Hybrid Synergy Drive combines a powerful electric motor with a gasoline engine to optimize fuel efficiency and provide seamless acceleration, making it ideal for full hybrid vehicles. Mild Hybrid Systems use a smaller electric motor to assist the engine and recover energy during braking but cannot power the vehicle on electricity alone, resulting in moderate fuel savings. The choice between these systems depends on the desired balance between performance, fuel economy, and cost efficiency.
Table of Comparison
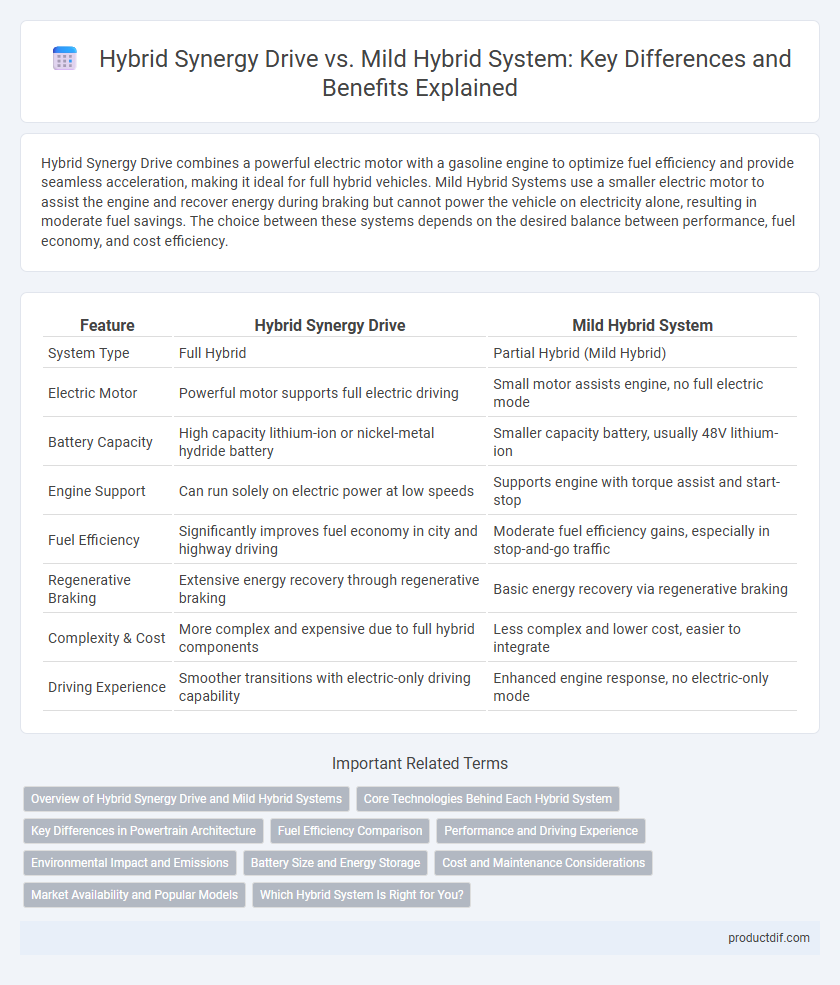
| Feature | Hybrid Synergy Drive | Mild Hybrid System |
|---|---|---|
| System Type | Full Hybrid | Partial Hybrid (Mild Hybrid) |
| Electric Motor | Powerful motor supports full electric driving | Small motor assists engine, no full electric mode |
| Battery Capacity | High capacity lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride battery | Smaller capacity battery, usually 48V lithium-ion |
| Engine Support | Can run solely on electric power at low speeds | Supports engine with torque assist and start-stop |
| Fuel Efficiency | Significantly improves fuel economy in city and highway driving | Moderate fuel efficiency gains, especially in stop-and-go traffic |
| Regenerative Braking | Extensive energy recovery through regenerative braking | Basic energy recovery via regenerative braking |
| Complexity & Cost | More complex and expensive due to full hybrid components | Less complex and lower cost, easier to integrate |
| Driving Experience | Smoother transitions with electric-only driving capability | Enhanced engine response, no electric-only mode |
Overview of Hybrid Synergy Drive and Mild Hybrid Systems
Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD) combines a gasoline engine with electric motors and a high-capacity battery to deliver seamless power and regenerative braking, optimizing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions in vehicles like the Toyota Prius. Mild Hybrid Systems use a smaller electric motor and battery to assist the internal combustion engine during acceleration and to enable start-stop functionality, enhancing fuel economy without full electric propulsion. The HSD achieves greater electric-only driving capability and overall efficiency compared to Mild Hybrid Systems, which primarily support engine operation rather than replace it.
