Clad cookware features multiple layers of metal fused together, offering superior heat distribution and durability compared to unclad options. Unclad cookware, typically made from a single metal layer, can result in uneven cooking and hotspots. Choosing clad cookware enhances cooking performance and longevity, making it ideal for precise temperature control and even heat conduction.
Table of Comparison
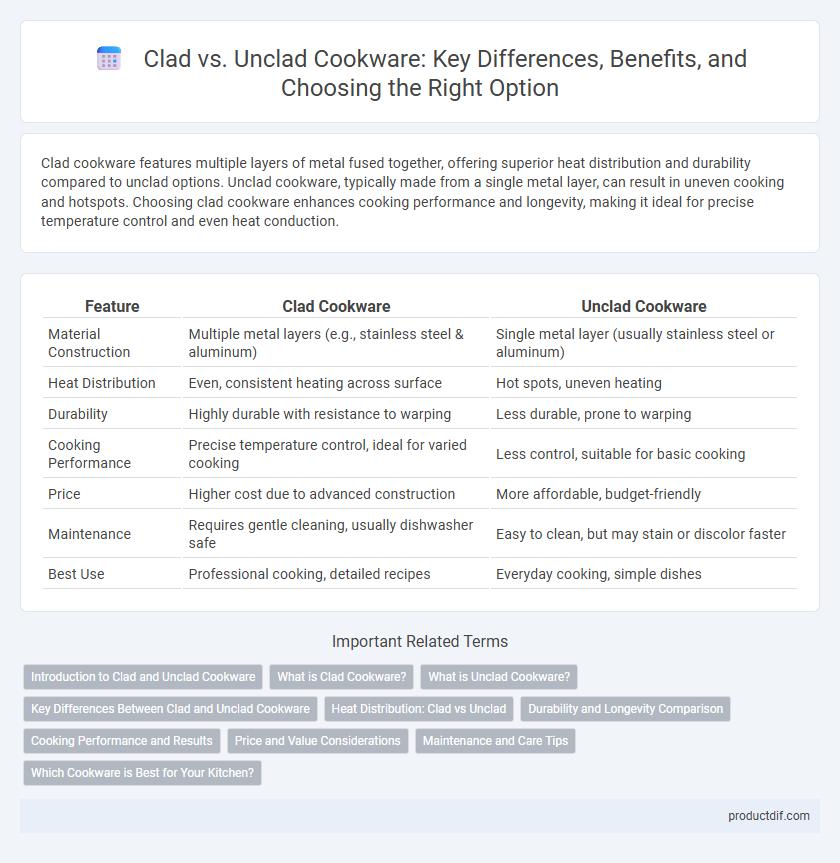
| Feature | Clad Cookware | Unclad Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Construction | Multiple metal layers (e.g., stainless steel & aluminum) | Single metal layer (usually stainless steel or aluminum) |
| Heat Distribution | Even, consistent heating across surface | Hot spots, uneven heating |
| Durability | Highly durable with resistance to warping | Less durable, prone to warping |
| Cooking Performance | Precise temperature control, ideal for varied cooking | Less control, suitable for basic cooking |
| Price | Higher cost due to advanced construction | More affordable, budget-friendly |
| Maintenance | Requires gentle cleaning, usually dishwasher safe | Easy to clean, but may stain or discolor faster |
| Best Use | Professional cooking, detailed recipes | Everyday cooking, simple dishes |
Introduction to Clad and Unclad Cookware
Clad cookware features multiple layers of metal, typically stainless steel bonded with aluminum or copper, providing excellent heat distribution and durability. Unclad cookware consists of a single metal layer, usually stainless steel or cast iron, which may result in uneven heating and requires more careful temperature management. Understanding these differences helps in selecting cookware that balances performance, maintenance, and cooking style needs.
What is Clad Cookware?
Clad cookware consists of multiple layers of metal bonded together, typically combining stainless steel with an inner core of aluminum or copper for enhanced heat conductivity and even cooking. This multilayer construction prevents hot spots and provides superior heat distribution compared to unclad cookware, which is usually a single metal layer. Clad pans offer durability, improved cooking performance, and are often favored by professional chefs for precision and consistency.
What is Unclad Cookware?
Unclad cookware consists of a single layer of metal, typically stainless steel or aluminum, without additional bonding to other materials for improved heat conduction. This type of cookware heats unevenly compared to clad cookware, often resulting in hot spots and less efficient cooking performance. Unclad pans are usually lighter and less expensive, but they lack the superior heat distribution and durability found in multi-ply, clad cookware.
Key Differences Between Clad and Unclad Cookware
Clad cookware features multiple layers of metal, typically combining stainless steel with an aluminum or copper core, which ensures even heat distribution and prevents hot spots. Unclad cookware usually consists of a single metal layer, often stainless steel or aluminum, resulting in less efficient heat conduction and increased risk of uneven cooking. The key differences lie in heat retention, cooking performance, and price, with clad cookware offering superior durability and temperature control for professional and home chefs.
Heat Distribution: Clad vs Unclad
Clad cookware features multiple layers of metals, often combining aluminum or copper cores with stainless steel exteriors, which provide superior heat distribution and even cooking temperatures. Unclad cookware, typically made from a single metal like stainless steel or cast iron, tends to have uneven heat distribution, leading to hot spots and inconsistent cooking. The multi-layer construction of clad pans minimizes thermal hot spots, making them ideal for precise temperature control in cooking.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Clad cookware features multiple bonded layers of metal, typically stainless steel and aluminum or copper, enhancing durability by preventing warping and improving heat distribution. Unclad cookware, usually made from a single metal layer, is more prone to warping and uneven heating, reducing its lifespan compared to clad options. The multi-layer construction of clad cookware ensures superior longevity, making it a preferred choice for consistent performance over time.
Cooking Performance and Results
Clad cookware features multiple layers of metal, typically combining stainless steel with an aluminum or copper core, which ensures even heat distribution and minimizes hot spots for consistent cooking results. Unclad cookware, often made from a single metal like stainless steel or aluminum, may experience uneven heating, leading to potential food sticking or burning in certain areas. The superior heat conductivity of clad cookware enhances precise temperature control, resulting in better searing, browning, and overall cooking performance compared to unclad options.
Price and Value Considerations
Clad cookware typically commands a higher price due to its multi-layer construction, which enhances heat distribution and durability, offering better long-term value despite the initial investment. Unclad cookware, often made from a single material like stainless steel or aluminum, is generally more affordable but may sacrifice even heating and longevity. Evaluating price against performance, clad cookware provides superior value for frequent cooks seeking consistent results and durability.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Clad cookware, featuring multiple bonded metal layers, offers superior heat distribution and durability but requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to maintain its polished finish. Unclad cookware, typically made of single metal like stainless steel or cast iron, demands regular seasoning or thorough drying to prevent rust and maintain non-stick properties. Proper maintenance, including hand washing and avoiding harsh detergents, extends the lifespan and performance of both clad and unclad cookware.
Which Cookware is Best for Your Kitchen?
Clad cookware features multiple metal layers, usually stainless steel enveloping an aluminum or copper core, providing superior heat conductivity and even cooking performance. Unclad cookware typically consists of a single metal layer, offering less efficient heat distribution but often at a lower price point and lighter weight. For home chefs prioritizing precise temperature control and durability, clad cookware is the optimal choice, while unclad options suit budget-conscious cooks seeking basic functionality.
Clad vs Unclad Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com