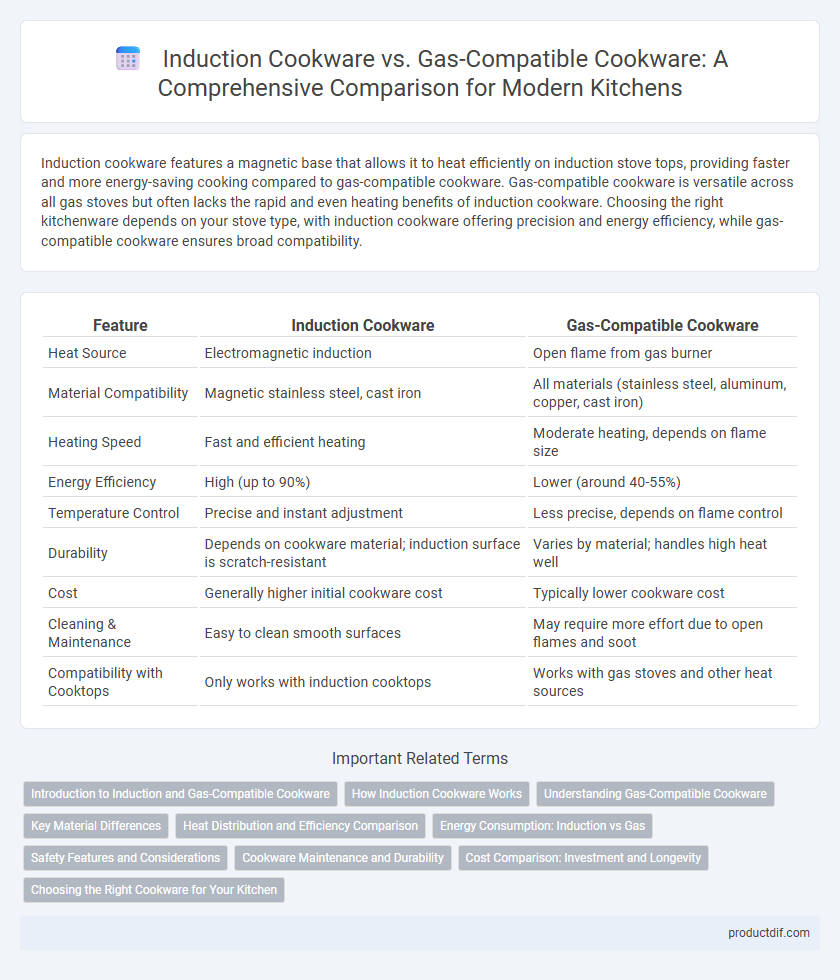
Induction cookware features a magnetic base that allows it to heat efficiently on induction stove tops, providing faster and more energy-saving cooking compared to gas-compatible cookware. Gas-compatible cookware is versatile across all gas stoves but often lacks the rapid and even heating benefits of induction cookware. Choosing the right kitchenware depends on your stove type, with induction cookware offering precision and energy efficiency, while gas-compatible cookware ensures broad compatibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Induction Cookware | Gas-Compatible Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Electromagnetic induction | Open flame from gas burner |
| Material Compatibility | Magnetic stainless steel, cast iron | All materials (stainless steel, aluminum, copper, cast iron) |
| Heating Speed | Fast and efficient heating | Moderate heating, depends on flame size |
| Energy Efficiency | High (up to 90%) | Lower (around 40-55%) |
| Temperature Control | Precise and instant adjustment | Less precise, depends on flame control |
| Durability | Depends on cookware material; induction surface is scratch-resistant | Varies by material; handles high heat well |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cookware cost | Typically lower cookware cost |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean smooth surfaces | May require more effort due to open flames and soot |
| Compatibility with Cooktops | Only works with induction cooktops | Works with gas stoves and other heat sources |
Introduction to Induction and Gas-Compatible Cookware
Induction cookware requires magnetic-based materials such as cast iron or stainless steel to function efficiently with induction cooktops that generate heat via electromagnetic fields. Gas-compatible cookware, typically made from materials like copper, aluminum, or stainless steel with a flat bottom, ensures even heat distribution on open flame burners. Choosing the right cookware depends on the heat source, with induction emphasizing magnetic properties and gas prioritizing heat conduction and durability.
