Analog synthesizers generate sound through continuous electrical signals, offering warm, rich tones favored by many musicians. Digital synthesizers use digital signal processing to produce a broader range of sounds with greater precision and versatility. Choosing between analog and digital synthesizers depends on desired sound quality, flexibility, and personal preference.
Table of Comparison
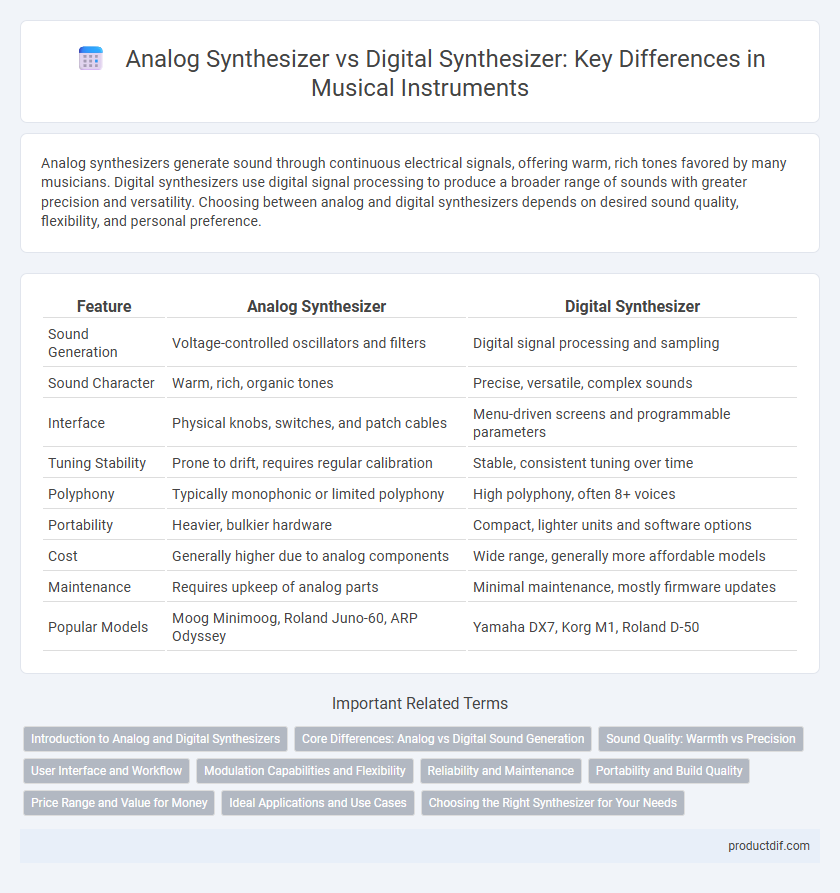
| Feature | Analog Synthesizer | Digital Synthesizer |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Generation | Voltage-controlled oscillators and filters | Digital signal processing and sampling |
| Sound Character | Warm, rich, organic tones | Precise, versatile, complex sounds |
| Interface | Physical knobs, switches, and patch cables | Menu-driven screens and programmable parameters |
| Tuning Stability | Prone to drift, requires regular calibration | Stable, consistent tuning over time |
| Polyphony | Typically monophonic or limited polyphony | High polyphony, often 8+ voices |
| Portability | Heavier, bulkier hardware | Compact, lighter units and software options |
| Cost | Generally higher due to analog components | Wide range, generally more affordable models |
| Maintenance | Requires upkeep of analog parts | Minimal maintenance, mostly firmware updates |
| Popular Models | Moog Minimoog, Roland Juno-60, ARP Odyssey | Yamaha DX7, Korg M1, Roland D-50 |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Synthesizers
Analog synthesizers generate sound through continuous electrical signals using voltage-controlled oscillators, filters, and amplifiers, delivering warm and rich tones favored in classic music production. Digital synthesizers create sound by processing digital signals with complex algorithms, offering greater versatility, precise control, and the ability to emulate a wide range of instruments and effects. Understanding the core differences in signal generation and sound manipulation highlights the distinct sonic characteristics and practical applications of analog versus digital synthesizers.
