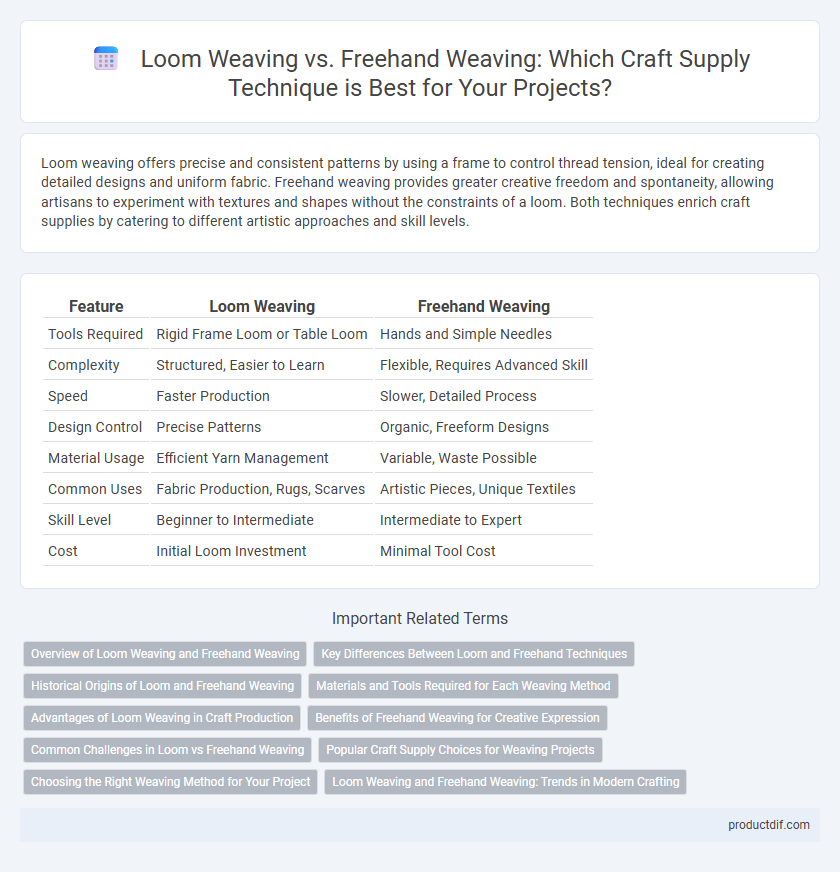
Loom weaving offers precise and consistent patterns by using a frame to control thread tension, ideal for creating detailed designs and uniform fabric. Freehand weaving provides greater creative freedom and spontaneity, allowing artisans to experiment with textures and shapes without the constraints of a loom. Both techniques enrich craft supplies by catering to different artistic approaches and skill levels.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Loom Weaving | Freehand Weaving |
|---|---|---|
| Tools Required | Rigid Frame Loom or Table Loom | Hands and Simple Needles |
| Complexity | Structured, Easier to Learn | Flexible, Requires Advanced Skill |
| Speed | Faster Production | Slower, Detailed Process |
| Design Control | Precise Patterns | Organic, Freeform Designs |
| Material Usage | Efficient Yarn Management | Variable, Waste Possible |
| Common Uses | Fabric Production, Rugs, Scarves | Artistic Pieces, Unique Textiles |
| Skill Level | Beginner to Intermediate | Intermediate to Expert |
| Cost | Initial Loom Investment | Minimal Tool Cost |
Overview of Loom Weaving and Freehand Weaving
Loom weaving utilizes a structured frame or loom to interlace warp and weft threads, creating consistent patterns and tension ideal for producing uniform textiles and intricate designs. Freehand weaving, by contrast, is a manual technique without a loom, relying on hand manipulation of threads for more organic, varied textures and often smaller-scale projects. Each method offers distinct advantages for craft supply users, with loom weaving delivering precision and repeatability, while freehand weaving allows greater creative freedom and improvisation.
