Touchscreen interfaces offer sleek design and intuitive interaction for electronics pets, enabling users to navigate features with simple taps and gestures. Physical buttons provide tactile feedback and reliable control, often preferred for precise actions and durability in various environments. Choosing between touchscreen and physical buttons depends on user preference for ease of use versus tactile responsiveness in the pet's electronic interface.
Table of Comparison
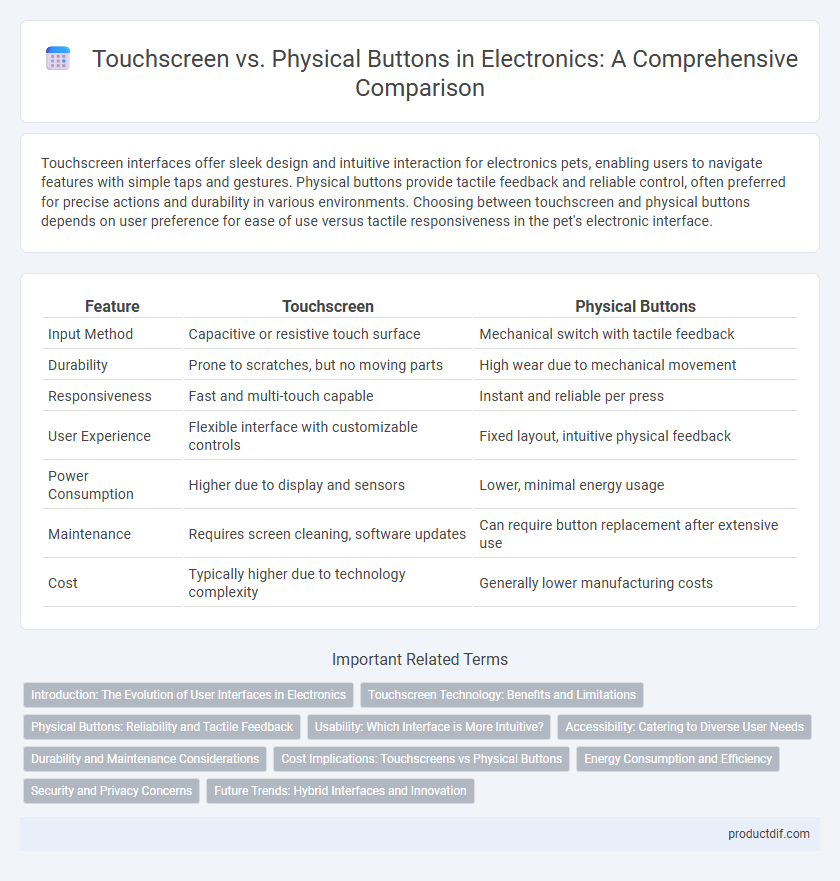
| Feature | Touchscreen | Physical Buttons |
|---|---|---|
| Input Method | Capacitive or resistive touch surface | Mechanical switch with tactile feedback |
| Durability | Prone to scratches, but no moving parts | High wear due to mechanical movement |
| Responsiveness | Fast and multi-touch capable | Instant and reliable per press |
| User Experience | Flexible interface with customizable controls | Fixed layout, intuitive physical feedback |
| Power Consumption | Higher due to display and sensors | Lower, minimal energy usage |
| Maintenance | Requires screen cleaning, software updates | Can require button replacement after extensive use |
| Cost | Typically higher due to technology complexity | Generally lower manufacturing costs |
Introduction: The Evolution of User Interfaces in Electronics
Touchscreen technology revolutionized electronics by enabling intuitive, gesture-based interactions that replaced traditional physical buttons. The shift from mechanical interfaces to capacitive and resistive touchscreens enhanced device versatility, allowing seamless access to complex functions through a single display. This evolution in user interfaces accelerated the adoption of smartphones, tablets, and modern consumer electronics, emphasizing sleek design and dynamic content control.
