The concertina offers a more compact and lightweight design compared to the accordion, making it ideal for portability and ease of playing in tight spaces. While the accordion features a piano-style keyboard or buttons with a broader range of notes and dynamic control, the concertina's button layout allows for quicker, more intricate finger movements. Both instruments share a free-reed mechanism, but the accordion's larger size supports greater tonal variety and volume, making it popular in diverse musical genres.
Table of Comparison
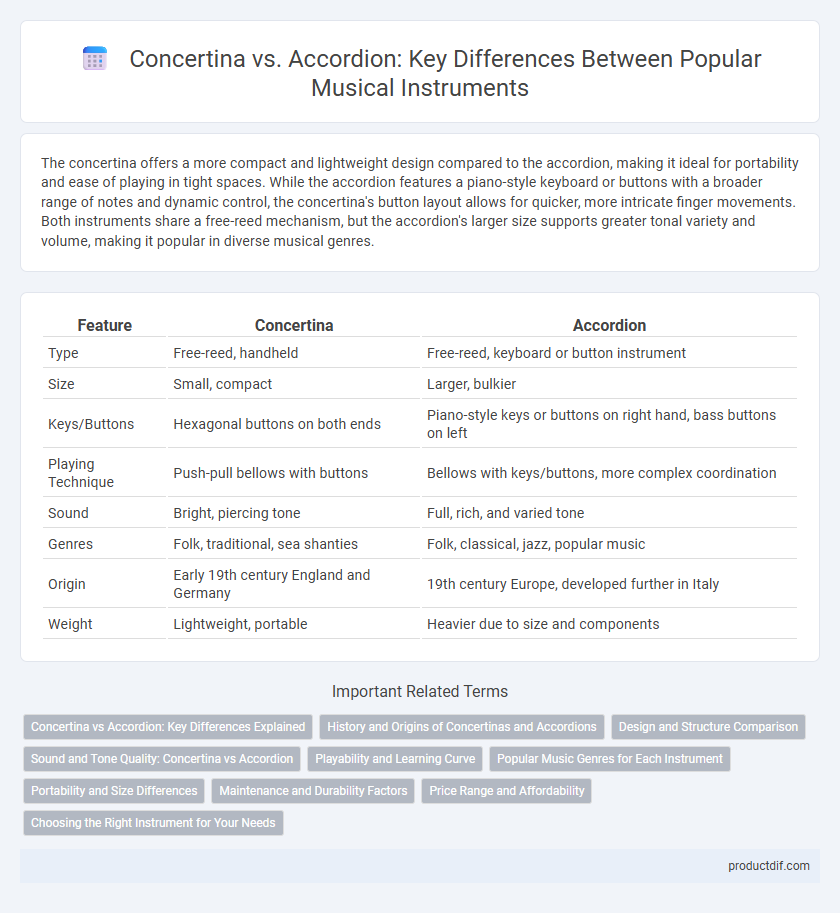
| Feature | Concertina | Accordion |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Free-reed, handheld | Free-reed, keyboard or button instrument |
| Size | Small, compact | Larger, bulkier |
| Keys/Buttons | Hexagonal buttons on both ends | Piano-style keys or buttons on right hand, bass buttons on left |
| Playing Technique | Push-pull bellows with buttons | Bellows with keys/buttons, more complex coordination |
| Sound | Bright, piercing tone | Full, rich, and varied tone |
| Genres | Folk, traditional, sea shanties | Folk, classical, jazz, popular music |
| Origin | Early 19th century England and Germany | 19th century Europe, developed further in Italy |
| Weight | Lightweight, portable | Heavier due to size and components |
Concertina vs Accordion: Key Differences Explained
The concertina features a compact, hexagonal or octagonal shape with buttons on both ends, producing sound by pushing or pulling bellows in a more direct manner compared to the accordion's larger, rectangular design with a piano-style keyboard and bass buttons. Unlike accordions that offer greater volume and chordal accompaniment suited for ensemble performances, concertinas deliver a distinctive, reedy tone favored in folk and traditional music. The concertina's button layout provides a more uniform note arrangement, while the accordion's keyboard allows for more complex melodies and harmonies, highlighting functional differences between these two free-reed instruments.
