Vinyl synths offer a unique blend of retro aesthetics and tactile control through their iconic vinyl record-inspired interfaces, delivering warm, textured sounds that appeal to experimental musicians and vinyl enthusiasts. Analog synths produce rich, warm tones by manipulating continuous electrical signals through oscillators and filters, prized for their authentic, dynamic sound quality and hands-on modulation capabilities. Both instruments cater to different creative needs, with vinyl synths emphasizing visual and physical interaction, while analog synths prioritize sonic depth and classic synthesis techniques.
Table of Comparison
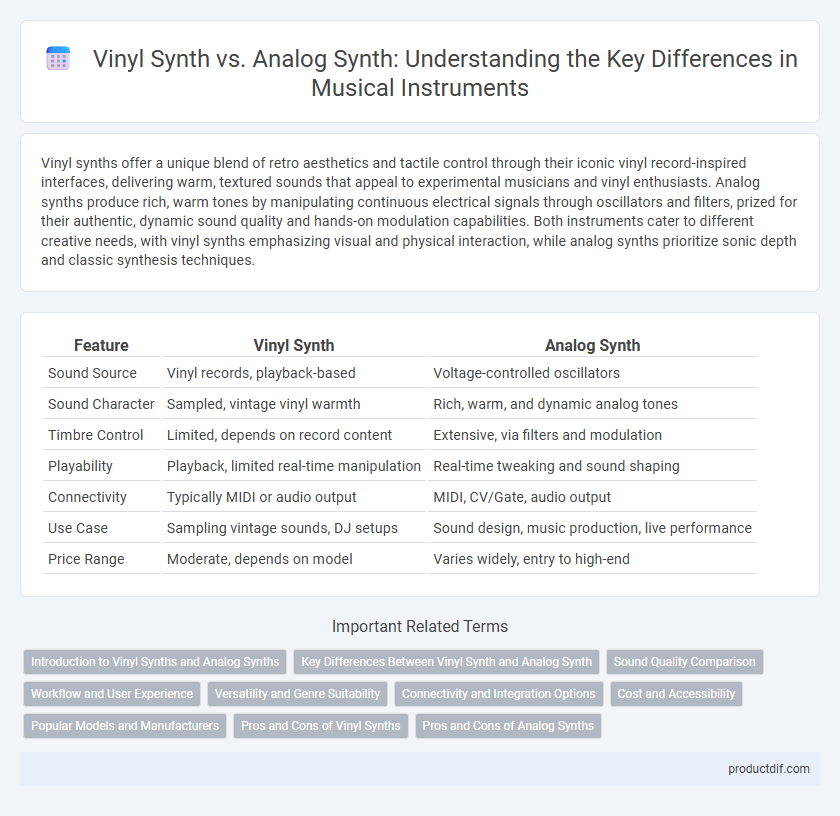
| Feature | Vinyl Synth | Analog Synth |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Source | Vinyl records, playback-based | Voltage-controlled oscillators |
| Sound Character | Sampled, vintage vinyl warmth | Rich, warm, and dynamic analog tones |
| Timbre Control | Limited, depends on record content | Extensive, via filters and modulation |
| Playability | Playback, limited real-time manipulation | Real-time tweaking and sound shaping |
| Connectivity | Typically MIDI or audio output | MIDI, CV/Gate, audio output |
| Use Case | Sampling vintage sounds, DJ setups | Sound design, music production, live performance |
| Price Range | Moderate, depends on model | Varies widely, entry to high-end |
Introduction to Vinyl Synths and Analog Synths
Vinyl synths combine traditional analog synthesis with unique vinyl record sampling, allowing musicians to manipulate sounds through spinning records for expressive audio textures. Analog synths generate sounds using continuous electrical signals and oscillators, producing rich, warm tones prized in classic and modern music production. Both instruments offer distinct sonic characteristics, with vinyl synths providing tactile interaction with analog audio sources and analog synths delivering pure, hands-on sound shaping capabilities.
