A blender excels at creating smooth liquids and purees, making it ideal for soups, smoothies, and sauces. A food processor offers more versatility with its multiple attachments, perfect for chopping, slicing, and kneading dough. Choosing between them depends on whether you prioritize liquid blending or versatile food preparation tasks.
Table of Comparison
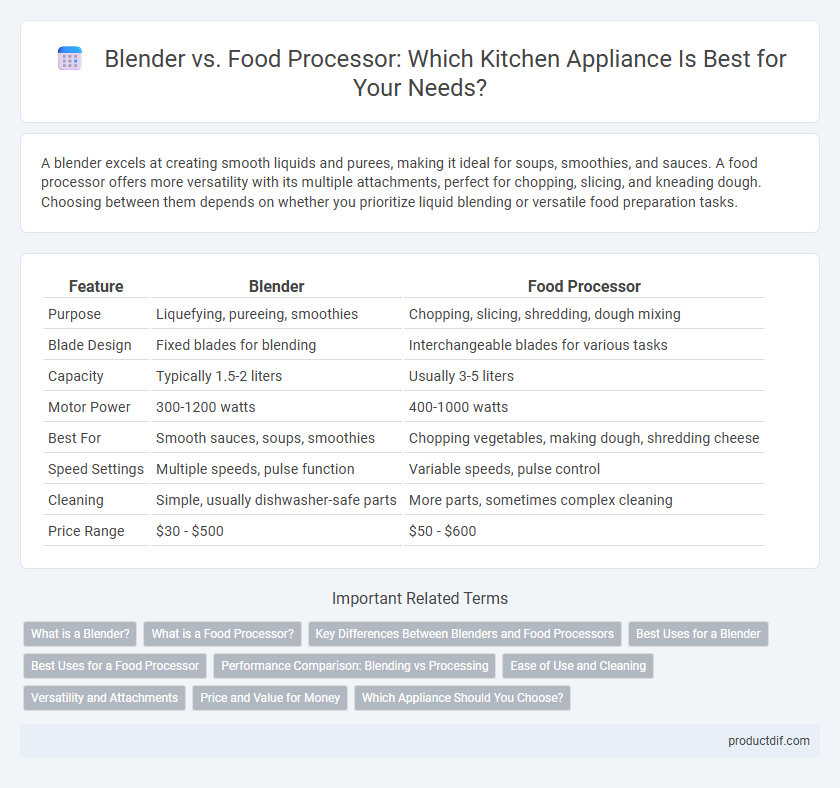
| Feature | Blender | Food Processor |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Liquefying, pureeing, smoothies | Chopping, slicing, shredding, dough mixing |
| Blade Design | Fixed blades for blending | Interchangeable blades for various tasks |
| Capacity | Typically 1.5-2 liters | Usually 3-5 liters |
| Motor Power | 300-1200 watts | 400-1000 watts |
| Best For | Smooth sauces, soups, smoothies | Chopping vegetables, making dough, shredding cheese |
| Speed Settings | Multiple speeds, pulse function | Variable speeds, pulse control |
| Cleaning | Simple, usually dishwasher-safe parts | More parts, sometimes complex cleaning |
| Price Range | $30 - $500 | $50 - $600 |
What is a Blender?
A blender is a high-speed appliance designed to liquefy, puree, and emulsify food and liquids using rotating blades within a tall container. It excels at creating smoothies, soups, and sauces by breaking down fruits, vegetables, and ice into smooth, consistent textures. Blenders typically feature variable speed controls and powerful motors ranging from 300 to 1500 watts, optimizing performance for various blending tasks.
What is a Food Processor?
A food processor is a versatile kitchen appliance designed for chopping, slicing, shredding, and mixing a wide variety of ingredients with high precision. Equipped with multiple interchangeable blades and discs, it can handle tougher tasks such as kneading dough or grating cheese that a blender cannot efficiently perform. Food processors typically feature a wider and shorter bowl compared to blenders, enabling better control over solid foods and reducing preparation time.
Key Differences Between Blenders and Food Processors
Blenders excel at creating smooth liquids and purees due to their powerful motors and sharp blades designed for high-speed blending, making them ideal for smoothies and soups. Food processors feature wider, flatter bowls with multiple blade attachments tailored for chopping, slicing, and kneading, providing versatility in food preparation tasks like dough making and shredding. The key difference lies in their design purpose: blenders prioritize liquid consistency, while food processors handle a broader range of solid food textures and cutting techniques.
Best Uses for a Blender
Blenders excel at creating smooth purees, smoothies, and liquid-based recipes, making them ideal for blending fruits, vegetables, and ice with precision. Their powerful motor and sharp blades efficiently crush and liquefy ingredients, perfect for soups, sauces, and dairy-free milk. Unlike food processors, blenders are less suited for chopping or shredding but excel in emulsifying and combining liquids seamlessly.
Best Uses for a Food Processor
Food processors excel at chopping, slicing, and shredding large quantities of vegetables and fruits quickly, making them ideal for meal prepping and batch cooking. They handle thick doughs and purees with ease, perfect for making bread, pastry dough, or hummus. Their wide, flat blades and large capacity bowls optimize efficiency for shredding cheese, grinding nuts, or preparing chunky salsas.
Performance Comparison: Blending vs Processing
Blenders excel in liquefying and pureeing ingredients quickly, making them ideal for smoothies, soups, and sauces, while food processors outperform in chopping, slicing, and shredding tasks due to their versatile blade attachments. The motor power in blenders typically ranges from 300 to 1200 watts, optimized for high-speed blending, whereas food processors feature a stronger torque suited for heavier dough kneading and precise cutting. Choosing between a blender and a food processor ultimately depends on the preparation method required, with blenders offering smooth texture consistency and food processors delivering uniform ingredient processing.
Ease of Use and Cleaning
Blenders offer straightforward controls with simple speed settings, making them easy to operate for quick blending tasks. Food processors typically feature multiple attachments and buttons, which can complicate usage but provide versatile functions. Cleaning blenders is often faster due to fewer parts, whereas food processors require disassembly of more components, making cleanup more time-consuming.
Versatility and Attachments
Blenders excel in versatility by handling liquids, smoothies, and purees with various speed settings, while food processors offer multiple attachments for slicing, shredding, kneading, and chopping tougher ingredients. Food processors typically include discs and blades for diverse food prep tasks, making them ideal for complex recipes requiring precise texture control. Blenders focus on liquid blending with fewer attachments, emphasizing smooth consistency over multifunctional food processing.
Price and Value for Money
Blenders typically offer a lower price point compared to food processors, making them a budget-friendly choice for smoothies and purees. Food processors provide greater versatility with multiple attachments, often justifying their higher cost through enhanced value for chopping, slicing, and dough-making tasks. Consumers seeking multifunctional kitchen appliances generally find food processors deliver better value for money despite the initial investment.
Which Appliance Should You Choose?
Choosing between a blender and a food processor depends on your culinary needs and kitchen tasks. Blenders excel at creating smooth liquids like smoothies, soups, and sauces due to their high-speed blades and sealed containers. Food processors offer versatile functions such as chopping, slicing, shredding, and mixing solid ingredients, making them ideal for dough preparation and meal prep tasks requiring precision.
Blender vs food processor Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com