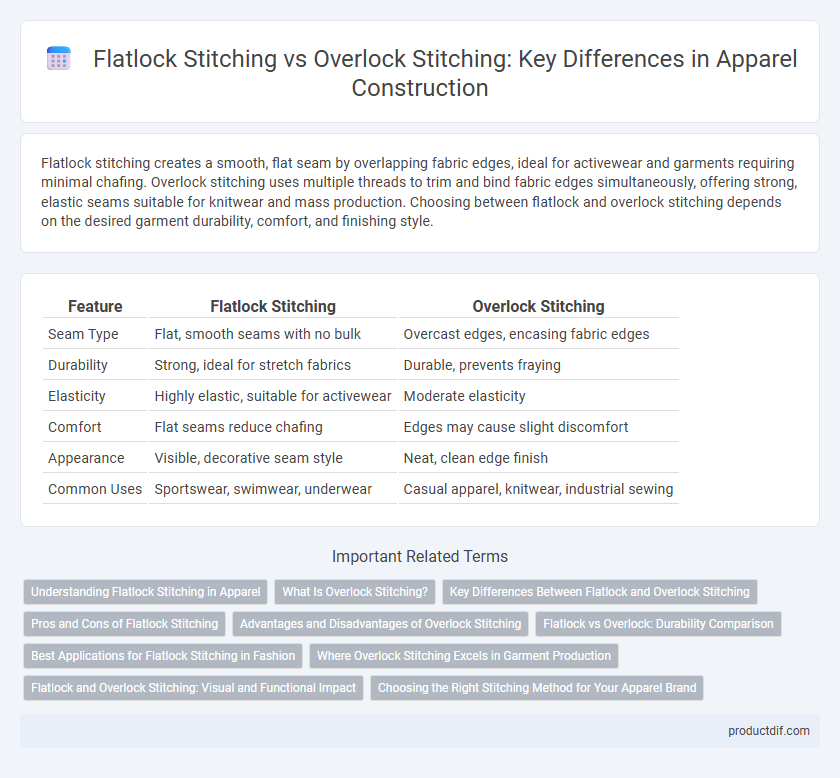
Flatlock stitching creates a smooth, flat seam by overlapping fabric edges, ideal for activewear and garments requiring minimal chafing. Overlock stitching uses multiple threads to trim and bind fabric edges simultaneously, offering strong, elastic seams suitable for knitwear and mass production. Choosing between flatlock and overlock stitching depends on the desired garment durability, comfort, and finishing style.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flatlock Stitching | Overlock Stitching |
|---|---|---|
| Seam Type | Flat, smooth seams with no bulk | Overcast edges, encasing fabric edges |
| Durability | Strong, ideal for stretch fabrics | Durable, prevents fraying |
| Elasticity | Highly elastic, suitable for activewear | Moderate elasticity |
| Comfort | Flat seams reduce chafing | Edges may cause slight discomfort |
| Appearance | Visible, decorative seam style | Neat, clean edge finish |
| Common Uses | Sportswear, swimwear, underwear | Casual apparel, knitwear, industrial sewing |
Understanding Flatlock Stitching in Apparel
Flatlock stitching in apparel creates a strong, durable seam by joining fabric edges edge-to-edge without overlapping, resulting in a flat and smooth finish that reduces bulk and chafing. This technique is ideal for activewear and performance garments, enhancing comfort and flexibility while maintaining seam strength. Unlike overlock stitching, flatlock stitching exposes both seam allowances on the inside, allowing for easier seam repairs and added stretchability in knit fabrics.
What Is Overlock Stitching?
Overlock stitching is a sewing technique used to sew over the edge of one or two pieces of fabric for edging, hemming, or seaming. It uses multiple threads to create a strong, stretchable seam that prevents fabric from fraying, commonly seen in knitwear and activewear. The overlock machine trims the fabric while stitching, providing a clean and professional finish.
Key Differences Between Flatlock and Overlock Stitching
Flatlock stitching creates a flat seam by joining fabric edges edge-to-edge, ideal for activewear and seamless designs, while overlock stitching trims fabric edges and encloses them with thread to prevent fraying, commonly used in garment construction. Flatlock seams provide greater comfort against the skin and a decorative, exposed seam appearance, whereas overlock seams prioritize durability and edge reinforcement. The choice between flatlock and overlock stitching depends on fabric type, garment purpose, and desired seam aesthetics.
Pros and Cons of Flatlock Stitching
Flatlock stitching offers superior comfort and flexibility in apparel by creating flat seams that reduce chafing and irritation, making it ideal for activewear and sports clothing. This technique also provides a clean, decorative finish but may be less durable under heavy stress compared to overlock stitching, which offers stronger seam reinforcement. Flatlock stitching requires specialized machinery and can be more time-consuming, impacting production efficiency and cost.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Overlock Stitching
Overlock stitching offers strong seam durability and prevents fabric fraying, making it ideal for stretch fabrics commonly used in activewear and knitwear. Its speed and efficiency in production lower manufacturing costs but may require specialized machinery and skilled operators, increasing initial investment. However, overlock stitches have limited elasticity compared to flatlock stitching, which can compromise comfort in certain apparel applications.
Flatlock vs Overlock: Durability Comparison
Flatlock stitching provides superior durability by creating a flat seam that reduces fabric stress and resists unraveling, making it ideal for activewear and sports apparel. Overlock stitching, while efficient for seam finishing and edge protection, generally offers less strength and is more prone to seam damage under heavy tension. Garments with flatlock seams demonstrate enhanced longevity and comfort, especially in high-stress areas, compared to those using overlock stitching.
Best Applications for Flatlock Stitching in Fashion
Flatlock stitching is ideal for activewear and seamless garments, providing a smooth, chafe-free finish that enhances comfort during high-movement activities. This technique is highly favored for athleisure and swimwear due to its durability and aesthetic appeal, allowing garments to lie flat against the skin without bulky seams. Flatlock seams also offer increased flexibility and breathability, making them perfect for performance-driven fashion designs.
Where Overlock Stitching Excels in Garment Production
Overlock stitching excels in garment production by providing strong, stretchy seams ideal for knit fabrics, enhancing durability and flexibility in activewear and casual apparel. This technique also trims fabric edges while sealing them, reducing fraying and improving garment longevity. Manufacturers favor overlock stitching for fast, efficient seam assembly, which supports high-volume production with consistent quality.
Flatlock and Overlock Stitching: Visual and Functional Impact
Flatlock stitching creates a smooth, flat seam that reduces bulk and enhances comfort, making it ideal for activewear and garments requiring minimal chafing. Overlock stitching secures fabric edges and prevents fraying with a more raised seam, providing durability and a clean finish but potentially adding slight bulk. The visual impact of flatlock stitching is sleek and seamless, while overlock stitching appears more traditional with visible looping threads, influencing both garment aesthetics and wearability.
Choosing the Right Stitching Method for Your Apparel Brand
Flatlock stitching offers a smooth, flat seam ideal for activewear and garments requiring minimal bulk, enhancing comfort and durability. Overlock stitching securely binds fabric edges and prevents fraying, making it suitable for mass production of t-shirts, knitwear, and casual apparel. Selecting the right stitching method depends on fabric type, garment function, and desired seam strength to ensure product quality and consumer satisfaction.
Flatlock Stitching vs Overlock Stitching Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com