Analog synths produce warm, rich sounds through continuous electrical signals, favored for their organic and vintage tones. Digital synths generate sounds using digital signal processing, offering versatile sound design, precise control, and a wider range of timbres. Musicians often choose analog for character and depth, while digital synths excel in flexibility and integration with modern music production.
Table of Comparison
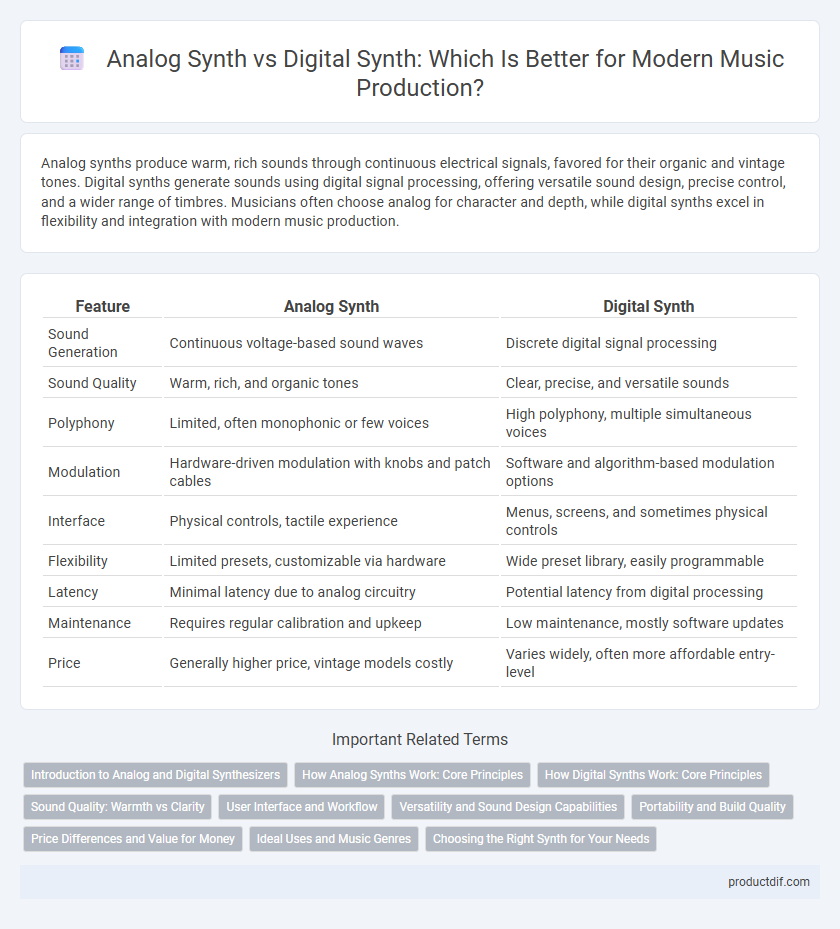
| Feature | Analog Synth | Digital Synth |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Generation | Continuous voltage-based sound waves | Discrete digital signal processing |
| Sound Quality | Warm, rich, and organic tones | Clear, precise, and versatile sounds |
| Polyphony | Limited, often monophonic or few voices | High polyphony, multiple simultaneous voices |
| Modulation | Hardware-driven modulation with knobs and patch cables | Software and algorithm-based modulation options |
| Interface | Physical controls, tactile experience | Menus, screens, and sometimes physical controls |
| Flexibility | Limited presets, customizable via hardware | Wide preset library, easily programmable |
| Latency | Minimal latency due to analog circuitry | Potential latency from digital processing |
| Maintenance | Requires regular calibration and upkeep | Low maintenance, mostly software updates |
| Price | Generally higher price, vintage models costly | Varies widely, often more affordable entry-level |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Synthesizers
Analog synthesizers generate sound using continuous electrical signals through voltage-controlled oscillators, filters, and amplifiers, offering rich, warm tones favored in classic music production. Digital synthesizers create sounds using digital signal processing algorithms, enabling a vast palette of sounds and effects with precise control and programmability. Both types provide unique sonic characteristics and performance features crucial in shaping modern and vintage music styles.
