Sous vide cooking provides precise temperature control, resulting in evenly cooked dishes with enhanced flavor and texture compared to traditional boiling. Unlike boiling, which often leads to nutrient loss and uneven cooking due to high temperatures and water immersion, sous vide uses vacuum-sealed bags and low-temperature water baths to preserve moisture and nutrients. This method is ideal for delicate proteins and ensures consistent, restaurant-quality results every time.
Table of Comparison
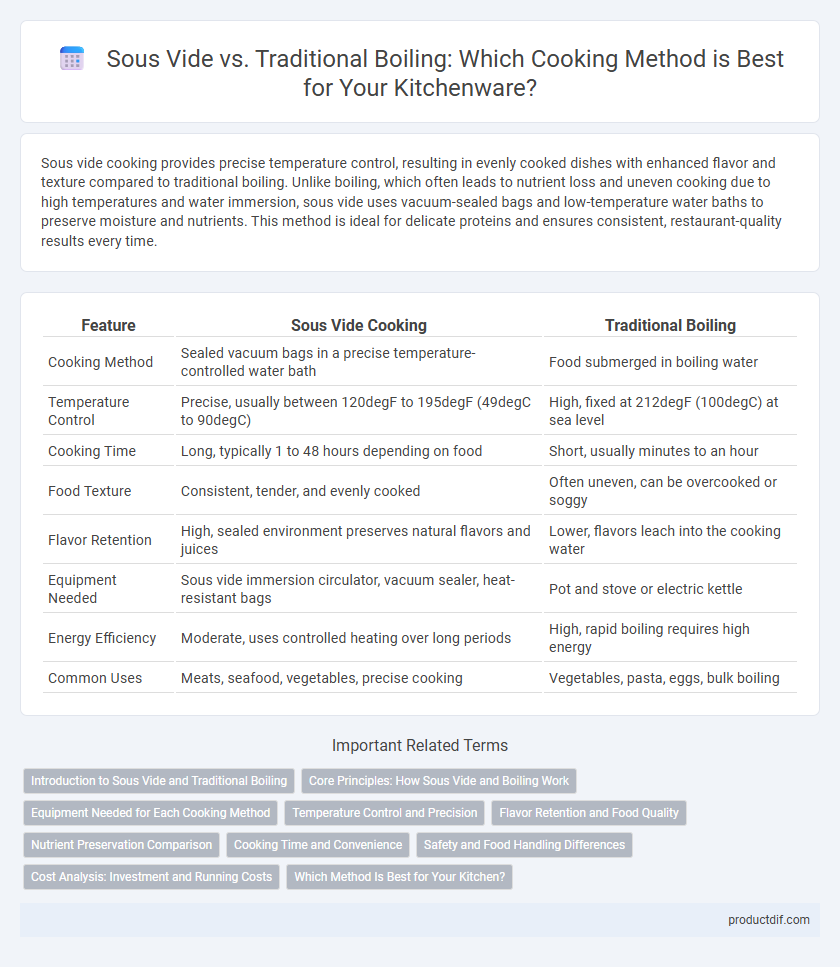
| Feature | Sous Vide Cooking | Traditional Boiling |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Sealed vacuum bags in a precise temperature-controlled water bath | Food submerged in boiling water |
| Temperature Control | Precise, usually between 120degF to 195degF (49degC to 90degC) | High, fixed at 212degF (100degC) at sea level |
| Cooking Time | Long, typically 1 to 48 hours depending on food | Short, usually minutes to an hour |
| Food Texture | Consistent, tender, and evenly cooked | Often uneven, can be overcooked or soggy |
| Flavor Retention | High, sealed environment preserves natural flavors and juices | Lower, flavors leach into the cooking water |
| Equipment Needed | Sous vide immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, heat-resistant bags | Pot and stove or electric kettle |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate, uses controlled heating over long periods | High, rapid boiling requires high energy |
| Common Uses | Meats, seafood, vegetables, precise cooking | Vegetables, pasta, eggs, bulk boiling |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Traditional Boiling
Sous vide cooking involves sealing food in airtight bags and immersing them in water at precise, controlled low temperatures, ensuring even cooking and enhanced flavor retention. Traditional boiling uses high heat to cook food rapidly in boiling water, often leading to nutrient loss and uneven texture. Sous vide preserves moisture and nutrients better than boiling, making it ideal for tender cuts and delicate ingredients.