Core Technologies Behind Each Hybrid System
Hybrid Synergy Drive combines a powerful electric motor with a sophisticated planetary gearset and a high-capacity battery pack to deliver seamless transitions between electric and gasoline power, optimizing fuel efficiency and performance. The Mild Hybrid System integrates a smaller electric motor-generator and a 48-volt battery, primarily assisting the combustion engine during acceleration and enabling regenerative braking without the capability for full electric propulsion. Core technologies in Hybrid Synergy Drive emphasize regenerative braking, electric-only driving mode, and engine optimization, while Mild Hybrid Systems focus on start-stop functionality and torque assistance to reduce fuel consumption.
Key Differences in Powertrain Architecture
The Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD) utilizes a full hybrid powertrain combining a gasoline engine with two electric motor-generators, enabling electric-only driving, regenerative braking, and seamless power blending. In contrast, the Mild Hybrid System features a smaller electric motor integrated with the engine, primarily providing start-stop functionality and supplemental torque without allowing for purely electric propulsion. HSD's complex planetary gear set allows for continuous power split and optimized efficiency, whereas Mild Hybrid relies on a belt-driven or integrated starter-generator to assist the engine and improve fuel economy.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison
Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD) delivers superior fuel efficiency by combining a full electric motor with a gasoline engine, enabling extended electric-only driving and regenerative braking. Mild Hybrid Systems (MHS) use a smaller electric motor to assist the engine during acceleration and recover energy during deceleration but cannot power the vehicle independently. As a result, HSD typically achieves higher miles per gallon (MPG) ratings and greater reductions in fuel consumption compared to mild hybrid technology.
Performance and Driving Experience
Hybrid Synergy Drive delivers seamless power blending between electric and gasoline engines, resulting in improved acceleration and fuel efficiency compared to Mild Hybrid Systems, which primarily assist the combustion engine with minimal electric propulsion. The full hybrid capability of Hybrid Synergy Drive allows for electric-only driving modes, enhancing quietness and reducing emissions during low-speed urban driving, whereas Mild Hybrid Systems rely on electric motor assistance to improve start-stop functionality and torque fill without full electric drive. Drivers experience a smoother and more responsive performance with Hybrid Synergy Drive, especially in stop-and-go traffic and highway cruising, due to its advanced energy management and regenerative braking technologies.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
The Hybrid Synergy Drive significantly reduces emissions by combining a gasoline engine with an electric motor, resulting in lower CO2 output and improved fuel efficiency compared to conventional engines. Mild Hybrid Systems use a small electric motor to assist the engine, reducing emissions moderately but not eliminating fuel consumption during acceleration. Studies show that Hybrid Synergy Drive vehicles can lower greenhouse gas emissions by up to 30% compared to mild hybrid systems, highlighting their stronger environmental benefits.
Battery Size and Energy Storage
The Hybrid Synergy Drive features a larger battery pack, typically around 1.3 to 1.6 kWh, enabling substantial electric-only driving and efficient regenerative energy storage. Mild Hybrid Systems incorporate smaller batteries, usually under 1 kWh, primarily supporting engine assist and start-stop functions without solely powering the vehicle. The difference in battery capacity directly affects energy storage capabilities, electric motor power, and overall fuel efficiency in hybrid vehicles.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Hybrid Synergy Drive systems, used in Toyota hybrids, typically involve higher upfront costs due to complex components like large battery packs and power-split devices, but offer long-term savings through better fuel efficiency and lower fuel expenses. Mild Hybrid Systems are generally less expensive to produce and maintain, as they use smaller batteries and simpler electric motors mainly for start-stop and regenerative braking functions. Maintenance for Hybrid Synergy Drive can be more costly, given the intricate drivetrain and battery care requirements, while Mild Hybrid Systems benefit from lower maintenance demands and reduced repair costs over the vehicle's lifespan.
Market Availability and Popular Models
Hybrid Synergy Drive, pioneered by Toyota, dominates the global market with widespread availability in models like the Prius, Camry Hybrid, and RAV4 Hybrid offering full hybrid capabilities and better fuel efficiency. Mild Hybrid Systems, used in vehicles such as the Audi A6 and Honda Civic, have gained traction mainly in European and Asian markets due to lower complexity and cost, providing fuel savings through a small electric motor assist without pure electric mode. Market adoption favors Hybrid Synergy Drive for larger-scale hybrid performance, while Mild Hybrid Systems appeal to customers seeking incremental efficiency improvements in traditional gasoline vehicles.
Which Hybrid System Is Right for You?
Hybrid Synergy Drive offers fully electric driving capabilities with seamless transitions between electric and gasoline power, ideal for those seeking fuel efficiency and low emissions in daily commuting. Mild Hybrid Systems provide a smaller electric boost to enhance fuel economy and reduce emissions without full electric propulsion, making them suitable for drivers wanting improved performance without the complexity of full hybrids. Choosing between these systems depends on your driving habits, budget, and preference for electric-only driving range versus incremental efficiency gains.
Hybrid Synergy Drive vs Mild Hybrid System Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com