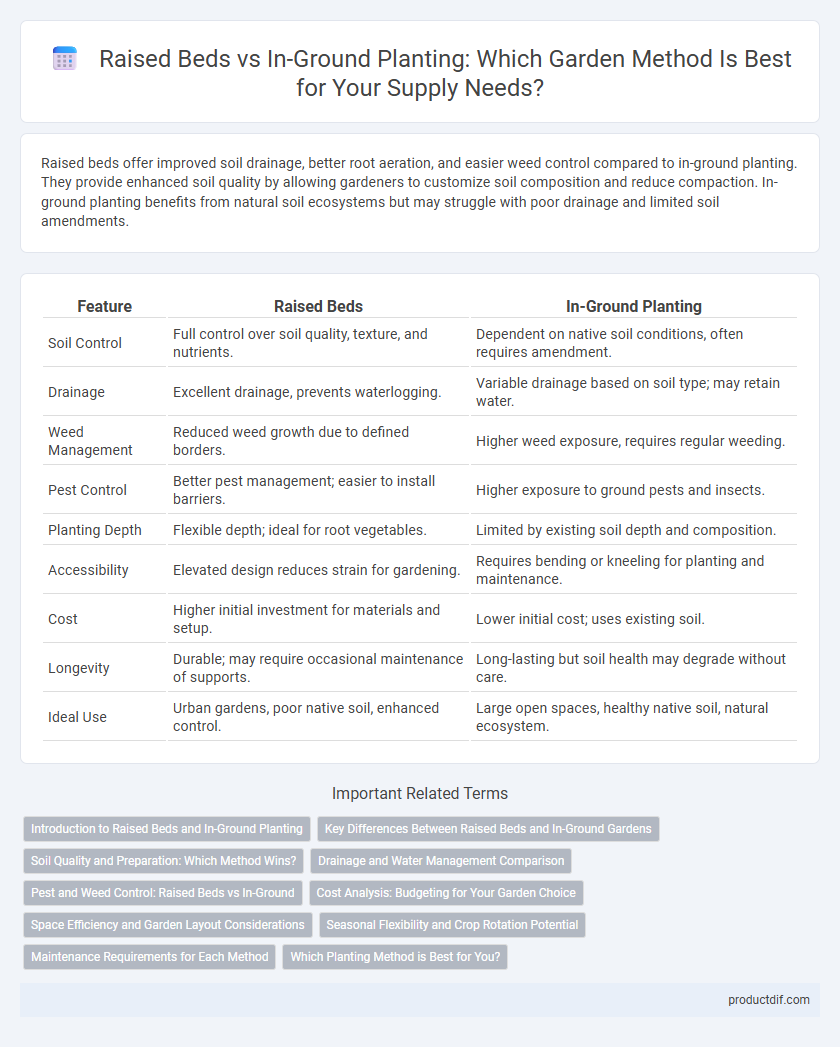
Raised beds offer improved soil drainage, better root aeration, and easier weed control compared to in-ground planting. They provide enhanced soil quality by allowing gardeners to customize soil composition and reduce compaction. In-ground planting benefits from natural soil ecosystems but may struggle with poor drainage and limited soil amendments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raised Beds | In-Ground Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Control | Full control over soil quality, texture, and nutrients. | Dependent on native soil conditions, often requires amendment. |
| Drainage | Excellent drainage, prevents waterlogging. | Variable drainage based on soil type; may retain water. |
| Weed Management | Reduced weed growth due to defined borders. | Higher weed exposure, requires regular weeding. |
| Pest Control | Better pest management; easier to install barriers. | Higher exposure to ground pests and insects. |
| Planting Depth | Flexible depth; ideal for root vegetables. | Limited by existing soil depth and composition. |
| Accessibility | Elevated design reduces strain for gardening. | Requires bending or kneeling for planting and maintenance. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for materials and setup. | Lower initial cost; uses existing soil. |
| Longevity | Durable; may require occasional maintenance of supports. | Long-lasting but soil health may degrade without care. |
| Ideal Use | Urban gardens, poor native soil, enhanced control. | Large open spaces, healthy native soil, natural ecosystem. |
Introduction to Raised Beds and In-Ground Planting
Raised beds offer improved soil drainage, better weed control, and enhanced root development by elevating the planting area above ground level. In-ground planting utilizes the natural soil ecosystem, allowing deeper root systems and easier access to native nutrients, but may face challenges with soil compaction and drainage. Selecting between raised beds and in-ground planting depends on soil quality, gardening goals, and space constraints to optimize plant growth and yield.
