Agile methodology emphasizes iterative development, flexibility, and continuous feedback, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements. Waterfall follows a linear, sequential approach with predefined phases, making it suitable for projects with clear, unchanging objectives. Agile suits dynamic environments, while Waterfall is preferred for projects needing strict structure and documentation.
Table of Comparison
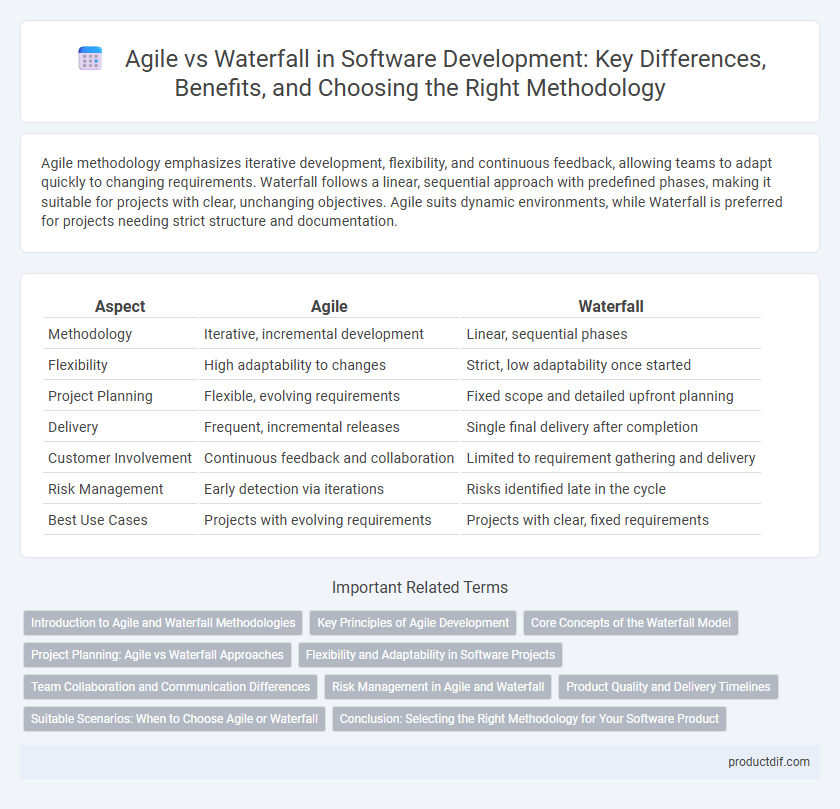
| Aspect | Agile | Waterfall |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology | Iterative, incremental development | Linear, sequential phases |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to changes | Strict, low adaptability once started |
| Project Planning | Flexible, evolving requirements | Fixed scope and detailed upfront planning |
| Delivery | Frequent, incremental releases | Single final delivery after completion |
| Customer Involvement | Continuous feedback and collaboration | Limited to requirement gathering and delivery |
| Risk Management | Early detection via iterations | Risks identified late in the cycle |
| Best Use Cases | Projects with evolving requirements | Projects with clear, fixed requirements |
Introduction to Agile and Waterfall Methodologies
Agile methodology emphasizes iterative development, flexibility, and continuous feedback, enabling teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements. Waterfall methodology follows a linear, sequential approach with distinct phases such as requirements gathering, design, implementation, and testing, making it suitable for projects with well-defined scope. Agile promotes collaboration and incremental delivery, while Waterfall relies on upfront planning and documentation for project execution.
Key Principles of Agile Development
Agile development emphasizes iterative progress through small, cross-functional teams delivering working software frequently, enhancing flexibility and customer collaboration. Key principles include embracing change even late in development, continuous feedback loops, and prioritizing individuals and interactions over rigid processes. This approach contrasts with Waterfall's linear, phase-based structure by promoting adaptive planning and faster value delivery.
Core Concepts of the Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model follows a linear and sequential approach where each phase--requirements, design, implementation, verification, and maintenance--must be completed before the next begins. Core concepts emphasize strict documentation, fixed project scope, and early requirement definition, minimizing changes during development. This model suits projects with well-understood requirements and low tolerance for scope changes, offering clear milestones and deliverables.
Project Planning: Agile vs Waterfall Approaches
Agile project planning emphasizes iterative development with flexible, adaptive schedules that accommodate changing requirements through continuous feedback and collaboration. Waterfall project planning follows a linear, sequential process with clearly defined phases and fixed timelines, enabling comprehensive upfront documentation and milestone-based progress tracking. Agile suits projects needing rapid adjustments, while Waterfall is ideal for well-defined projects with stable scope and predictable deliverables.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Software Projects
Agile software development offers greater flexibility and adaptability by allowing iterative progress and continuous feedback, enabling teams to respond swiftly to changing requirements. In contrast, the Waterfall model follows a linear, sequential approach with rigid phases, making it difficult to accommodate changes once the project is underway. Agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban enhance project adaptability, leading to improved risk management and higher client satisfaction in dynamic environments.
Team Collaboration and Communication Differences
Agile promotes continuous team collaboration through daily stand-ups, iterative feedback loops, and cross-functional team involvement, enabling adaptive communication and quick response to changes. Waterfall follows a linear approach where communication is typically formal and phase-based, with limited interaction between teams until project milestones are reached. The iterative nature of Agile fosters transparency and shared responsibility, contrasting with Waterfall's structured documentation-driven communication.
Risk Management in Agile and Waterfall
Agile risk management involves iterative assessment and continuous stakeholder feedback, enabling early detection and mitigation of potential issues throughout the development cycle. In contrast, Waterfall emphasizes upfront risk analysis during planning phases, with limited flexibility to adapt once the project progresses, increasing the likelihood of overlooked risks. Agile's adaptive approach reduces uncertainty and enhances project resilience compared to Waterfall's linear and rigid structure.
Product Quality and Delivery Timelines
Agile methodology enhances product quality by promoting iterative testing and continuous feedback, allowing for early detection and resolution of defects. In contrast, Waterfall's linear approach often delays testing until the end, increasing the risk of undiscovered issues that can affect final quality. Agile also accelerates delivery timelines by enabling incremental releases, whereas Waterfall's sequential phases can extend project duration due to rigid milestone dependencies.
Suitable Scenarios: When to Choose Agile or Waterfall
Agile is suitable for projects requiring flexibility, rapid iteration, and frequent customer feedback, such as software development with evolving requirements or startups launching minimum viable products. Waterfall works best for projects with well-defined, fixed requirements and a clear timeline, like regulatory compliance systems or construction software where sequential phases and documentation are critical. Choosing Agile or Waterfall depends on project complexity, stakeholder involvement, and the need for adaptability versus predictability.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Methodology for Your Software Product
Choosing the right methodology depends on project complexity, team size, and flexibility requirements. Agile suits dynamic projects with evolving requirements, fostering continuous collaboration and iterative delivery. Waterfall works best for well-defined projects with fixed scopes, offering structured phases and clear milestones for predictable outcomes.
Agile vs Waterfall Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com