Active components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, require an external power source to operate and can amplify or control electrical signals. Passive components, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not need external power and primarily store or dissipate energy without signal gain. Understanding the distinct roles of active and passive components is essential for designing effective electronic circuits.
Table of Comparison
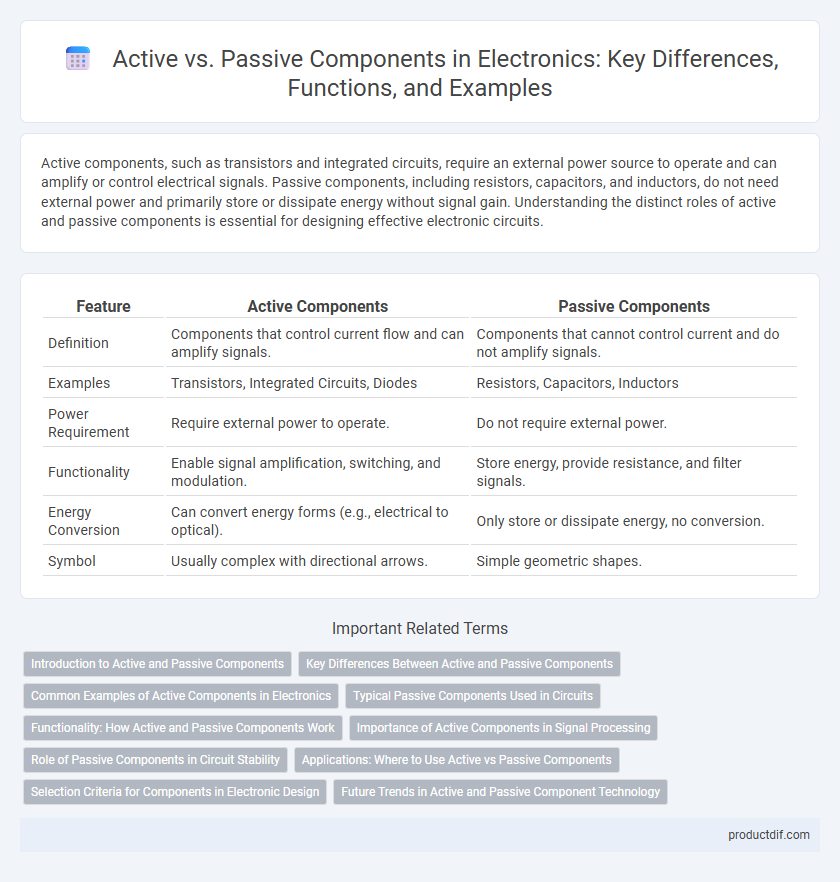
| Feature | Active Components | Passive Components |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Components that control current flow and can amplify signals. | Components that cannot control current and do not amplify signals. |
| Examples | Transistors, Integrated Circuits, Diodes | Resistors, Capacitors, Inductors |
| Power Requirement | Require external power to operate. | Do not require external power. |
| Functionality | Enable signal amplification, switching, and modulation. | Store energy, provide resistance, and filter signals. |
| Energy Conversion | Can convert energy forms (e.g., electrical to optical). | Only store or dissipate energy, no conversion. |
| Symbol | Usually complex with directional arrows. | Simple geometric shapes. |
Introduction to Active and Passive Components
Active components in electronics, such as transistors and integrated circuits, require an external power source to operate and can amplify signals or control current flow. Passive components, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not need external power and primarily store or dissipate energy without amplification. Understanding the fundamental roles of active and passive components is essential for designing and analyzing electronic circuits.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Components
Active components, such as transistors, integrated circuits, and diodes, require an external power source to operate and can amplify or switch electrical signals. Passive components, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not need external power and only respond to electrical signals by storing or dissipating energy without amplification. The key differences lie in their functionality, power requirements, and the ability to control current flow within electronic circuits.
Common Examples of Active Components in Electronics
Active components in electronics include transistors, diodes, integrated circuits, and operational amplifiers, which can control current flow and amplify signals. Transistors act as switches or amplifiers, essential in digital circuits and signal processing. Integrated circuits combine multiple active components to perform complex functions in devices such as microprocessors and memory modules.
Typical Passive Components Used in Circuits
Typical passive components used in electronic circuits include resistors, capacitors, and inductors, each serving fundamental roles such as controlling current, storing energy, and filtering signals. Resistors regulate voltage and current flow by providing resistance, capacitors store electrical energy temporarily and smooth out voltage fluctuations, while inductors store energy magnetically and are essential in tuning and filtering applications. These components do not require an external power source to operate and are crucial in defining circuit behavior and performance.
Functionality: How Active and Passive Components Work
Active components, such as transistors and integrated circuits, control current flow and can amplify signals by using external power sources. Passive components, including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, do not generate energy but instead store, dissipate, or regulate electrical energy within a circuit. The functionality of active components enables signal modulation and power gain, while passive components primarily influence voltage, current, and frequency without amplification.
Importance of Active Components in Signal Processing
Active components such as transistors, operational amplifiers, and integrated circuits play a crucial role in signal processing by amplifying, switching, and modulating electronic signals. These components enable complex operations including filtering, signal conditioning, and analog-to-digital conversion, essential for accurate data transmission and communication systems. Passive components alone cannot provide gain or control signal flow, making active components indispensable for enhancing signal strength and quality in electronic circuits.
Role of Passive Components in Circuit Stability
Passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors play a crucial role in maintaining circuit stability by controlling voltage, current, and frequency responses within electronic circuits. These components help filter signals, reduce noise, and prevent oscillations, ensuring consistent and reliable circuit operation. Proper selection and placement of passive components are essential for enhancing performance and protecting active devices from damage due to unstable conditions.
Applications: Where to Use Active vs Passive Components
Active components such as transistors and integrated circuits are crucial in amplification, switching, and signal modulation applications, making them ideal for complex circuits like amplifiers, radios, and computers. Passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors are essential for filtering, energy storage, and impedance matching, often used in power supplies, signal tuning, and filtering circuits. Choosing between active and passive components depends on the need for power gain, control, and signal processing versus simple functions like energy storage or signal conditioning.
Selection Criteria for Components in Electronic Design
Selection criteria for active and passive components in electronic design emphasize electrical characteristics such as voltage, current ratings, power dissipation, and frequency response. Active components like transistors and integrated circuits require considerations of gain, bandwidth, noise figure, and thermal stability, while passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors demand accuracy, tolerance, and equivalent series resistance (ESR) specifications. Reliability, cost, size, and packaging type also influence component choice to ensure optimal circuit performance and longevity.
Future Trends in Active and Passive Component Technology
Future trends in active components emphasize miniaturization, enhanced power efficiency, and integration with AI-driven functionalities, enabling smarter electronic devices. Passive components are evolving with advanced materials like graphene and nanotechnology to improve performance, reduce size, and withstand higher frequencies in 5G and beyond. Innovations in both active and passive components drive the development of flexible electronics and IoT applications, shaping the next generation of smart, connected devices.
Active vs Passive Components Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com