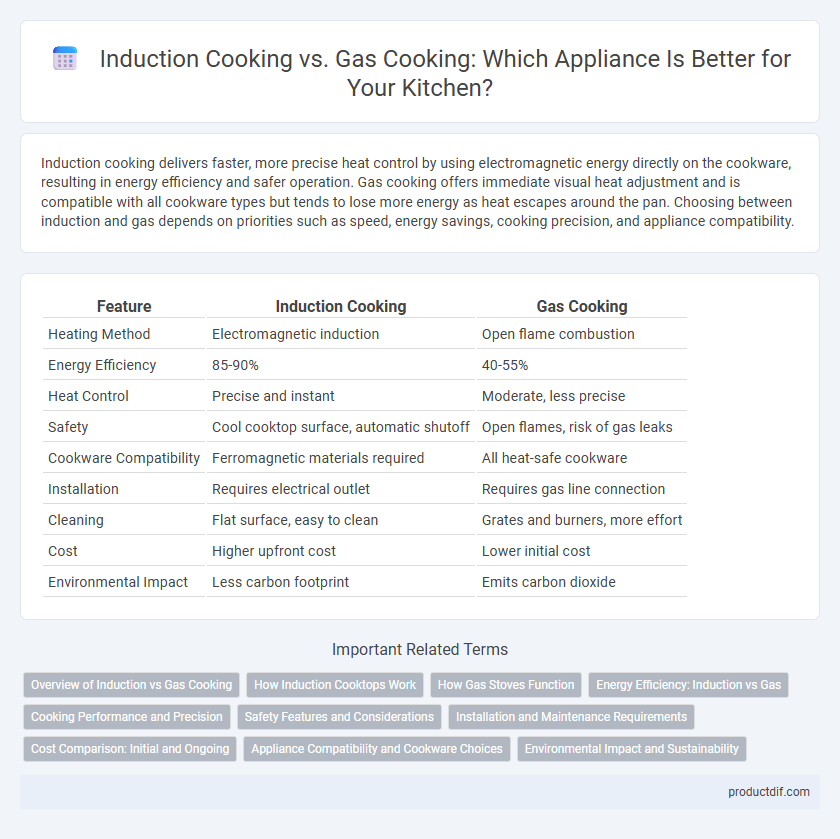
Induction cooking delivers faster, more precise heat control by using electromagnetic energy directly on the cookware, resulting in energy efficiency and safer operation. Gas cooking offers immediate visual heat adjustment and is compatible with all cookware types but tends to lose more energy as heat escapes around the pan. Choosing between induction and gas depends on priorities such as speed, energy savings, cooking precision, and appliance compatibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Induction Cooking | Gas Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic induction | Open flame combustion |
| Energy Efficiency | 85-90% | 40-55% |
| Heat Control | Precise and instant | Moderate, less precise |
| Safety | Cool cooktop surface, automatic shutoff | Open flames, risk of gas leaks |
| Cookware Compatibility | Ferromagnetic materials required | All heat-safe cookware |
| Installation | Requires electrical outlet | Requires gas line connection |
| Cleaning | Flat surface, easy to clean | Grates and burners, more effort |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Less carbon footprint | Emits carbon dioxide |
Overview of Induction vs Gas Cooking
Induction cooking uses electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, offering faster and more energy-efficient cooking compared to gas stoves, which rely on open flames for heat transfer. Induction cooktops provide precise temperature control and enhanced safety features, as the surface remains cool to touch, while gas cooking allows for immediate flame adjustment and is preferred for traditional culinary techniques. Energy efficiency and ease of cleaning make induction a modern choice, whereas gas cooking maintains popularity for its versatility and compatibility with all types of cookware.
How Induction Cooktops Work
Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to directly heat compatible cookware, providing precise temperature control and energy efficiency. The magnetic field induces electric currents in the ferrous metal pan, generating heat only in the cookware and not on the cooktop surface itself. This method results in faster cooking times and enhanced safety compared to traditional gas cooking, which relies on an open flame to transfer heat.
How Gas Stoves Function
Gas stoves function by burning natural gas or propane to produce an open flame that directly heats cookware, offering precise temperature control and immediate heat adjustment. The gas flows through burners with small ports, where it mixes with air and ignites, allowing users to visually gauge and modify the flame size for cooking needs. This combustion process produces heat energy that cooks food efficiently but also generates indoor emissions requiring proper ventilation.
Energy Efficiency: Induction vs Gas
Induction cooking offers significantly higher energy efficiency, converting about 90% of the energy directly into heat for cooking, compared to gas cooking which only converts approximately 40-55%. The precise electromagnetic induction process reduces heat loss, making induction stoves more environmentally friendly and cost-effective over time. Gas cooking, while traditional, dissipates a large portion of energy as ambient heat, leading to increased energy consumption and higher utility bills.
Cooking Performance and Precision
Induction cooking offers superior cooking performance by using electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, resulting in faster temperature changes and precise heat control. Gas cooking provides visible flames and immediate heat adjustment but often lacks the exact temperature precision achievable with induction technology. Induction cooktops maintain consistent heat levels, reducing the risk of overcooking or burning, which enhances overall cooking accuracy.
Safety Features and Considerations
Induction cooking offers enhanced safety through its electromagnetic heating method, which heats the cookware directly while keeping the cooktop surface cool to the touch, reducing burn risks. Gas cooking involves an open flame, posing higher risks of fire hazards and gas leaks, requiring vigilant ventilation and regular maintenance. Induction cooktops also feature automatic shut-off and child lock functions, providing extra protection not commonly found in traditional gas stoves.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Induction cooking requires a compatible induction cooktop and specialized cookware, often necessitating professional installation for proper electrical connections. Gas cooking involves installing gas lines and ensuring adequate ventilation, demands regular inspection to prevent leaks, and requires maintenance of burner cleanliness and ignition systems. Maintenance for induction cooktops is generally simpler, focusing on surface cleaning, while gas stoves need routine checks for gas flow and burner efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Ongoing
Induction cooking typically has a higher initial cost due to the price of induction cooktops and compatible cookware, while gas stoves are generally more affordable upfront with widely available equipment. Ongoing expenses for induction cooking are lower because of higher energy efficiency and reduced heat loss compared to gas cooking, which incurs higher utility bills driven by natural gas consumption. Maintenance costs for gas stoves can be higher due to burner cleaning and gas line inspections, whereas induction cooktops require less frequent servicing.
Appliance Compatibility and Cookware Choices
Induction cooking requires compatible cookware with ferromagnetic properties, such as cast iron or stainless steel, to generate heat efficiently through electromagnetic induction. Gas cooking works with virtually any type of cookware, including copper, aluminum, and glass, offering greater flexibility in appliance compatibility and cookware choices. Consumers must consider these differences when selecting appliances to ensure optimal performance and durability of their cookware.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Induction cooking offers superior environmental benefits compared to gas cooking by utilizing electricity that can be sourced from renewable energy, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions. Gas cooking releases methane and carbon dioxide, contributing significantly to indoor and outdoor air pollution and climate change. Energy efficiency of induction cooktops, which convert up to 90% of energy directly to the cookware, also reduces overall energy consumption and supports sustainable kitchen practices.
Induction cooking vs Gas cooking Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com