Core Principles: How Sous Vide and Boiling Work
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control by immersing vacuum-sealed food in a water bath, ensuring even cooking and moisture retention. Traditional boiling involves submerging food directly in boiling water at 100degC, leading to faster cooking but potential nutrient loss and texture changes. The core principle of sous vide is controlled low-temperature cooking over an extended period, while boiling relies on high heat for rapid heat transfer.
Equipment Needed for Each Cooking Method
Sous vide cooking requires a precision immersion circulator and a vacuum-sealed bag to maintain precise temperature control over extended periods, ensuring even cooking and retention of moisture. Traditional boiling only necessitates a pot filled with water and a heat source, making it straightforward but less controlled in temperature consistency. The investment in sous vide equipment typically results in more precise and consistent results, while boiling relies on simpler, widely available tools.
Temperature Control and Precision
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control by maintaining water at a consistent, exact temperature, ensuring even cooking and optimal texture. Traditional boiling lacks this precision, as water temperature typically hovers around 100degC, which can lead to overcooking or uneven results. The precise temperature control in sous vide enhances flavor retention and tenderness in food compared to traditional boiling methods.
Flavor Retention and Food Quality
Sous vide cooking ensures superior flavor retention by sealing ingredients in vacuum bags and cooking at precise, low temperatures, preserving natural juices and enhancing taste complexity. Traditional boiling often leads to nutrient loss and diluted flavors as food is submerged in water at high temperatures, causing essential compounds to leach out. Consequently, sous vide produces more tender, evenly cooked food with heightened texture and nutrient preservation compared to traditional boiling methods.
Nutrient Preservation Comparison
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control, minimizing nutrient loss by preventing overcooking, unlike traditional boiling, which exposes food to high temperatures that can leach water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex. Studies show sous vide retains up to 30% more nutrients compared to boiling, preserving antioxidants and minerals crucial for health. This method enhances flavor and texture while maintaining higher nutritional value, making it a superior choice for nutrient preservation in kitchenware applications.
Cooking Time and Convenience
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, resulting in consistent doneness with cooking times ranging from 1 to 4 hours, depending on the food type, while traditional boiling is much faster, often completing in under 30 minutes. Sous vide requires specialized immersion circulators and vacuum-sealed bags, offering convenience for hands-off cooking but with longer preparation, whereas boiling uses basic kitchenware like pots and requires constant monitoring to avoid overcooking. The choice between sous vide and boiling impacts meal scheduling, with sous vide excelling in slow, even cooking and boiling in quick, straightforward preparation.
Safety and Food Handling Differences
Sous vide cooking offers enhanced food safety by maintaining precise, controlled temperatures that eliminate harmful bacteria without overcooking, unlike traditional boiling which can create uneven heat distribution and increase the risk of foodborne illness. Vacuum-sealed bags used in sous vide prevent cross-contamination and retain moisture, ensuring safer handling compared to the direct water immersion of boiling. Proper temperature monitoring and sealed environments in sous vide reduce oxidation and contamination risks prevalent in traditional boiling methods.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Running Costs
Sous vide cooking requires an initial investment in precision immersion circulators, typically ranging from $100 to $300, which is higher than the minimal cost of traditional boiling equipment like pots and stoves. Running costs for sous vide are generally lower due to energy-efficient water baths that maintain precise temperatures, reducing electricity consumption compared to prolonged boiling on gas or electric stovetops. Over time, sous vide offers better cost-effectiveness through energy savings and reduced food waste, despite a higher upfront equipment expense.
Which Method Is Best for Your Kitchen?
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control that preserves nutrients and enhances flavor, making it ideal for gourmet meal preparation and consistent results. Traditional boiling is faster and more accessible, suitable for everyday cooking tasks like pasta or vegetables where speed is essential. Choosing between sous vide and boiling depends on your kitchen priorities: sous vide excels in precision and texture, while boiling provides simplicity and convenience.
Sous vide vs Traditional boiling Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com