Hot glue provides strong, quick-setting bonds ideal for fabric, wood, and plastic, making it perfect for fast-paced craft projects. Cold glue, often white or clear school glue, is slower to dry but excels in paper crafts, providing a flexible, non-toxic adhesive suitable for children. Choosing between hot glue and cold glue depends on the craft's material, drying time, and the desired bond strength.
Table of Comparison
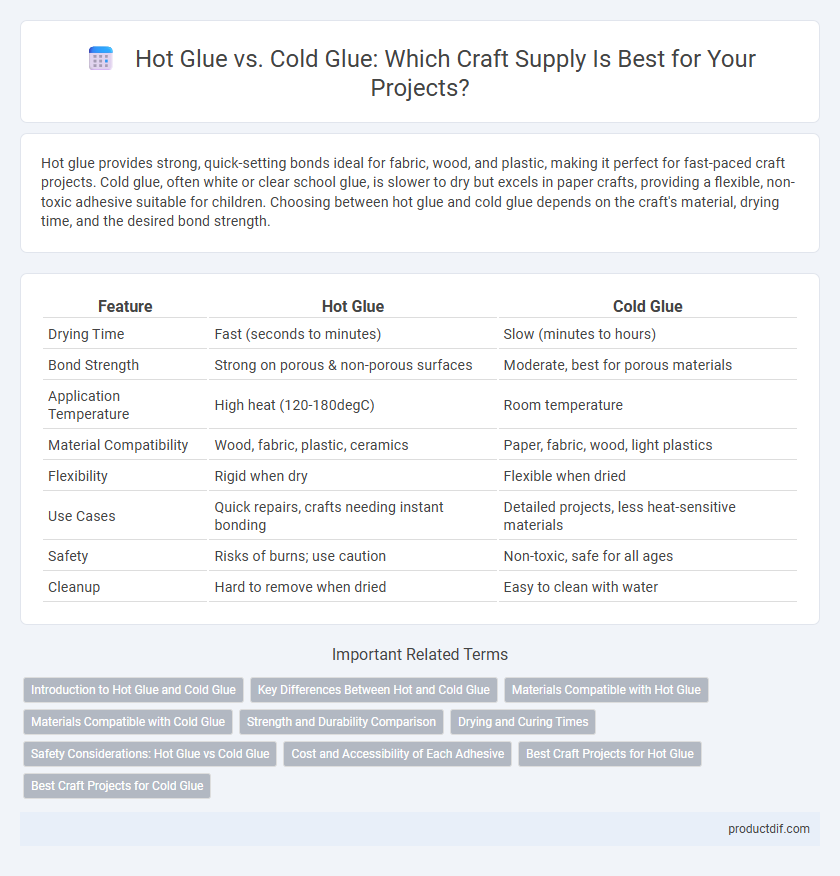
| Feature | Hot Glue | Cold Glue |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | Fast (seconds to minutes) | Slow (minutes to hours) |
| Bond Strength | Strong on porous & non-porous surfaces | Moderate, best for porous materials |
| Application Temperature | High heat (120-180degC) | Room temperature |
| Material Compatibility | Wood, fabric, plastic, ceramics | Paper, fabric, wood, light plastics |
| Flexibility | Rigid when dry | Flexible when dried |
| Use Cases | Quick repairs, crafts needing instant bonding | Detailed projects, less heat-sensitive materials |
| Safety | Risks of burns; use caution | Non-toxic, safe for all ages |
| Cleanup | Hard to remove when dried | Easy to clean with water |
Introduction to Hot Glue and Cold Glue
Hot glue, made from thermoplastic adhesives, melts at high temperatures and solidifies quickly, providing strong, flexible bonds ideal for various craft projects. Cold glue, typically PVA-based or rubber cement, cures at room temperature and is best suited for porous materials like paper or fabric with slower drying times. Understanding these properties helps crafters select the appropriate adhesive based on project requirements and material compatibility.
Key Differences Between Hot and Cold Glue
Hot glue, typically made from thermoplastic adhesives, melts at high temperatures and sets quickly upon cooling, making it ideal for fast bonding on materials like fabric, wood, and plastic. Cold glue, often water-based such as polyvinyl acetate (PVA), cures by evaporation and offers longer open time, making it suitable for paper, cardboard, and porous surfaces where precision and flexibility are needed. Key differences include bonding strength, drying time, temperature handling, and material compatibility, influencing the choice between hot glue guns and cold glue bottles in various craft projects.
Materials Compatible with Hot Glue
Hot glue adheres effectively to a wide range of materials including fabric, wood, plastic, metal, and ceramics, making it versatile for various craft projects. Its strong bond on porous surfaces like fabric and wood is ideal for durable assemblies. However, hot glue is less suitable for heat-sensitive materials such as thin plastics or delicate papers, which can warp or melt under high temperatures.
Materials Compatible with Cold Glue
Cold glue is ideal for porous materials such as paper, fabric, foam, and wood, providing strong adhesion without heat damage. It bonds well with lightweight crafting materials like cardboard and felt, making it suitable for delicate or heat-sensitive projects. Unlike hot glue, cold glue ensures safer handling and longer open working time, enhancing precision with intricate crafts.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Hot glue offers superior bonding strength and faster drying times, making it ideal for heavy-duty materials like wood, fabric, and plastics. Cold glue generally provides a less rigid bond and requires longer curing time, which can compromise durability under stress or heat exposure. For projects requiring maximum durability and strength, hot glue remains the preferred adhesive choice among craft supplies.
Drying and Curing Times
Hot glue dries within seconds due to its molten adhesive state, enabling rapid bonding and minimal wait times during crafting projects. Cold glue requires significantly longer drying and curing periods, often taking several hours to fully set and achieve maximum strength. Understanding these differences helps crafters choose the appropriate adhesive based on project speed and material compatibility.
Safety Considerations: Hot Glue vs Cold Glue
Hot glue poses burn risks due to its high temperature, requiring caution and protective equipment during use, especially around children. Cold glue, often non-toxic and water-based, offers a safer alternative with minimal risk of skin injury. Proper ventilation is essential for some hot glue formulations to avoid inhaling fumes, while cold glue generally presents fewer health hazards and easier cleanup.
Cost and Accessibility of Each Adhesive
Hot glue offers a cost-effective solution with glue sticks priced typically between $0.10 and $0.30 each, making it accessible for bulk purchases and frequent use in craft projects. Cold glue, such as white PVA adhesives, tends to be slightly more expensive per ounce but is widely available in various retail stores, providing convenience for occasional crafters. Hot glue guns require an initial investment, whereas cold glue uses simple applicators, affecting overall cost and ease of access depending on user needs.
Best Craft Projects for Hot Glue
Hot glue is ideal for craft projects requiring quick bonding and flexibility, such as fabric decorations, floral arrangements, and wood crafts. Its fast drying time and strong adhesion make it perfect for assembling DIY home decor, jewelry, and model building where durability and immediate handling are essential. Unlike cold glue, hot glue works seamlessly on diverse surfaces including plastic, metal, and ceramics, enhancing its versatility for various creative applications.
Best Craft Projects for Cold Glue
Cold glue works best for delicate materials like paper, fabric, and lightweight wood, providing a non-toxic and easy-to-use adhesive option for kids' crafts and scrapbooking. It dries clear, making it ideal for detailed projects such as card making, decoupage, and school art projects where precision is key. Unlike hot glue, cold glue minimizes the risk of burns and warping, ensuring safer craft sessions with intricate designs.
Hot glue vs Cold glue Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com