Acrylic pouring offers vibrant, fluid artworks with unpredictable patterns formed by pouring acrylic paints onto a surface, making it ideal for abstract designs and quick projects. Resin casting provides a durable, glossy finish ideal for embedding objects or creating detailed, dimensional pieces, requiring careful mixing and curing times. Choosing between acrylic pouring and resin casting depends on the desired texture, durability, and project complexity in craft supply applications.
Table of Comparison
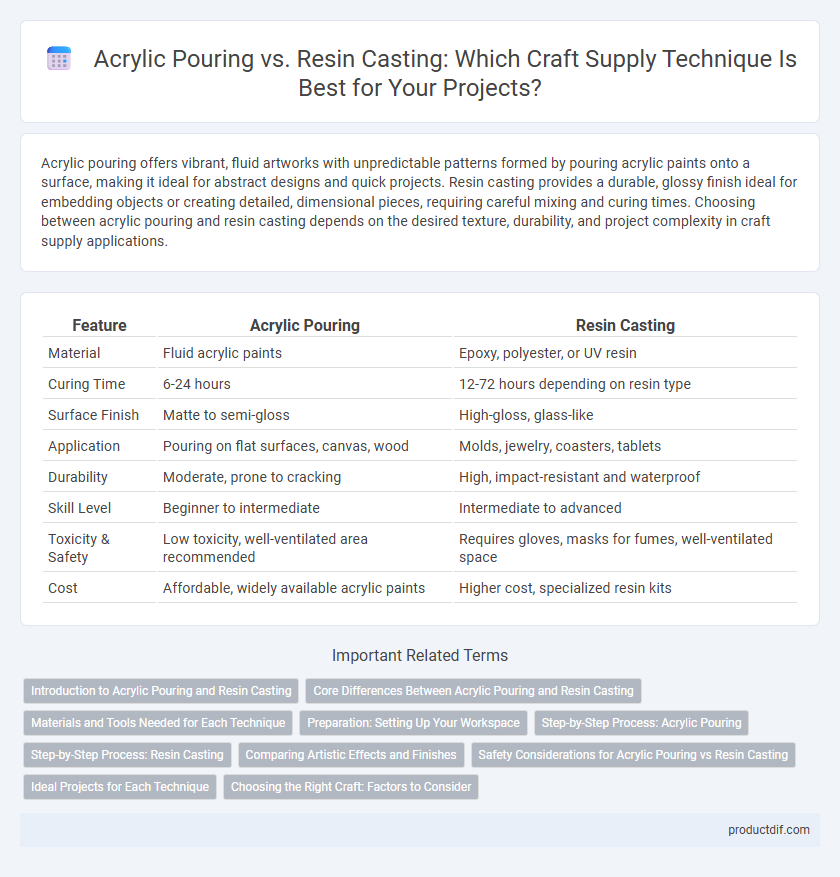
| Feature | Acrylic Pouring | Resin Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Fluid acrylic paints | Epoxy, polyester, or UV resin |
| Curing Time | 6-24 hours | 12-72 hours depending on resin type |
| Surface Finish | Matte to semi-gloss | High-gloss, glass-like |
| Application | Pouring on flat surfaces, canvas, wood | Molds, jewelry, coasters, tablets |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, impact-resistant and waterproof |
| Skill Level | Beginner to intermediate | Intermediate to advanced |
| Toxicity & Safety | Low toxicity, well-ventilated area recommended | Requires gloves, masks for fumes, well-ventilated space |
| Cost | Affordable, widely available acrylic paints | Higher cost, specialized resin kits |
Introduction to Acrylic Pouring and Resin Casting
Acrylic pouring involves mixing acrylic paints with a pouring medium to create fluid, abstract art through controlled flows and cells. Resin casting utilizes epoxy resin and hardeners, poured into molds to produce durable, glossy, and three-dimensional decorative pieces. Both techniques require specific materials and curing times, offering unique textures and finishes ideal for different creative projects.