Key Differences Between Vinyl Synth and Analog Synth
Vinyl synths utilize digitally sampled vinyl records to generate sounds, offering authentic vintage textures and organic imperfections, while analog synths produce sound through continuous electrical signals, delivering warm, rich tones with greater modulation flexibility. Unlike analog synths that rely on oscillators, filters, and envelopes to shape sound in real-time, vinyl synths depend on playback of pre-recorded audio, limiting real-time sound manipulation. Key differences include signal generation, sound customization capabilities, and the overall tactile interaction, with analog synths favored for dynamic sound design and vinyl synths prized for classic, sample-based timbres.
Sound Quality Comparison
Vinyl synths deliver a raw, gritty texture with subtle imperfections that create a warm, organic sound, often prized in lo-fi and retro music genres. Analog synths produce rich, full-bodied tones with smooth modulation capabilities, offering dynamic warmth and depth due to their circuitry and voltage-controlled oscillators. Sound quality in vinyl synths is characterized by a vintage charm whereas analog synths excel in providing versatile, high-fidelity audio with nuanced harmonic content.
Workflow and User Experience
Vinyl synths offer tactile, hands-on control with intuitive knob and slider layouts that enhance real-time sound shaping, ideal for musicians who prioritize immediacy and organic interaction. Analog synths provide a warmer, more consistent tonal character with straightforward signal paths, favored for their reliability and classic workflow in studio and live settings. The user experience diverges as vinyl synths emphasize creative exploration through physical engagement, while analog synths streamline sound design with predictable, stable interfaces.
Versatility and Genre Suitability
Vinyl synths excel in producing warm, textured sounds ideal for retro, hip-hop, and experimental genres due to their characteristic analog warmth and unique imperfections. Analog synths offer greater versatility with rich, customizable tones suitable for a wide range of genres including electronic, pop, and rock, thanks to their extensive modulation capabilities and intuitive controls. Musicians seeking specific vintage textures may prefer vinyl synths, while those requiring adaptable sound design favor analog synths for diverse musical styles.
Connectivity and Integration Options
Vinyl synths typically feature limited connectivity, relying mostly on basic audio outputs and simple control interfaces, which restricts their integration with modern studio equipment. Analog synths offer extensive connectivity options, including MIDI, CV/Gate, USB, and multiple audio outputs, enabling seamless integration with digital audio workstations and modular synth setups. This broad compatibility makes analog synths more versatile for live performances and complex production environments.
Cost and Accessibility
Vinyl synths generally offer a more affordable entry point for musicians seeking unique sound textures, with prices often lower than traditional analog synths. Analog synths, known for their rich, warm tones, tend to be costlier due to intricate circuitry and higher production values, limiting accessibility for beginners. The availability of used analog synth models and affordable vinyl synth alternatives provides diverse options catering to different budget levels and musical needs.
Popular Models and Manufacturers
Popular vinyl synth models include the Roland Juno-106 and Yamaha DX7, revered for their distinctive digital waveforms and iconic vinyl-era sounds. Analog synth giants like Moog, with the Minimoog Model D, and Korg, featuring the MS-20, dominate the market with warm, rich tones crafted through traditional voltage-controlled oscillators. Manufacturers such as Roland and Moog continue to push innovation, blending vintage appeal with modern functionality in both vinyl and analog synthesizers.
Pros and Cons of Vinyl Synths
Vinyl synths offer a unique tactile experience with authentic vinyl record manipulation that enhances creativity and sound design, making them ideal for DJs and producers seeking vintage textures. Their limitation lies in less precision and fewer sound-modulation options compared to modern digital or analog synths, which might affect versatility in studio settings. Vinyl synth sound quality may degrade over time due to physical wear, posing maintenance challenges absent in fully digital or purely analog synthesizers.
Pros and Cons of Analog Synths
Analog synths offer rich, warm tones with natural harmonic distortion that many musicians prefer for their organic sound quality. They provide tactile control through knobs and sliders, enabling intuitive sound design but can be prone to tuning instability and require regular maintenance. The vintage circuitry often results in unique, unpredictable sonic characteristics, though they tend to be bulkier and less versatile compared to digital counterparts like vinyl synth emulations.
Vinyl synth vs Analog synth Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com