, and programmable options. Choosing between analog and digital control impacts the appliance's ease of use, accuracy, and available features.
Table of Comparison
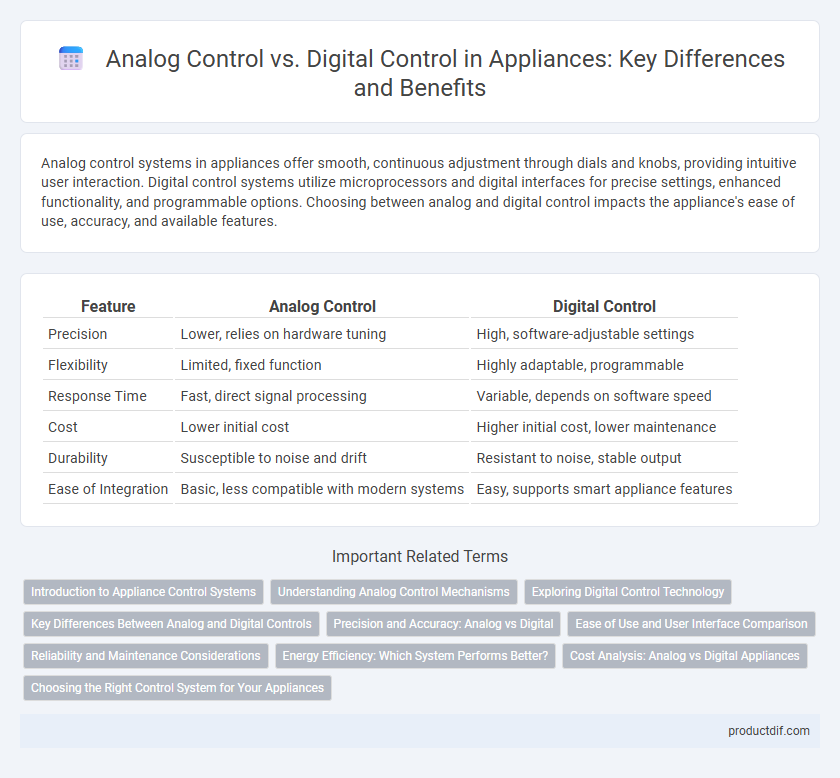
| Feature | Analog Control | Digital Control |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Lower, relies on hardware tuning | High, software-adjustable settings |
| Flexibility | Limited, fixed function | Highly adaptable, programmable |
| Response Time | Fast, direct signal processing | Variable, depends on software speed |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance |
| Durability | Susceptible to noise and drift | Resistant to noise, stable output |
| Ease of Integration | Basic, less compatible with modern systems | Easy, supports smart appliance features |
Introduction to Appliance Control Systems
Appliance control systems utilize either analog control or digital control to regulate performance and functionality. Analog control relies on continuous voltage or current signals for real-time adjustments, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness in basic appliances. Digital control employs microprocessors and software algorithms, enabling precise, programmable, and adaptive management of complex appliance operations.
Understanding Analog Control Mechanisms
Analog control mechanisms utilize continuous signals to regulate appliance functions, allowing for real-time adjustments based on varying input levels. These systems rely on components such as potentiometers, resistors, and capacitors to modulate voltage and current, enabling smooth transitions and precise control. Understanding the behavior of analog signals is essential for optimizing appliance performance and ensuring consistent operation in applications like temperature regulation and motor speed control.
Exploring Digital Control Technology
Digital control technology in appliances offers precise temperature regulation, energy efficiency, and enhanced user interfaces compared to traditional analog control. Microprocessors enable adaptive algorithms that optimize performance and reduce power consumption in devices such as HVAC systems, washing machines, and refrigerators. Integration with IoT further allows remote monitoring and real-time adjustments, elevating convenience and functionality.
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Controls
Analog control systems operate with continuous signals that vary smoothly over time, allowing precise and real-time modulation of appliance functions such as temperature or speed. Digital control relies on discrete signals, typically binary code, enabling programmable logic, easier integration with microprocessors, and enhanced automation capabilities in modern appliances. Key differences include the analog system's sensitivity to noise and drift compared to the digital system's robustness, accuracy, and ability to store and process complex algorithms.
Precision and Accuracy: Analog vs Digital
Digital control in appliances offers superior precision and accuracy compared to analog control due to its ability to process exact numerical data and maintain consistent performance. Analog control can suffer from signal degradation and noise interference, leading to less accurate adjustments and variability in appliance operation. Digital systems enable precise temperature settings, timing, and sensor feedback, enhancing overall reliability and user experience.
Ease of Use and User Interface Comparison
Analog control offers a straightforward, tactile interface with physical knobs and dials that allow users to make quick adjustments without navigating menus, making it intuitive for those familiar with traditional appliances. Digital control features touchscreens or buttons that provide precise settings, customizable options, and often display detailed feedback, enhancing ease of use for tech-savvy individuals. User interface design in digital controls integrates visual indicators and programmable functions, improving accuracy and convenience over the simpler, less flexible analog systems.
Reliability and Maintenance Considerations
Analog control systems in appliances offer simplicity and easier field repairs, but they often suffer from drift and component wear that can affect long-term reliability. Digital control systems provide precise, consistent operation with built-in diagnostics that simplify maintenance by enabling predictive troubleshooting. The use of microprocessors in digital controls enhances appliance durability by minimizing manual adjustments and improving fault detection accuracy.
Energy Efficiency: Which System Performs Better?
Digital control systems optimize energy efficiency by precisely managing appliance functions through real-time data and adaptive algorithms, reducing unnecessary power consumption. Analog control, while simpler, lacks the capability for dynamic adjustments and often leads to higher energy use due to fixed settings and less accurate regulation. Consequently, appliances equipped with digital controls consistently outperform analog counterparts in minimizing energy waste and enhancing overall efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Analog vs Digital Appliances
Analog appliances typically incur lower initial costs due to simpler circuitry and manufacturing processes, making them budget-friendly for basic functions. Digital appliances offer enhanced precision and programmability but involve higher upfront expenses tied to complex microprocessors and software development. Long-term operational costs often favor digital models through energy efficiency and reduced maintenance, balancing the higher initial investment over time.
Choosing the Right Control System for Your Appliances
Selecting the right control system for appliances hinges on the precision and flexibility required; digital control offers advanced programmability and energy efficiency through microprocessor integration, while analog control provides simplicity and cost-effectiveness with continuous signal management. Appliances demanding complex functions and user interfaces benefit from digital controls, which support remote operation and diagnostics, whereas basic or budget-friendly models may perform adequately with analog systems. Evaluating factors such as appliance functionality, user experience, maintenance needs, and overall lifespan ensures the optimal choice between analog and digital control architectures.
Analog Control vs Digital Control Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com