Core Differences Between Acrylic Pouring and Resin Casting
Acrylic pouring involves creating fluid, abstract art by layering and manipulating poured acrylic paints on a surface, emphasizing color blending and flow patterns. Resin casting uses liquid resin poured into molds to create solid, durable, three-dimensional objects with a glossy finish, often incorporating pigments, inclusions, or embedded items. The core difference lies in acrylic pouring producing flat, painterly textures, while resin casting results in solid, sculptural pieces with high durability and clarity.
Materials and Tools Needed for Each Technique
Acrylic pouring requires fluid acrylic paints, pouring mediums, silicone oil for cells, and disposable cups or mixing sticks, along with a level workspace and gloves to manage spills. Resin casting involves epoxy or polyester resin, hardeners, molds, gloves, and a respirator mask due to fumes, plus mixing containers and pipettes for precision. Both techniques demand protective surfaces and ventilation, but resin casting necessitates stricter safety measures and specialized curing environments.
Preparation: Setting Up Your Workspace
Preparing your workspace for acrylic pouring requires protecting surfaces with plastic sheets or silicone mats to prevent paint stains and ensuring ample ventilation to handle paint fumes. Resin casting demands a dust-free environment, precise temperature control between 70-75degF (21-24degC), and use of gloves and respirators due to resin's chemical fumes. Organizing tools like mixing cups, stir sticks, and molds within easy reach optimizes workflow and minimizes contamination risks in both crafts.
Step-by-Step Process: Acrylic Pouring
Acrylic pouring involves mixing acrylic paints with a pouring medium to achieve the right consistency before layering colors onto the canvas. The artist then tilts and manipulates the surface to create fluid, abstract patterns that blend seamlessly. Curing requires several hours of drying, ensuring the paint solidifies into a glossy, textured finish perfect for unique craft projects.
Step-by-Step Process: Resin Casting
Resin casting involves carefully measuring and mixing resin and hardener in precise ratios, typically 1:1 or 2:1, to ensure optimal curing properties. After mixing, the resin is poured into molds, allowing for slow curing times ranging from 12 to 48 hours depending on the resin type and environmental conditions. Post-curing steps include demolding, sanding, and polishing to achieve a smooth, glossy finish ideal for jewelry, coasters, and decorative items.
Comparing Artistic Effects and Finishes
Acrylic pouring produces vibrant, fluid patterns with a glossy, marbled finish that highlights color blending and organic flow effects, ideal for abstract art. Resin casting offers a crystal-clear, glass-like finish with depth and dimensionality, perfect for encapsulating objects or creating smooth, durable surfaces. Both techniques provide unique artistic textures, with acrylic pouring favoring dynamic color mixing and resin casting emphasizing clarity and structural integrity.
Safety Considerations for Acrylic Pouring vs Resin Casting
Acrylic pouring involves water-based acrylic paints that are generally low in toxicity, but using gloves and masks is advised to avoid skin irritation and inhalation of fumes during prolonged exposure. Resin casting requires more stringent safety measures due to the use of chemical resins and hardeners, which can emit harmful fumes and cause allergic reactions or respiratory issues without proper ventilation and protective gear. Both crafts demand careful handling of materials, but resin casting carries higher risks that necessitate extensive use of gloves, respirators, and well-ventilated workspaces to ensure user safety.
Ideal Projects for Each Technique
Acrylic pouring is ideal for creating vibrant, abstract art pieces, fluid landscapes, and dynamic backgrounds on canvas or wood panels, offering quick drying times and easy layering. Resin casting excels in producing durable, clear, and glossy objects such as jewelry, coasters, and home decor pieces, with the ability to embed items and achieve a glass-like finish. Selecting the right technique depends on the desired project outcome, with acrylic pouring favoring expressive, large-scale art and resin casting suited for detailed, three-dimensional crafts.
Choosing the Right Craft: Factors to Consider
Selecting between acrylic pouring and resin casting involves evaluating factors such as drying time, finish durability, and desired visual effects. Acrylic pouring offers vibrant, fluid patterns with quicker drying times but less structure, while resin casting provides a glossy, durable surface ideal for encapsulating objects and creating three-dimensional effects. Consider project complexity, safety precautions, and curing conditions to determine the most suitable craft supply for your artistic goals.
Acrylic Pouring vs Resin Casting Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com