Core Differences: Analog vs Digital Sound Generation
Analog synthesizers generate sound through continuous electrical signals using voltage-controlled oscillators, filters, and amplifiers, producing warm, rich, and often unpredictable tones characteristic of vintage electronic music. Digital synthesizers create sounds by processing discrete digital data with algorithms or samples, offering precise control, complex modulation options, and a wide variety of sound textures that can mimic acoustic instruments or create entirely new sonic landscapes. The core difference lies in analog's organic, tactile sound production versus digital's versatile, high-fidelity sound generation and manipulation capabilities.
Sound Quality: Warmth vs Precision
Analog synthesizers produce rich, warm sound characterized by natural imperfections and continuous voltage variations that create harmonic complexity. Digital synthesizers deliver precise, clean tones with high stability and consistency, often emulating a wide range of sounds through advanced algorithms. Sound quality in analog synths offers organic warmth ideal for expressive music, while digital synths provide exact replication and versatility suited for diverse modern genres.
User Interface and Workflow
Analog synthesizers offer tactile controls such as knobs, sliders, and patch cables, enabling hands-on manipulation and immediate sound shaping. Digital synthesizers often provide menu-driven interfaces with LCD screens, requiring navigation through multiple layers for parameter editing. Workflow on analog machines emphasizes intuitive, real-time interaction, while digital synthesizers prioritize versatility and complex sound design through programmable presets.
Modulation Capabilities and Flexibility
Analog synthesizers offer rich, warm modulation through voltage-controlled oscillators and filters, providing unique, organic sound variations prized in classic analog tones. Digital synthesizers excel in modulation flexibility by utilizing complex algorithms and extensive parameter control, enabling precise and diverse sound design options unattainable in purely analog systems. The choice depends on a musician's preference for either the tactile, evolving character of analog modulation or the expansive, customizable modulation matrices available in digital synths.
Reliability and Maintenance
Analog synthesizers require more frequent calibration and component replacements due to their reliance on voltage-controlled circuits, which can drift over time. Digital synthesizers offer greater reliability with stable tuning and fewer mechanical parts, reducing maintenance needs significantly. However, analog units often benefit from skilled technicians for repairs, whereas digital models depend more on software updates and firmware integrity.
Portability and Build Quality
Analog synthesizers typically feature robust, handcrafted components and metal chassis, offering superior build quality but often resulting in heavier, less portable instruments compared to digital synthesizers. Digital synthesizers leverage lightweight materials and compact designs, enhancing portability ideal for touring musicians and mobile setups while maintaining reliable durability. Users must balance the analog warmth and tactile control against digital convenience and ease of transport when selecting between these synthesizer types.
Price Range and Value for Money
Analog synthesizers generally command higher price ranges due to their vintage components and warm, rich sound quality, often appealing to professional musicians and enthusiasts seeking authentic tonality. Digital synthesizers offer broader affordability with diverse sound capabilities and features, delivering excellent value for money for beginners and budget-conscious buyers. Choosing between the two depends on whether the priority lies in analog warmth and tactile control or versatile sound engines and cost-effectiveness.
Ideal Applications and Use Cases
Analog synthesizers excel in producing warm, rich tones ideal for genres like electronic, funk, and vintage sound design, favored in live performances and studio recordings seeking classic sonic textures. Digital synthesizers offer extensive versatility with complex sound manipulation, perfect for modern electronic music, film scoring, and experimental soundscapes requiring diverse and evolving timbres. Both types serve unique roles, with analog suited for hands-on, expressive play and digital optimized for precision, multi-layered compositions, and integration with digital audio workstations (DAWs).
Choosing the Right Synthesizer for Your Needs
Analog synthesizers deliver warm, rich sounds with organic modulation, ideal for musicians seeking classic tones and hands-on control. Digital synthesizers offer extensive sound design possibilities, complex waveforms, and presets suited for versatility and modern production environments. Evaluating factors such as sound character, workflow preferences, and intended application helps determine the optimal synthesizer for your musical needs.
Analog synthesizer vs Digital synthesizer Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com