Tube amps deliver warm, rich tones favored by guitarists for their natural compression and harmonic distortion, creating dynamic and expressive sound. Solid-state amps offer reliable, lightweight performance with clean, crisp audio and greater durability, making them ideal for consistent practice and gigging. Musicians often choose tube amps for vintage warmth and solid-state amps for affordability and ease of maintenance.
Table of Comparison
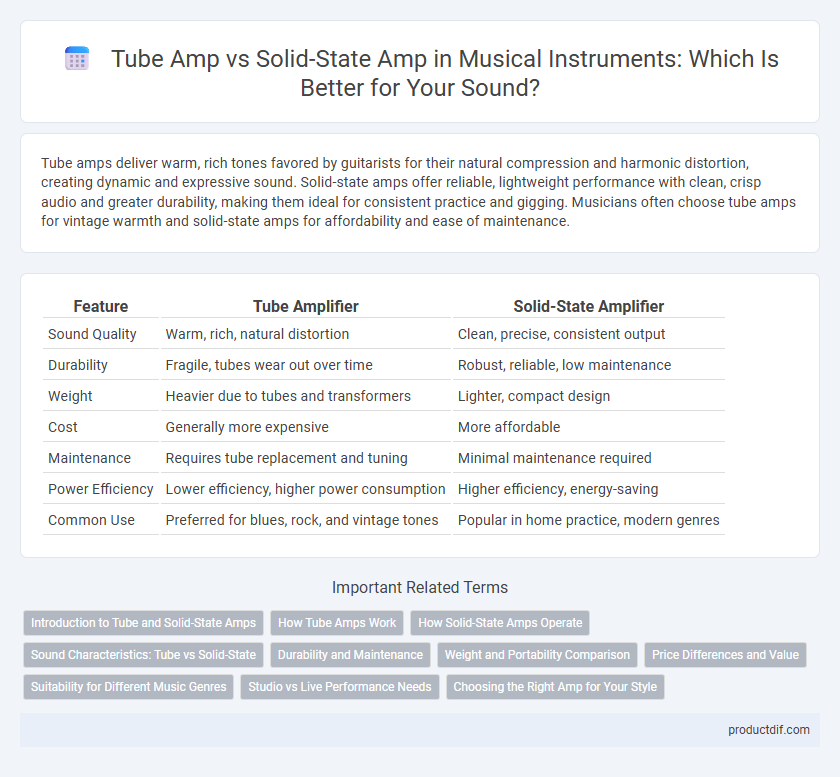
| Feature | Tube Amplifier | Solid-State Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Quality | Warm, rich, natural distortion | Clean, precise, consistent output |
| Durability | Fragile, tubes wear out over time | Robust, reliable, low maintenance |
| Weight | Heavier due to tubes and transformers | Lighter, compact design |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More affordable |
| Maintenance | Requires tube replacement and tuning | Minimal maintenance required |
| Power Efficiency | Lower efficiency, higher power consumption | Higher efficiency, energy-saving |
| Common Use | Preferred for blues, rock, and vintage tones | Popular in home practice, modern genres |
Introduction to Tube and Solid-State Amps
Tube amps use vacuum tubes to amplify sound, producing warm, rich tones favored in genres like blues and rock; they exhibit natural compression and harmonic distortion valued by musicians. Solid-state amps utilize semiconductor transistors for amplification, offering greater reliability, lighter weight, and cleaner, more consistent sound ideal for various music styles and live performances. Understanding the fundamental difference between tube and solid-state technology helps musicians choose the right amplifier based on tonal preference and practical needs.
How Tube Amps Work
Tube amps use vacuum tubes to amplify the electrical signal from an instrument by controlling electron flow through a heated cathode and anode. This process introduces natural harmonic distortion and warmth, contributing to their distinctive rich, warm sound preferred by many musicians. The circuitry relies on amplification stages within the vacuum tubes, which shape tone characteristics by generating dynamic response and natural compression.
How Solid-State Amps Operate
Solid-state amps operate using transistors that amplify the electrical signals from musical instruments with high efficiency and durability. These amplifiers convert the analog input into electronic signals controlled by semiconductor components, resulting in consistent sound output and lower maintenance compared to tube amps. Solid-state technology enables precise tone shaping and lightweight designs favored in various musical genres.
Sound Characteristics: Tube vs Solid-State
Tube amps deliver warm, rich, and harmonically complex tones with natural compression and dynamic response, prized for their musicality and smooth overdrive characteristics. Solid-state amps provide clean, precise, and consistent sound with high headroom, offering clarity and reliability for a wide range of musical styles and volume levels. Guitarists often choose tube amps for vintage warmth and organic distortion, while solid-state amps excel in accuracy and low maintenance.
Durability and Maintenance
Tube amps typically require more maintenance due to fragile vacuum tubes that wear out and need periodic replacement, impacting long-term durability. Solid-state amps feature robust transistor components, offering greater resistance to physical damage and lower upkeep demands. Musicians seeking longevity and minimal maintenance often prefer solid-state amplifiers for consistent performance.
Weight and Portability Comparison
Tube amps typically weigh more than solid-state amps due to heavy transformers and glass tubes, affecting portability for musicians who travel frequently. Solid-state amplifiers use lighter, more compact electronic components, making them ideal for gigging artists seeking easy transport. Choosing a solid-state amp often results in less physical strain and faster setup times during performances or rehearsals.
Price Differences and Value
Tube amps generally have higher price points due to their complex design and premium components, often ranging from $500 to over $3,000. Solid-state amps are more affordable, typically priced between $100 and $800, providing cost-effective options for beginners or budget-conscious musicians. The value of tube amps lies in their warm, dynamic sound quality, justifying the investment for pros, whereas solid-state amps offer durable, lightweight, and low-maintenance performance for everyday use.
Suitability for Different Music Genres
Tube amps deliver warm, rich tones favored in blues, jazz, and classic rock for their natural harmonic distortion and dynamic response. Solid-state amps excel in genres requiring clean, precise sounds or high gain, such as metal, pop, and electronic music, by providing consistent performance and durability. Musicians select tube or solid-state amps based on the tonal characteristics and reliability demanded by their specific music style.
Studio vs Live Performance Needs
Tube amps deliver warm, rich tones favored in studio recording for their natural harmonic distortion and dynamic response. Solid-state amps provide consistent power output and reliability, making them ideal for live performances where durability and low maintenance are crucial. Musicians often choose tube amps to capture authentic sound textures in controlled environments, while solid-state amps support sturdier stage setups and louder venues.
Choosing the Right Amp for Your Style
Tube amps deliver warm, rich tones with natural compression favored by blues, rock, and jazz guitarists seeking vintage sound. Solid-state amps provide reliable, lightweight performance with clean, crisp output ideal for genres like pop, metal, and funk requiring high gain and clarity. Musicians should consider their preferred tonal characteristics, gigging frequency, and maintenance preferences when selecting between tube and solid-state amplifiers.
Tube amp vs Solid-state amp Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com