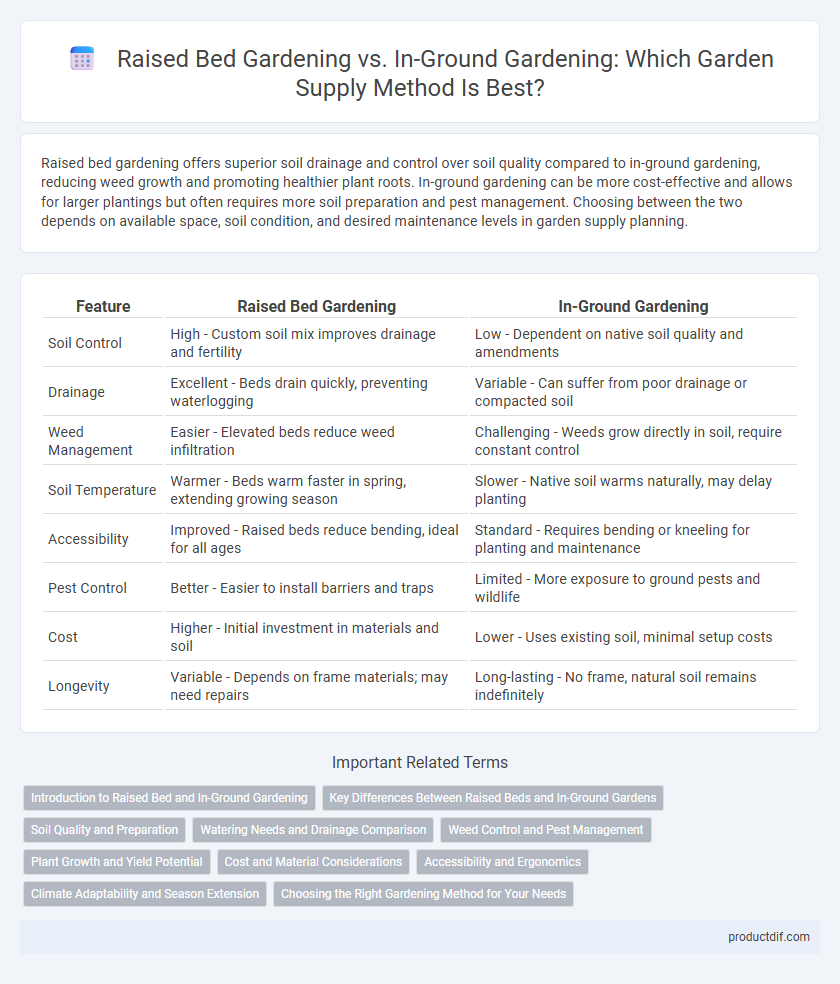
Raised bed gardening offers superior soil drainage and control over soil quality compared to in-ground gardening, reducing weed growth and promoting healthier plant roots. In-ground gardening can be more cost-effective and allows for larger plantings but often requires more soil preparation and pest management. Choosing between the two depends on available space, soil condition, and desired maintenance levels in garden supply planning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raised Bed Gardening | In-Ground Gardening |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Control | High - Custom soil mix improves drainage and fertility | Low - Dependent on native soil quality and amendments |
| Drainage | Excellent - Beds drain quickly, preventing waterlogging | Variable - Can suffer from poor drainage or compacted soil |
| Weed Management | Easier - Elevated beds reduce weed infiltration | Challenging - Weeds grow directly in soil, require constant control |
| Soil Temperature | Warmer - Beds warm faster in spring, extending growing season | Slower - Native soil warms naturally, may delay planting |
| Accessibility | Improved - Raised beds reduce bending, ideal for all ages | Standard - Requires bending or kneeling for planting and maintenance |
| Pest Control | Better - Easier to install barriers and traps | Limited - More exposure to ground pests and wildlife |
| Cost | Higher - Initial investment in materials and soil | Lower - Uses existing soil, minimal setup costs |
| Longevity | Variable - Depends on frame materials; may need repairs | Long-lasting - No frame, natural soil remains indefinitely |
Introduction to Raised Bed and In-Ground Gardening
Raised bed gardening involves cultivating plants in soil contained within framed structures above ground level, offering improved drainage, soil control, and easier access for planting and maintenance. In-ground gardening entails planting directly into the existing soil, which allows roots to extend naturally but may face challenges such as poor soil quality and drainage issues. Both methods have distinct benefits depending on garden size, soil conditions, and crop preferences.
