Heavy-gauge cookware offers superior heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for slow simmering and searing. Thin-gauge cookware heats up quickly and is lightweight, but it may warp and cook unevenly over time. Choosing between heavy-gauge and thin-gauge depends on your cooking style and durability preference.
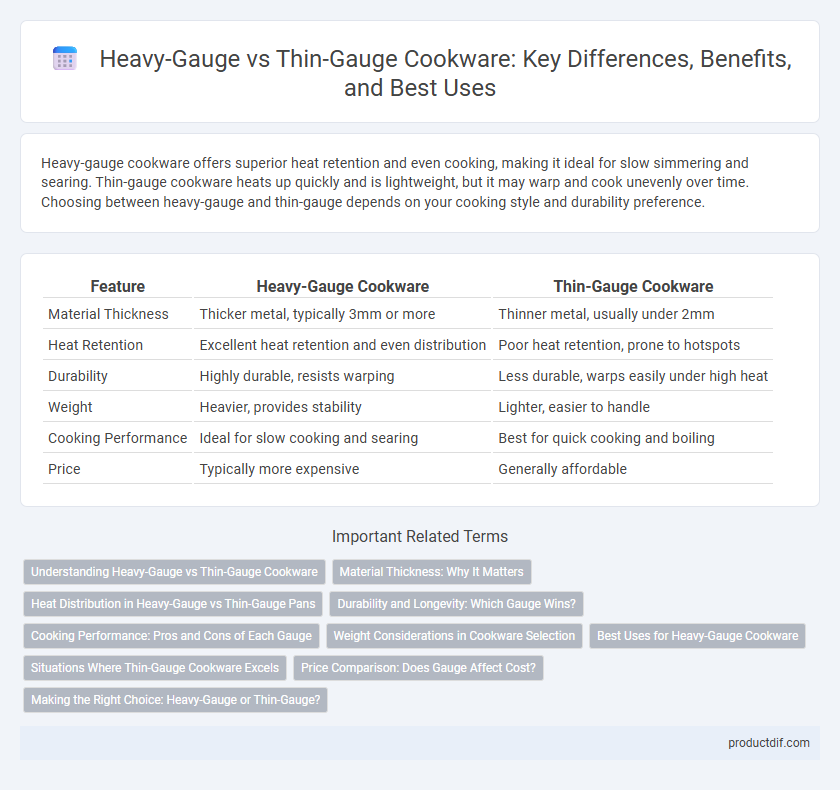
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heavy-Gauge Cookware | Thin-Gauge Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | Thicker metal, typically 3mm or more | Thinner metal, usually under 2mm |
| Heat Retention | Excellent heat retention and even distribution | Poor heat retention, prone to hotspots |
| Durability | Highly durable, resists warping | Less durable, warps easily under high heat |
| Weight | Heavier, provides stability | Lighter, easier to handle |
| Cooking Performance | Ideal for slow cooking and searing | Best for quick cooking and boiling |
| Price | Typically more expensive | Generally affordable |
Understanding Heavy-Gauge vs Thin-Gauge Cookware
Heavy-gauge cookware features thicker metal, usually ranging from 3mm to 5mm, providing superior heat retention and even cooking, essential for tasks demanding precise temperature control. Thin-gauge cookware, often under 2mm, heats up quickly but can suffer from hotspots and warping, making it less durable but more lightweight and responsive for quick meals. Selecting between heavy-gauge and thin-gauge cookware depends on cooking style, with heavy-gauge ideal for slow simmering and searing while thin-gauge suits fast cooking and easy handling.
Material Thickness: Why It Matters
Material thickness in cookware directly impacts heat retention, distribution, and overall cooking performance. Heavy-gauge cookware, often made from thick stainless steel or cast iron, maintains even heat and resists warping, ideal for searing and slow cooking. Thin-gauge pans heat quickly but tend to develop hot spots and deform under high temperatures, affecting food quality and durability.
Heat Distribution in Heavy-Gauge vs Thin-Gauge Pans
Heavy-gauge cookware offers superior heat distribution due to its thicker material, which ensures even cooking and minimizes hot spots. Thin-gauge pans heat up quickly but often suffer from uneven temperature spread, leading to inconsistent cooking results. For precise temperature control and durability, heavy-gauge pans provide a significant advantage in maintaining uniform heat across the cooking surface.
Durability and Longevity: Which Gauge Wins?
Heavy-gauge cookware offers superior durability and longevity due to its thicker metal construction, which resists warping, dents, and heat damage over time. Thin-gauge cookware, while lighter and more responsive to temperature changes, tends to wear out faster and can warp under high heat, reducing its lifespan. For long-term investment and consistent cooking performance, heavy-gauge cookware is the preferred choice.
Cooking Performance: Pros and Cons of Each Gauge
Heavy-gauge cookware offers superior heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for slow cooking and searing, but it requires longer preheating and can be cumbersome to handle. Thin-gauge cookware heats up quickly and responds rapidly to temperature changes, providing better control for delicate cooking tasks, yet it is prone to hot spots and warping over time. Choosing between heavy and thin gauges depends on the cooking style, with heavy-gauge favored for durability and consistent heat, while thin-gauge suits quick, precise cooking.
Weight Considerations in Cookware Selection
Heavy-gauge cookware offers superior heat retention and durability due to its thicker and heavier materials, making it ideal for consistent cooking performance. Thin-gauge cookware is lighter and heats up quickly but may warp or distribute heat unevenly, affecting cooking results. Weight considerations directly influence handling comfort, cooking efficiency, and long-term cookware maintenance.
Best Uses for Heavy-Gauge Cookware
Heavy-gauge cookware excels in even heat distribution and retention, making it ideal for slow cooking, braising, and searing meats. Its thick construction reduces hot spots and prevents warping, ensuring durability and consistent cooking performance. Professional chefs and home cooks favor heavy-gauge pots and pans for recipes requiring steady, prolonged heat and precise temperature control.
Situations Where Thin-Gauge Cookware Excels
Thin-gauge cookware excels in situations requiring rapid heating and quick temperature changes, such as sauteing delicate vegetables or preparing eggs. Its lightweight design allows for easy maneuverability and precise control over cooking, making it ideal for tasks that demand speed and agility. Thin-gauge pans are also preferred for their affordability and ease of storage, especially in kitchens with limited space.
Price Comparison: Does Gauge Affect Cost?
Heavy-gauge cookware typically costs more than thin-gauge due to the increased amount of metal and enhanced durability that extends the pan's lifespan. Thin-gauge pans are generally less expensive but may wear out faster and conduct heat less evenly, leading to potential replacement costs over time. Investing in heavy-gauge cookware provides better heat retention and long-term value despite the initially higher price.
Making the Right Choice: Heavy-Gauge or Thin-Gauge?
Heavy-gauge cookware offers superior heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for searing and slow simmering, while thin-gauge pans heat up quickly and are lightweight, perfect for quick sauteing and everyday use. Choosing between heavy-gauge and thin-gauge cookware depends on your cooking style, heat control preferences, and durability needs. Prioritize heavy-gauge for professional-grade performance and longevity, and thin-gauge for budget-friendly, fast-cooking convenience.
Heavy-Gauge vs Thin-Gauge Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com