Key Differences Between Raised Beds and In-Ground Gardens
Raised beds offer improved soil drainage, enhanced root growth, and easier weed control compared to in-ground gardens. In-ground planting relies on native soil quality, which can vary widely and may require significant amendment for optimal plant health. Maintenance for raised beds tends to be more accessible, reducing soil compaction and extending the growing season by warming earlier in spring.
Soil Quality and Preparation: Which Method Wins?
Raised beds offer superior soil quality control by allowing gardeners to customize soil composition, enhance drainage, and reduce compaction, making them ideal for optimal root growth. In-ground planting depends heavily on the native soil, which may require extensive amendment and tilling to achieve similar nutrient levels and texture. Therefore, raised beds generally win for soil preparation efficiency and quality, especially in areas with poor or contaminated soil.
Drainage and Water Management Comparison
Raised beds offer superior drainage compared to in-ground planting by allowing excess water to drain freely through the elevated soil, reducing root rot and waterlogging risks. In-ground planting relies on native soil composition, which can lead to poor drainage in clay-heavy or compacted soils, making water management more challenging. Effective water management in raised beds is enhanced by controlled soil mixtures that retain moisture while preventing oversaturation, optimizing plant health and growth.
Pest and Weed Control: Raised Beds vs In-Ground
Raised beds offer superior pest and weed control due to improved soil drainage and the ability to install physical barriers such as weed fabric or mesh easily, reducing weed growth and deterring burrowing pests. In-ground planting typically faces higher weed invasion from surrounding soil and increased vulnerability to soil-borne pests, requiring more frequent maintenance and chemical treatments. Effective pest management in raised beds often leads to healthier plants and higher yields compared to traditional in-ground gardening.
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for Your Garden Choice
Raised beds typically require higher upfront costs due to materials such as wood, soil, and soil amendments, averaging $150 to $300 per bed depending on size and quality. In-ground planting is generally more cost-effective initially, involving fewer materials but may incur ongoing expenses for soil improvement and pest control. Budgeting for your garden should consider long-term maintenance costs alongside initial investments to determine the best value for your gardening goals.
Space Efficiency and Garden Layout Considerations
Raised beds maximize space efficiency by allowing intensive planting and better soil control, making them ideal for small or irregular garden layouts. In-ground planting requires more space for pathways and often results in less dense crop arrangement, which can limit overall yield. Gardeners should consider raised beds for compact, organized layouts that optimize available area and improve plant health.
Seasonal Flexibility and Crop Rotation Potential
Raised beds offer enhanced seasonal flexibility by warming up faster in spring and draining better, allowing earlier planting and extended growing seasons compared to in-ground planting. They facilitate efficient crop rotation due to defined planting areas, reducing soil-borne diseases and nutrient depletion by simplifying soil amendment applications. In-ground planting, while traditional, often faces limitations in altering soil structure swiftly, impacting both seasonal timing and effective crop rotation practices.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Method
Raised beds require less frequent weeding due to improved soil structure and better drainage, reducing maintenance time compared to in-ground planting. In-ground planting demands more regular soil amendment and pest control efforts because of natural soil variability and exposure to pests. Both methods benefit from consistent watering, but raised beds often need closer monitoring to prevent soil drying out quickly.
Which Planting Method is Best for You?
Raised beds offer superior soil control, drainage, and easier access, making them ideal for gardeners with poor soil quality or limited mobility. In-ground planting provides a natural root environment and larger planting area but may require more soil preparation and weed management. Choosing the best method depends on your garden space, soil condition, and physical accessibility preferences.
Raised Beds vs In-Ground Planting Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com