Touchscreen Technology: Benefits and Limitations
Touchscreen technology offers intuitive user interaction, enabling faster navigation and multi-touch capabilities, which enhances productivity in electronics such as smartphones and tablets. It supports dynamic interface customization and reduces mechanical wear, increasing device longevity. However, touchscreens can suffer from reduced responsiveness in wet conditions and may not provide the tactile feedback users rely on for precise control.
Physical Buttons: Reliability and Tactile Feedback
Physical buttons offer superior reliability due to their distinct mechanical design, which reduces the risk of accidental activation and maintains functionality in wet or gloved-hand conditions. Their tactile feedback provides users with precise, immediate confirmation of input, enhancing accuracy in operation especially in critical or low-visibility environments. This physical interaction often results in longer device lifespan as buttons withstand repeated use without the issues associated with touchscreens, such as screen responsiveness degradation or damage from scratches.
Usability: Which Interface is More Intuitive?
Touchscreen interfaces offer dynamic, context-sensitive controls that adapt to different applications, enhancing usability through visual feedback and gesture-based navigation. Physical buttons provide tactile feedback and muscle memory advantages, allowing users to operate devices without visual confirmation, which can improve accuracy and speed in certain environments. Usability depends on application context; touchscreens excel in flexibility and modern user experiences, while physical buttons ensure reliable, intuitive operation in situations requiring precision or glove use.
Accessibility: Catering to Diverse User Needs
Touchscreen interfaces offer customizable accessibility features such as adjustable font sizes, voice commands, and tactile feedback, accommodating users with visual or motor impairments. Physical buttons provide consistent tactile feedback and ease of use for individuals with limited dexterity or those who find touchscreens less responsive. Combining both options in electronic devices enhances usability for a wider range of users with diverse accessibility requirements.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Touchscreens often face durability challenges due to scratches, cracks, and sensitivity to environmental factors, requiring screen protectors or replacements over time. Physical buttons typically offer greater longevity, with tactile feedback and fewer issues related to accidental activation or wear under frequent use. Maintenance for physical buttons is generally straightforward, involving cleaning and occasional lubrication, whereas touchscreen repairs can be more complex and costly, especially for advanced multi-touch systems.
Cost Implications: Touchscreens vs Physical Buttons
Touchscreens generally incur higher initial costs due to advanced display technology and integration of sensors, while physical buttons are less expensive to produce with simpler components. Maintenance expenses for touchscreens can be higher because of their sensitivity to damage and complexity in repairs compared to the durability and straightforward replacement of physical buttons. In applications requiring ruggedness and low budget, physical buttons remain cost-effective, whereas touchscreens offer versatility and reduced mechanical wear in more premium electronic devices.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Touchscreens generally consume more energy than physical buttons due to their constant need for backlighting and sensor activation, impacting overall device efficiency. Physical buttons operate with minimal power, activating only when pressed, which extends battery life in portable electronics. Choosing physical buttons over touchscreens can significantly reduce energy consumption in devices where power efficiency is critical.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Touchscreen interfaces can pose significant security risks due to susceptibility to smudge attacks and shoulder surfing, which expose sensitive input patterns. Physical buttons offer enhanced privacy by providing tactile feedback and reducing on-screen visible traces of user actions. Biometric sensors integrated with both input types require robust encryption to protect user data from potential breaches.
Future Trends: Hybrid Interfaces and Innovation
Hybrid interfaces combining touchscreen technology with physical buttons are emerging as a key future trend in electronics, offering enhanced usability and tactile feedback. Innovations in haptic technology and adaptive interfaces enable seamless transitions between virtual controls and physical inputs, improving user experience in devices like smartphones, automotive dashboards, and wearable gadgets. This convergence leverages the precision of touchscreens with the reliability of physical buttons to meet diverse user needs and accessibility standards.
Touchscreen vs Physical Buttons Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com