How Induction Cookware Works
Induction cookware works through electromagnetic fields that generate heat directly within the metal of the pan, enabling rapid and efficient cooking. This technology requires cookware made of ferromagnetic materials such as cast iron or stainless steel to ensure compatibility with induction stovetops. Unlike gas-compatible cookware that relies on an open flame, induction cookware heats faster, uses less energy, and offers precise temperature control for consistent cooking results.
Understanding Gas-Compatible Cookware
Gas-compatible cookware features materials such as stainless steel, cast iron, and aluminum with magnetic bases that efficiently withstand high heat and direct flame exposure. Unlike induction cookware that requires magnetic properties for electromagnetic heat transfer, gas-compatible pots and pans offer versatile use on a variety of stove types. Proper heat distribution and durability in gas cookware ensure optimal cooking performance on traditional gas burners.
Key Material Differences
Induction cookware requires magnetic materials such as cast iron or stainless steel with a ferromagnetic base to generate heat through electromagnetic induction, whereas gas-compatible cookware can be made from a wider range of materials including aluminum, copper, and non-magnetic stainless steel. The key material difference lies in the induction cookware's need for a flat, magnetic surface to ensure efficient heat transfer, while gas cookware relies on direct flame contact, allowing for more diverse material choices. This distinction influences durability, heat distribution, and compatibility with different cooking technologies.
Heat Distribution and Efficiency Comparison
Induction cookware offers superior heat distribution by using electromagnetic energy to heat the pan directly, resulting in faster and more even cooking. Gas-compatible cookware relies on an open flame, which can create hot spots due to uneven heat transfer, leading to less efficient cooking. Induction technology generally achieves higher energy efficiency, converting up to 90% of energy into heat, while gas stoves typically convert around 40-55%, making induction a more sustainable choice.
Energy Consumption: Induction vs Gas
Induction cookware operates with electromagnetic fields that directly heat the pot or pan, resulting in up to 90% energy efficiency, whereas gas-compatible cookware relies on combustion flames that typically achieve around 40-55% efficiency due to heat loss. The precise heat control offered by induction cooktops not only reduces energy waste but also shortens cooking times, contributing to lower overall energy consumption. Conversely, gas stoves convert much of the energy into ambient heat, making them less efficient and more costly to operate over time.
Safety Features and Considerations
Induction cookware offers enhanced safety features by using electromagnetic fields that heat only compatible cookware, reducing the risk of burns and fire hazards compared to open flames in gas-compatible cookware. Gas-compatible cookware requires careful handling of open flames, increasing the chances of accidental burns and gas leaks if not properly maintained or used. Choosing induction cookware minimizes exposure to direct heat sources, making it a safer option in kitchens focused on accident prevention.
Cookware Maintenance and Durability
Induction cookware features a magnetic base that ensures even heat distribution, reducing warping and extending lifespan with proper use, while typically requiring careful hand washing to preserve the non-stick coating. Gas-compatible cookware often endures direct flame exposure, which can cause discoloration and faster wear but allows for versatile material choices like stainless steel and cast iron, known for their robust durability and easy maintenance. Choosing cookware based on maintenance needs and durability involves considering heat source compatibility, cleaning methods, and resistance to deformation over time.
Cost Comparison: Investment and Longevity
Induction cookware typically requires a higher upfront investment due to specialized magnetic materials but offers greater energy efficiency and faster cooking times, which can reduce overall utility costs. Gas-compatible cookware is generally more affordable initially, but frequent exposure to open flames may decrease its durability, leading to more frequent replacements. Evaluating long-term costs, induction cookware often proves more economical through enhanced longevity and energy savings despite the higher initial price.
Choosing the Right Cookware for Your Kitchen
Induction cookware features magnetic bases made from stainless steel or cast iron, ensuring compatibility with induction cooktops by generating heat through electromagnetic fields. Gas-compatible cookware typically includes materials such as stainless steel, copper, and aluminum, which offer versatility and even heat distribution on open flames. Selecting the right cookware depends on your stove type, cooking style, and material durability preferences, with induction pots offering energy efficiency and gas cookware providing widespread usability.
Induction cookware vs Gas-compatible cookware Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com