Tankless water heaters provide hot water on demand, offering energy efficiency by heating only when needed, unlike tank-type heaters that store hot water constantly, leading to standby heat loss. Tank-type water heaters typically have a lower upfront cost but occupy more space and may deplete hot water during high usage periods. Choosing between these systems depends on household hot water needs, energy savings preferences, and installation space availability.
Table of Comparison
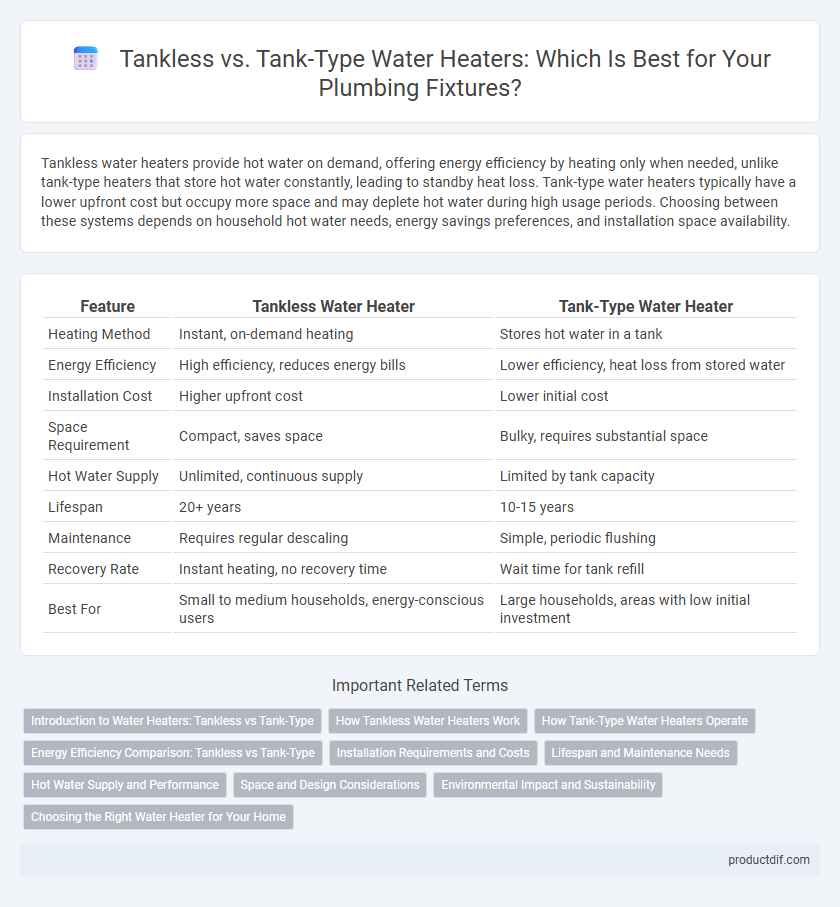
| Feature | Tankless Water Heater | Tank-Type Water Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Instant, on-demand heating | Stores hot water in a tank |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency, reduces energy bills | Lower efficiency, heat loss from stored water |
| Installation Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower initial cost |
| Space Requirement | Compact, saves space | Bulky, requires substantial space |
| Hot Water Supply | Unlimited, continuous supply | Limited by tank capacity |
| Lifespan | 20+ years | 10-15 years |
| Maintenance | Requires regular descaling | Simple, periodic flushing |
| Recovery Rate | Instant heating, no recovery time | Wait time for tank refill |
| Best For | Small to medium households, energy-conscious users | Large households, areas with low initial investment |
Introduction to Water Heaters: Tankless vs Tank-Type
Tankless water heaters provide hot water on demand, heating water directly without the use of a storage tank, which results in energy efficiency and endless hot water supply. Tank-type water heaters store a fixed volume of heated water in a tank, ready for use but can experience heat loss and limited capacity. Choosing between tankless and tank-type water heaters depends on factors such as household size, energy consumption preferences, and installation space.
How Tankless Water Heaters Work
Tankless water heaters heat water on demand by using powerful heating elements or burners that activate only when a faucet or shower is turned on, eliminating the need for a storage tank. This process ensures a continuous supply of hot water while reducing energy consumption compared to tank-type water heaters that store and constantly heat large volumes of water. Advanced flow sensors and thermostats regulate water temperature precisely, enhancing efficiency and providing consistent output without standby heat loss.
How Tank-Type Water Heaters Operate
Tank-type water heaters store and heat a fixed amount of water inside a heavily insulated tank until needed, maintaining the temperature through a thermostat-controlled heating element or gas burner. When hot water is drawn, cold water enters the bottom of the tank, ensuring a continuous supply as the water heats. This design provides immediate hot water but can lead to energy loss through standby heat.
Energy Efficiency Comparison: Tankless vs Tank-Type
Tankless water heaters deliver energy savings by heating water on demand, eliminating standby heat loss common in tank-type models which constantly maintain water temperature. Tank-type heaters consume more energy due to continuous reheating cycles to keep stored water hot, resulting in higher utility bills. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, tankless systems can be 24%-34% more energy-efficient for homes that use 41 gallons or less of hot water daily.
Installation Requirements and Costs
Tankless water heaters require specialized installation with high-powered electrical or gas connections, often increasing upfront labor costs compared to traditional tank-type water heaters that use standard plumbing and electrical setups. Tank-type water heaters have lower initial installation expenses but occupy more space and may need periodic maintenance due to sediment buildup. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints and available installation infrastructure, with tankless units generally offering long-term energy savings despite higher upfront costs.
Lifespan and Maintenance Needs
Tankless water heaters typically offer a lifespan of 20 years or more with minimal maintenance, requiring periodic descaling and filter cleaning to prevent mineral buildup. Traditional tank-type water heaters usually last 10 to 15 years and need regular flushing to avoid sediment accumulation that reduces efficiency and life. Choosing between them depends on long-term durability and the frequency of maintenance tasks required to sustain optimal performance.
Hot Water Supply and Performance
Tankless water heaters provide an endless supply of hot water by heating it on demand, ensuring consistent performance without the risk of running out during peak usage. Tank-type water heaters store a limited volume of hot water, which may be depleted during high-demand periods, resulting in fluctuating temperatures and delayed recovery times. The instant heating capability of tankless models enhances energy efficiency and delivers superior performance for continuous hot water supply in plumbing fixtures.
Space and Design Considerations
Tankless water heaters offer a compact design ideal for small spaces, mounting directly on walls and freeing up floor area compared to bulky tank-type models. Traditional tank water heaters require significant floor space due to their large storage tanks, limiting placement options in tight utility rooms or closets. Choosing between these types depends on available space, aesthetic preferences, and integration with existing plumbing layouts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tankless water heaters reduce energy consumption by heating water on demand, eliminating standby heat loss typical in tank-type models. This results in lower greenhouse gas emissions and less water waste due to quicker hot water delivery. The compact design of tankless units also reduces material usage and extends product lifespan, enhancing overall sustainability.
Choosing the Right Water Heater for Your Home
Choosing the right water heater for your home depends on factors like space, energy efficiency, and hot water demand. Tankless water heaters provide on-demand hot water and save energy by heating only when needed, making them ideal for smaller homes or those with limited space. Tank-type water heaters, with larger storage capacity, are suitable for households with high simultaneous hot water use or where water supply interruptions are common.
tankless vs tank-type water heater Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com