Key Differences Between Loom and Freehand Techniques
Loom weaving utilizes a structured frame to create uniform patterns with precise tension control, while freehand weaving relies on manual manipulation, offering greater flexibility and spontaneity. Loom techniques enable faster production of consistent textile designs, whereas freehand weaving emphasizes artistic expression and unique, intricate textures. Understanding these differences helps crafters select the appropriate method for specific project goals and skill levels.
Historical Origins of Loom and Freehand Weaving
Loom weaving dates back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia, where fixed-frame looms enabled consistent, intricate textile production essential for trade and daily use. Freehand weaving, with origins in early hunter-gatherer societies, relied on handheld tools or body tools, offering versatility in creating simple textiles and baskets without imposing structural constraints. The historical development of loom technology marked a shift towards standardized patterns and increased fabric durability, contrasting with the adaptive, spontaneous designs characteristic of freehand weaving.
Materials and Tools Required for Each Weaving Method
Loom weaving requires a structured frame called a loom, along with warp threads stretched tightly across it and weft threads woven through using a shuttle or needle, emphasizing precision and tension control. Freehand weaving relies on more flexible tools such as a simple frame or even just hands, using a variety of threads and yarns without the need for a fixed warp structure, allowing greater material diversity and improvisation. Both methods use fibers like cotton, wool, or acrylic, but loom weaving often demands more uniform yarns and specific loom accessories to maintain consistent patterns.
Advantages of Loom Weaving in Craft Production
Loom weaving offers precise tension control and consistent fabric density, enhancing the quality and uniformity of craft projects. It enables faster production speeds and efficient use of materials, reducing waste compared to freehand weaving. The structured framework of a loom supports intricate patterns and complex designs that are challenging to achieve with freehand techniques.
Benefits of Freehand Weaving for Creative Expression
Freehand weaving allows artisans to experiment with patterns and textures beyond the limitations of a loom, fostering unique and personalized textile art. This technique encourages spontaneity and intuition, making it ideal for creative exploration and custom designs. Artists benefit from the flexibility to incorporate unconventional materials and shapes, enhancing the expressive potential of their woven creations.
Common Challenges in Loom vs Freehand Weaving
Loom weaving often faces challenges such as tension control and maintaining consistent warp alignment, which are less prevalent in freehand weaving. Freehand weaving requires greater dexterity and skill to manage irregular patterns and uneven thread tension without the structured support of a loom. Both techniques demand patience and precision, but loom weaving offers more stability while freehand weaving allows for more creative flexibility, often leading to unique texture variations.
Popular Craft Supply Choices for Weaving Projects
Loom weaving materials typically include warp threads, weft yarns, and sturdy heddles, offering precise tension control for detailed patterns popular among beginners and experienced crafters alike. Freehand weaving relies on versatile supplies like textured yarns, natural fibers, and DIY frames, encouraging creativity and organic designs favored in art weaving and wall hangings. Both methods prioritize high-quality wool, cotton, and synthetic blends to ensure durability and vibrant color retention in diverse weaving projects.
Choosing the Right Weaving Method for Your Project
Loom weaving provides precise tension control and consistent patterns, making it ideal for intricate designs and large projects requiring uniformity. Freehand weaving offers greater creative freedom and spontaneity, suitable for smaller, textured pieces where unique variations are desired. Selecting the right method depends on project scale, design complexity, and the desired level of control over the weaving process.
Loom Weaving and Freehand Weaving: Trends in Modern Crafting
Loom weaving offers precision and consistency, making it ideal for detailed patterns and mass production, while freehand weaving emphasizes creativity and improvisation, appealing to artisans seeking unique, one-of-a-kind pieces. Modern crafting trends show a resurgence in loom weaving due to its efficiency and the availability of advanced loom designs, yet freehand weaving maintains popularity for its expressive, organic textures. Both techniques blend traditional craftsmanship with contemporary aesthetics, influencing the evolution of textile arts in the craft supply industry.
Loom weaving vs Freehand weaving Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com