Key Differences Between Raised Beds and In-Ground Gardens
Raised bed gardening offers improved soil drainage, better control over soil quality, and easier access for planting and maintenance compared to in-ground gardening. In-ground gardens typically allow for larger planting spaces but may suffer from soil compaction, poor drainage, and weed infiltration. Raised beds also warm up faster in spring, promoting earlier planting and extended growing seasons.
Soil Quality and Preparation
Raised bed gardening offers superior soil quality control by allowing gardeners to customize soil composition with optimal nutrients, drainage, and pH balance, minimizing compaction and weed growth. In-ground gardening relies on existing soil conditions, which often require extensive preparation such as tilling, amending with organic matter, and testing for nutrient deficiencies to improve fertility and structure. The enhanced soil management in raised beds typically results in healthier plant growth and higher yields compared to traditional in-ground gardening.
Watering Needs and Drainage Comparison
Raised bed gardening offers superior drainage due to elevated soil levels, reducing waterlogging and promoting healthier root systems compared to in-ground gardening. In-ground gardens often require more frequent watering because native soil can compact and retain excess moisture unevenly, leading to potential root rot. Enhanced soil control in raised beds allows for tailored watering schedules and improved moisture retention through better soil composition and aeration.
Weed Control and Pest Management
Raised bed gardening offers superior weed control by elevating soil above ground level, which reduces weed seed intrusion and allows for easier manual removal. In-ground gardening often faces higher weed competition due to direct soil exposure, making pest management more challenging as pests can easily access plants. Raised beds also improve drainage and soil warmth, creating less favorable conditions for many pests compared to traditional in-ground plots.
Plant Growth and Yield Potential
Raised bed gardening promotes enhanced plant growth and higher yield potential due to improved soil drainage, aeration, and root development compared to in-ground gardening. Elevated soil temperatures and controlled soil composition in raised beds support faster germination and healthier plants. Conversely, in-ground gardening may face challenges like soil compaction and poor drainage, which can limit root expansion and reduce overall productivity.
Cost and Material Considerations
Raised bed gardening often requires upfront investment in materials such as lumber, soil, and fasteners, but can reduce long-term costs by improving soil quality and drainage. In-ground gardening typically has lower initial costs due to natural soil use, yet may demand more frequent soil amendments and weed control products. Choosing between these methods depends on budget, soil condition, and the desired durability of garden infrastructure.
Accessibility and Ergonomics
Raised bed gardening offers improved accessibility by elevating planting areas, reducing the need for bending and kneeling, which benefits individuals with mobility challenges or back pain. In-ground gardening often requires more physical effort to reach lower soil levels, potentially causing strain during prolonged tasks. Ergonomically, raised beds can be customized in height and width to fit specific user needs, enhancing comfort and reducing injury risk during planting, maintenance, and harvesting activities.
Climate Adaptability and Season Extension
Raised bed gardening offers superior climate adaptability by improving soil drainage and temperature regulation, enabling plants to thrive in varied weather conditions. In-ground gardening, while traditional, is more vulnerable to soil temperature fluctuations and water retention issues that can limit growing seasons. Utilizing raised beds can extend the growing season by warming the soil earlier in spring and maintaining heat longer into fall, providing an advantage for early planting and late harvesting.
Choosing the Right Gardening Method for Your Needs
Raised bed gardening offers enhanced soil control and better drainage, ideal for gardeners with poor soil or limited space. In-ground gardening allows for deeper root growth and greater plant variety, suitable for large plots with naturally fertile soil. Selecting the right method depends on factors such as soil quality, garden size, crop type, and personal maintenance preferences.
Raised bed gardening vs In-ground gardening Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com