Direct drive turntables offer superior torque and precise speed control by connecting the platter directly to the motor, resulting in minimal signal distortion and faster start-up times. Belt drive models isolate motor vibrations through a flexible belt, reducing noise but potentially introducing slight speed inconsistencies and requiring more maintenance. Choosing between direct drive and belt drive depends on the balance between audio fidelity, durability, and user preference for sound quality and mechanical simplicity.
Table of Comparison
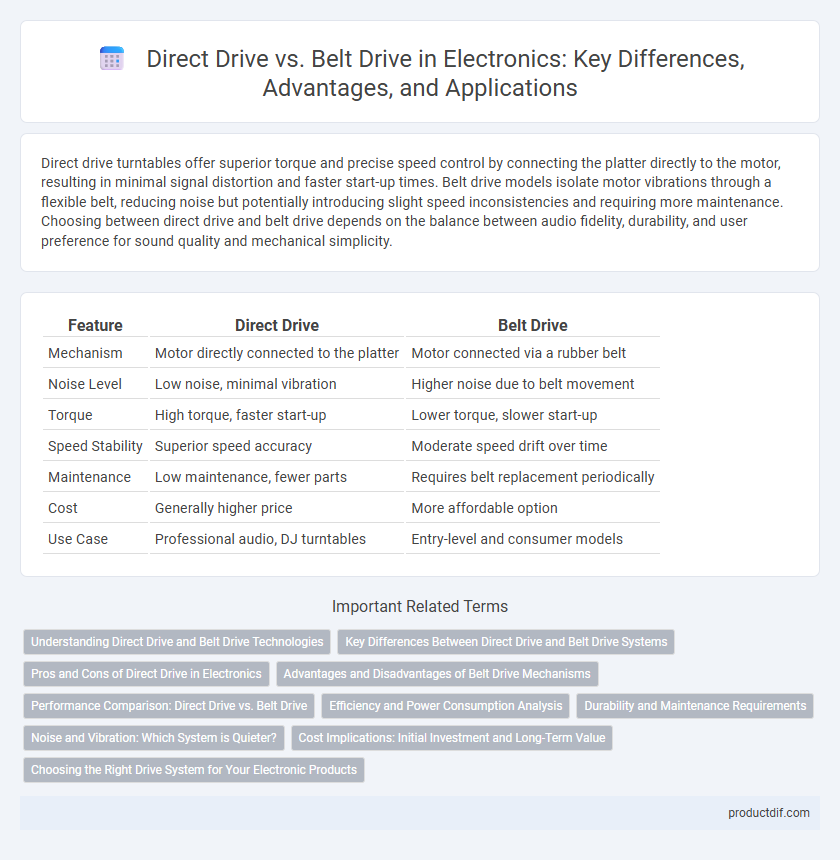
| Feature | Direct Drive | Belt Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Motor directly connected to the platter | Motor connected via a rubber belt |
| Noise Level | Low noise, minimal vibration | Higher noise due to belt movement |
| Torque | High torque, faster start-up | Lower torque, slower start-up |
| Speed Stability | Superior speed accuracy | Moderate speed drift over time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, fewer parts | Requires belt replacement periodically |
| Cost | Generally higher price | More affordable option |
| Use Case | Professional audio, DJ turntables | Entry-level and consumer models |
Understanding Direct Drive and Belt Drive Technologies
Direct drive technology connects the motor directly to the output device, eliminating belts or gears, resulting in higher precision, reduced maintenance, and minimal power loss. Belt drive systems use a flexible belt to transfer rotational motion between pulleys, offering smoother operation and vibration absorption but with potential slippage and wear over time. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for applications in turntables, printers, and industrial equipment where torque, speed control, and durability are key performance factors.
Key Differences Between Direct Drive and Belt Drive Systems
Direct drive systems connect the motor directly to the load, resulting in higher efficiency, reduced maintenance, and greater torque at low speeds, while belt drive systems use pulleys and belts to transfer motion, offering flexibility in speed variation and vibration damping. Direct drive eliminates backlash and slippage common in belt drives, improving precision, whereas belt drives generally cost less and provide easier shock absorption. Choosing between the two depends on application requirements such as noise levels, torque accuracy, and maintenance preferences.
Pros and Cons of Direct Drive in Electronics
Direct drive systems in electronics offer precise control and reduced mechanical complexity, resulting in lower maintenance and higher reliability compared to belt drive systems. They provide faster response times and improved torque accuracy, making them ideal for applications requiring high precision and durability. However, direct drive motors tend to be more expensive and generate more heat, which can necessitate advanced cooling solutions in sensitive electronic devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Belt Drive Mechanisms
Belt drive mechanisms offer advantages such as smooth and quiet operation, cost-effectiveness, and simple installation compared to direct drives. They provide flexibility in distance between shafts and can absorb shock loads, reducing wear on components. However, belt drives suffer from limitations like slippage, reduced efficiency under heavy loads, and regular maintenance needs due to belt tension and wear.
Performance Comparison: Direct Drive vs. Belt Drive
Direct drive systems offer superior performance with faster torque response and higher precision due to the direct coupling of the motor to the load, eliminating the backlash and elasticity found in belt drive mechanisms. Belt drive systems provide smoother operation and vibration damping, but tend to suffer from belt wear and slippage, which can reduce accuracy and require regular maintenance. In high-performance electronics applications like hard drives and CNC machines, direct drive solutions typically outperform belt drives by delivering consistent speed and enhanced control fidelity.
Efficiency and Power Consumption Analysis
Direct drive systems offer higher efficiency by minimizing mechanical losses, resulting in lower power consumption compared to belt drive mechanisms. Belt drives often experience energy loss due to belt slip and increased friction, which reduces overall system efficiency. Optimizing motor control in direct drive electronics further enhances power savings, making them ideal for energy-conscious applications.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Direct drive systems boast higher durability due to fewer moving parts and reduced wear, making them ideal for long-term use with minimal maintenance. Belt drive mechanisms, while generally quieter, require periodic belt replacements and tension adjustments to maintain optimal performance. Choosing between the two depends on the balance of durability needs and routine maintenance capabilities in electronic device applications.
Noise and Vibration: Which System is Quieter?
Direct drive systems generate less noise and vibration due to the absence of intermediary components, providing a quieter operation ideal for environments sensitive to sound. Belt drive systems introduce additional noise and vibration from the belt's tension and wear, often requiring regular maintenance to minimize sound disturbances. The inherent design of direct drive reduces mechanical noise, making it the preferred choice for high-fidelity audio and precision electronic applications.
Cost Implications: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Direct drive turntables typically have a higher initial investment due to complex motor technology and durable components, offering superior torque and longevity. Belt drive models usually cost less upfront, leveraging simpler mechanics but may incur additional maintenance expenses over time, such as belt replacements and motor wear. When evaluating cost implications, direct drive often delivers better long-term value through reduced maintenance and enhanced performance consistency, making it a cost-effective choice for serious audiophiles.
Choosing the Right Drive System for Your Electronic Products
Direct drive systems provide higher precision and reduced maintenance by eliminating belts, making them ideal for electronic products requiring accuracy and durability. Belt drive systems offer cost-effectiveness and noise reduction, suitable for applications where budget and quieter operation are priorities. Choosing the right drive system depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed control, and long-term reliability in the specific electronic device.
Direct Drive vs Belt Drive Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com