Mechanical action organs provide a tactile connection between the keys and the pipes, allowing for precise control over dynamics and articulation. Digital action organs, on the other hand, use electronic sensors and actuators to replicate the feel and response, offering greater flexibility in sound options and easier maintenance. While mechanical action is prized for its authentic touch and traditional craftsmanship, digital action excels in versatility and integration with modern technology.
Table of Comparison
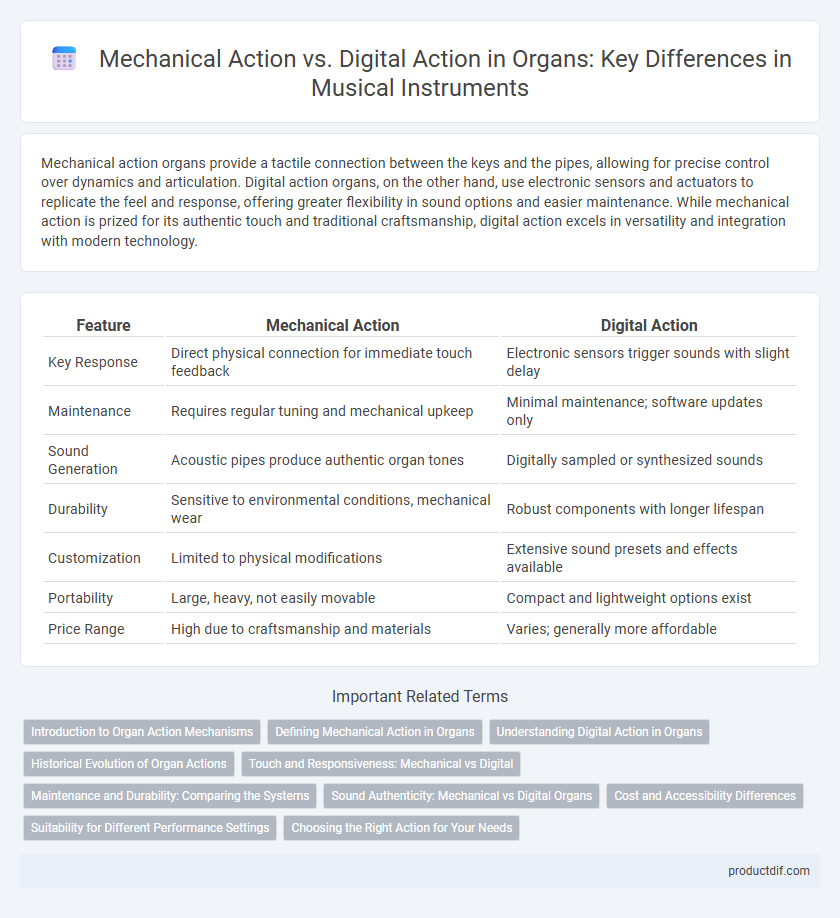
| Feature | Mechanical Action | Digital Action |
|---|---|---|
| Key Response | Direct physical connection for immediate touch feedback | Electronic sensors trigger sounds with slight delay |
| Maintenance | Requires regular tuning and mechanical upkeep | Minimal maintenance; software updates only |
| Sound Generation | Acoustic pipes produce authentic organ tones | Digitally sampled or synthesized sounds |
| Durability | Sensitive to environmental conditions, mechanical wear | Robust components with longer lifespan |
| Customization | Limited to physical modifications | Extensive sound presets and effects available |
| Portability | Large, heavy, not easily movable | Compact and lightweight options exist |
| Price Range | High due to craftsmanship and materials | Varies; generally more affordable |
Introduction to Organ Action Mechanisms
Mechanical action organs use a direct physical connection between the key and pipe valve, providing precise control and tactile feedback favored by traditionalists. Digital action organs employ electronic sensors and digital signals to trigger sound production, offering versatility and easier maintenance. Understanding these fundamental differences in organ action mechanisms highlights the balance between authenticity and technological advancement in organ design.