History and Origins of Concertinas and Accordions
The concertina, invented in the early 19th century by Sir Charles Wheatstone in England, features hexagonal ends and buttons on both sides, distinguishing it with a compact, bellows-driven design. The accordion, originating in early 19th-century Europe, particularly Austria, was independently developed with a keyboard or buttons on one or both sides, offering a fuller, more versatile sound suited for various musical styles. Both instruments evolved as portable, bellows-operated free-reed aerophones but emerged from distinct cultural and technological traditions reflecting their unique musical roles.
Design and Structure Comparison
The concertina features a compact, hexagonal or octagonal body with buttons on both ends, enabling a more symmetrical hand position, whereas the accordion boasts a larger, rectangular frame with a piano-style keyboard or buttons on one side and bass buttons on the other. Concertinas typically have bellows that expand and contract between two sets of reed chambers, offering a lighter and more portable design compared to the accordion's robust construction with multiple reed blocks and a more complex mechanism. The accordion's extensive keyboard range and bass system support richer harmonic capabilities, while the concertina's simpler button layout delivers crisp, staccato tones ideal for traditional folk music.
Sound and Tone Quality: Concertina vs Accordion
The concertina produces a bright, crisp sound with a clear, reedy tone that excels in traditional folk music and chamber settings. The accordion offers a richer, fuller sound with more dynamic range due to its larger reeds and multiple registers, making it versatile across genres like classical, jazz, and popular music. While the concertina's tone is more piercing and direct, the accordion's sound typically features layered harmonics and sustained resonance.
Playability and Learning Curve
Concertinas offer greater portability and simpler button layouts, making them easier for beginners to grasp compared to accordions. Accordions feature multiple keyboard rows and bass buttons, which provide a broader range but require significant practice to master. The learning curve for concertinas is generally shorter, while accordions demand more time to develop coordination between both hands.
Popular Music Genres for Each Instrument
The concertina is prominently featured in traditional Irish folk and English sea shanties, valued for its distinct, punchy tones that suit lively, melodic tunes. The accordion finds broader use across various popular music genres, notably in Cajun, Zydeco, Tejano, and some forms of European folk music, where its versatile range and rich harmonics enhance rhythmic and melodic layers. Both instruments offer unique textural qualities but cater to different stylistic traditions and regional musical expressions.
Portability and Size Differences
The concertina is notably more compact and lightweight compared to the accordion, making it highly portable for musicians who travel frequently. While accordions vary in size, they tend to be bulkier and heavier, often requiring straps and cases for easier handling. Concertinas generally fit into smaller carrying bags, enhancing convenience without sacrificing sound quality.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Concertinas require regular tuning and careful protection of their delicate reed chambers to maintain sound quality, while accordions often need periodic adjustments of bellows and buttons due to more complex mechanics. The wooden frames of concertinas are susceptible to humidity damage, necessitating controlled storage environments, whereas accordions typically feature reinforced plastic or metal components that enhance durability. Proper maintenance of both instruments extends their lifespan, but accordions generally withstand heavy usage better due to sturdier construction.
Price Range and Affordability
The concertina typically ranges from $150 to $800, making it more affordable for beginners and casual players compared to accordions, which start around $300 and can exceed $3,000 for professional models. Accordions' higher price reflects their complex mechanics and larger size, often including more keys and reed banks. Budget-conscious musicians may prefer concertinas for their portability and lower initial investment without sacrificing essential musical capabilities.
Choosing the Right Instrument for Your Needs
Choosing between a concertina and an accordion depends on your musical style and portability preferences. Concertinas are compact and ideal for traditional folk tunes, offering a distinctive, crisp sound with a button layout that varies by system (English, Anglo, or duet). Accordions provide a wider range of notes and dynamic expression, making them suitable for diverse genres from classical to jazz, though they tend to be bulkier and require more physical strength to play.
Concertina vs Accordion Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com