How Analog Synths Work: Core Principles
Analog synths generate sound through continuous electrical signals produced by voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs), filters (VCFs), and amplifiers (VCAs). Their core principle relies on manipulating these signals via analog circuits to create rich, warm tones with natural variations and subtle imperfections. This hands-on, circuit-based approach enables real-time modulation and dynamic sound shaping unique to analog synthesis.
How Digital Synths Work: Core Principles
Digital synthesizers generate sound by manipulating numerical data through algorithms that emulate waveforms and sound textures. Core principles include frequency modulation, wavetable synthesis, and sample playback, allowing precise control over tonal variation. These methods enable complex sound design by processing digital signals within the device's DSP (Digital Signal Processor) chip.
Sound Quality: Warmth vs Clarity
Analog synthesizers produce rich, warm tones due to their continuous voltage-controlled oscillators and filters, creating natural, organic sound textures favored in classic and vintage music production. Digital synthesizers generate precise, clean, and clear sound using complex algorithms and digital signal processing, enabling versatile and consistent tonal outputs ideal for modern genres and studio settings. Sound quality differences between analog synths' warmth and digital synths' clarity depend on user preference, musical context, and desired sonic characteristics.
User Interface and Workflow
Analog synths feature tactile knobs and sliders, offering immediate hands-on control that enhances creative spontaneity during sound design. Digital synths provide customizable interfaces and programmable presets, enabling complex sound manipulation and streamlined workflow efficiency. Users often prefer analog for expressive performance, while digital models excel in versatility and recall functions.
Versatility and Sound Design Capabilities
Analog synths offer rich, warm tones with hands-on modulation, favored for classic sound textures and dynamic real-time tweaking. Digital synths excel in versatility, providing expansive preset libraries, complex algorithms, and seamless integration with software environments for intricate sound design. Sound designers often combine both to leverage analog warmth and digital precision, achieving diverse sonic palettes.
Portability and Build Quality
Analog synths often feature robust, vintage-style hardware that offers superior tactile controls and durability but tend to be heavier and less portable due to bulky components and metal chassis. Digital synths prioritize lightweight design with modern materials like plastic and compact circuitry, enhancing portability and ease of transport for live performances. High-end digital models may still offer solid build quality, but analog units typically provide a more rugged and reliable construction favored by touring musicians.
Price Differences and Value for Money
Analog synthesizers often come with a higher price tag due to their complex circuitry and vintage appeal, making them a premium choice for enthusiasts seeking classic warmth and authenticity. Digital synthesizers typically offer more affordable options with versatile sound engines, extensive presets, and modern connectivity features, delivering excellent value for money for budget-conscious musicians. Comparing price differences reveals that while analog synths excel in sonic character, digital synths maximize functionality and affordability, catering to diverse musical needs.
Ideal Uses and Music Genres
Analog synths excel in producing warm, rich tones ideal for classic genres like funk, rock, and electronic dance music, where organic sound textures are prized. Digital synths offer versatile sound design and complex modulation capabilities, making them perfect for modern genres such as pop, hip-hop, and experimental music that demand precise control and innovative effects. Both synth types can be used in studio production and live performances, but analog synths are favored for their vintage character while digital synths are chosen for their flexibility and reliability.
Choosing the Right Synth for Your Needs
When selecting a synth, consider that analog synthesizers deliver rich, warm tones generated through continuous voltage changes, ideal for classic, textured sounds. Digital synthesizers provide greater versatility and precision via complex algorithms and sampling, suited for diverse music styles and modern production needs. Assess your preferred sound characteristics, workflow, and budget to determine whether the organic feel of analog or the expansive capabilities of digital synths best align with your creative goals.
Analog synth vs Digital synth Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com