Defining Mechanical Action in Organs
Mechanical action in organs refers to the traditional system where the keys are directly connected to the valves that control air flow into the pipes through a series of levers, trackers, and rollers. This precise physical linkage allows for tactile feedback and expressive control over the sound, providing organists with nuanced touch sensitivity unmatched by digital counterparts. Mechanical action organs require meticulous craftsmanship and maintenance due to the complex mechanical connections, but they offer authentic acoustic sound production integral to classical organ performance.
Understanding Digital Action in Organs
Digital action in organs utilizes electronic sensors and microprocessors to trigger sound generation, replacing traditional mechanical linkages. This system enhances responsiveness, allows for more precise control over stops and registers, and supports complex memory settings for different tonal combinations. Digital action also reduces maintenance needs compared to mechanical action by eliminating physical wear on parts.
Historical Evolution of Organ Actions
Mechanical action organs, also known as tracker organs, date back to the medieval period and rely on direct physical connections between keys and pipes, ensuring precise control and tactile feedback for the organist. Digital action organs emerged in the late 20th century, using electrical sensors and digital processors to trigger sounds, allowing for greater flexibility, multiple stops, and integration with modern technology. The historical evolution from mechanical to digital actions reflects advancements in engineering and musical expression, balancing tradition with innovation in organ performance.
Touch and Responsiveness: Mechanical vs Digital
Mechanical action organs offer tactile feedback and direct physical connection between the keys and the pipes, resulting in precise touch sensitivity and dynamic control. Digital action organs utilize sensors to translate key presses into electronic signals, providing consistent responsiveness but often lacking the nuanced touch variations found in mechanical systems. Musicians frequently note that mechanical action enhances expressive playing by allowing subtle control over attack and release, whereas digital action prioritizes reliability and maintenance ease.
Maintenance and Durability: Comparing the Systems
Mechanical action organs, featuring direct tracker connections, require regular tuning and lubrication to maintain responsiveness, but their robust construction often ensures longevity and ease of repair. Digital action organs rely on electronic sensors and circuit boards, which reduce mechanical wear but may face challenges with component obsolescence and require specialized technical support for repairs. Durability in mechanical systems benefits from traditional craftsmanship, while digital systems offer consistency but depend heavily on electronic maintenance and software updates.
Sound Authenticity: Mechanical vs Digital Organs
Mechanical action organs provide unparalleled sound authenticity through direct physical interaction between keys and pipes, resulting in natural acoustic resonance and dynamic tonal variation. In contrast, digital action organs replicate sounds via sampled or synthesized audio, which can include precise tonal characteristics but may lack the subtle nuances and organic feedback inherent to mechanical systems. Sound purists often prefer mechanical action for its genuine auditory experience that faithfully reproduces traditional pipe organ timbres.
Cost and Accessibility Differences
Mechanical action organs often have higher upfront costs due to intricate craftsmanship and use of traditional materials, limiting accessibility for budget-conscious musicians. Digital action organs provide a more affordable alternative by utilizing electronic components, making them widely accessible for institutions and beginners. Maintenance costs are generally lower for digital organs, enhancing long-term accessibility and usability.
Suitability for Different Performance Settings
Mechanical action organs offer precise tactile feedback and are ideal for historical and classical performances in churches and concert halls, where authenticity and nuanced control are essential. Digital action organs provide greater versatility, suitable for varied performance settings such as studios and modern venues, due to features like adjustable touch sensitivity and integrated sound libraries. Choice depends on whether the setting prioritizes traditional craftsmanship or adaptable, technology-enhanced sound production.
Choosing the Right Action for Your Needs
Mechanical action organs offer tactile feedback and precise control through direct key-to-pipe connection, ideal for traditionalists valuing authenticity. Digital action organs provide versatility with customizable sounds, lower maintenance, and easier installation, suiting modern environments and budget-conscious buyers. Selecting the right action depends on balancing historical sound quality with functionality, space, and intended use.
Mechanical Action vs Digital Action (in organs) Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com