An MVP (Minimum Viable Product) prioritizes essential features to quickly validate market demand and gather user feedback with minimal development effort. A full product delivers a comprehensive, polished experience incorporating advanced functionalities and extensive testing to meet broader user needs. Choosing between an MVP and a full product depends on project goals, budget, and time-to-market considerations.
Table of Comparison
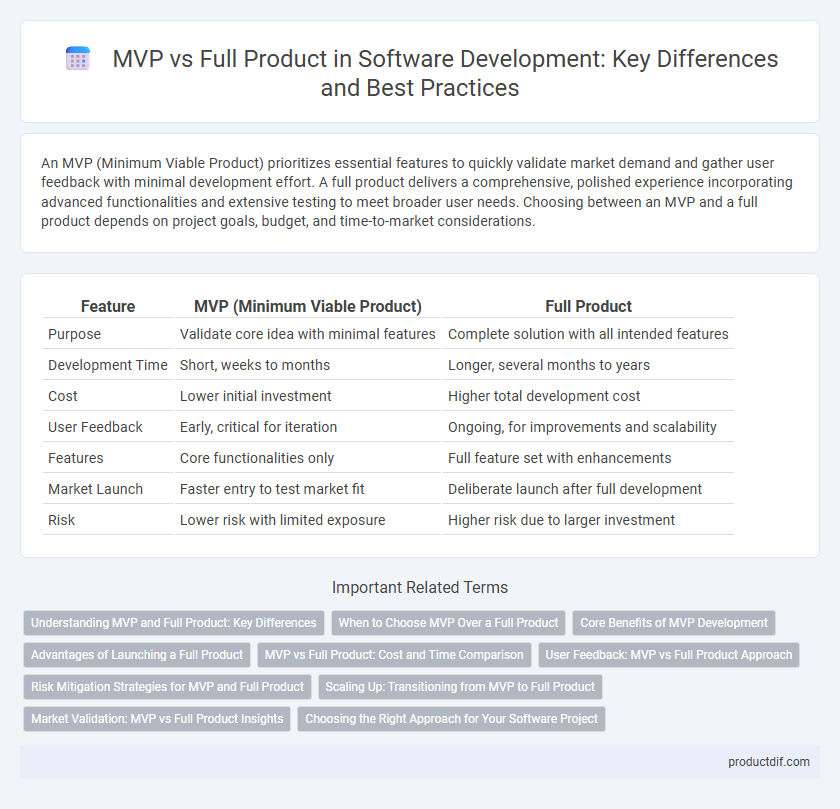
| Feature | MVP (Minimum Viable Product) | Full Product |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Validate core idea with minimal features | Complete solution with all intended features |
| Development Time | Short, weeks to months | Longer, several months to years |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher total development cost |
| User Feedback | Early, critical for iteration | Ongoing, for improvements and scalability |
| Features | Core functionalities only | Full feature set with enhancements |
| Market Launch | Faster entry to test market fit | Deliberate launch after full development |
| Risk | Lower risk with limited exposure | Higher risk due to larger investment |
Understanding MVP and Full Product: Key Differences
MVP (Minimum Viable Product) focuses on delivering the core features necessary to validate a product idea and gather user feedback quickly, minimizing development time and resources. A full product, however, encompasses a complete set of features, polished user experience, and robust functionality aimed at long-term market success and scalability. Understanding the differences between MVP and full product development is crucial for strategic planning, resource allocation, and iterative improvement in software projects.
When to Choose MVP Over a Full Product
Choosing an MVP over a full product is ideal during the early stages of software development when validating market demand and gathering user feedback is critical. MVPs allow rapid deployment with core features to test hypotheses while minimizing development costs and time-to-market. This approach reduces risk by enabling iterative improvements based on real user data before investing in a fully featured software product.
Core Benefits of MVP Development
MVP development accelerates time-to-market by focusing on essential features, enabling early user feedback and iterative improvement. It reduces development costs and risks by validating product-market fit before investing in full-scale production. This approach fosters agile innovation, ensuring the final product aligns closely with user needs and business goals.
Advantages of Launching a Full Product
Launching a full product provides users with a comprehensive experience that drives higher satisfaction and engagement, increasing the likelihood of positive reviews and long-term retention. A complete product often includes fully developed features and robust performance, reducing the need for frequent updates and patches, which enhances brand credibility. Full product launches also enable immediate revenue generation through various monetization strategies, supporting sustainable business growth and investor confidence.
MVP vs Full Product: Cost and Time Comparison
MVP development typically requires significantly lower costs and shorter timeframes compared to full product development, as it focuses on core features essential for market validation. Full product development demands higher investment in comprehensive functionalities, extensive testing, and scalability, leading to increased expenses and longer delivery schedules. Prioritizing an MVP allows startups to reduce financial risk and accelerate user feedback before committing resources to a complete product build.
User Feedback: MVP vs Full Product Approach
User feedback in an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) approach is gathered early and often, allowing rapid iteration based on real user interactions and pain points, which accelerates product-market fit. In contrast, a full product approach collects feedback post-launch, often leading to longer development cycles and delayed user validation. Leveraging MVP user feedback minimizes risks by prioritizing core features that address primary user needs before investing fully in feature-rich development.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for MVP and Full Product
Building an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) focuses on risk mitigation by validating core features with minimal investment, enabling rapid user feedback to identify and address potential market fit issues early. A full product incorporates comprehensive functionality, requiring extensive testing, robust architecture, and scalability planning to mitigate risks associated with deployment, performance, and user adoption. Prioritizing iterative development cycles and continuous integration in both MVP and full product strategies reduces operational risks and ensures timely delivery aligned with business objectives.
Scaling Up: Transitioning from MVP to Full Product
Scaling up from an MVP to a full product involves expanding features, enhancing system architecture, and improving user experience to meet broader market demands. This transition requires robust engineering practices, comprehensive testing, and scalable infrastructure to support increased user load and feature complexity. Prioritizing modular design and continuous integration facilitates smoother evolution from minimal viable functionality to a fully developed software solution.
Market Validation: MVP vs Full Product Insights
MVPs enable rapid market validation by delivering core functionalities to early adopters, minimizing development costs and gathering user feedback to iterate efficiently. Full products require more investment and time, making them riskier before confirming market demand. Leveraging MVPs accelerates product-market fit discovery, reducing uncertainty compared to launching fully featured solutions.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Software Project
Selecting an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) allows software teams to validate core functionalities quickly and gather user feedback with minimal resources. In contrast, building a full product demands greater investment and time but delivers a comprehensive feature set and polished user experience from launch. Prioritizing an MVP is ideal for reducing market risks and iterating based on real user insights, while a full product suits established markets with clear requirements.
MVP vs Full Product Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com