Heavy-gauge cookware offers superior heat retention and even cooking due to its thicker material, making it ideal for searing and slow cooking. Light-gauge cookware heats up quickly and is easier to handle, but it may warp or heat unevenly over time. Choosing between heavy-gauge and light-gauge depends on cooking style and durability preferences.
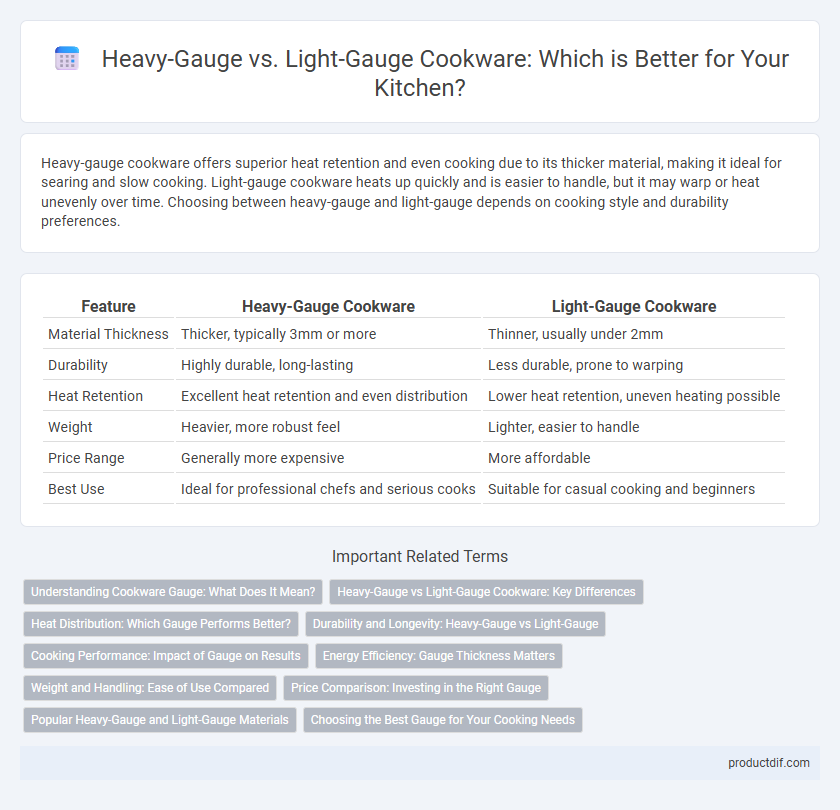
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heavy-Gauge Cookware | Light-Gauge Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | Thicker, typically 3mm or more | Thinner, usually under 2mm |
| Durability | Highly durable, long-lasting | Less durable, prone to warping |
| Heat Retention | Excellent heat retention and even distribution | Lower heat retention, uneven heating possible |
| Weight | Heavier, more robust feel | Lighter, easier to handle |
| Price Range | Generally more expensive | More affordable |
| Best Use | Ideal for professional chefs and serious cooks | Suitable for casual cooking and beginners |
Understanding Cookware Gauge: What Does It Mean?
Cookware gauge refers to the thickness of the metal used in pots and pans, with lower gauge numbers indicating thicker, heavier materials. Heavy-gauge cookware provides superior heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for professional chefs and slow cooking methods. Light-gauge cookware heats quickly but may warp or unevenly cook foods, often preferred for quick meals and budget-friendly options.
Heavy-Gauge vs Light-Gauge Cookware: Key Differences
Heavy-gauge cookware features thicker metal, often ranging from 3 to 5 mm, providing superior heat retention and even distribution essential for precise cooking. Light-gauge cookware, typically under 2 mm thick, heats quickly but can warp or cook unevenly under high heat. Choosing heavy-gauge ensures durability and consistent performance, while light-gauge offers faster heating and lighter weight for convenience.
Heat Distribution: Which Gauge Performs Better?
Heavy-gauge cookware excels in heat distribution, providing even and consistent cooking temperatures due to its thicker material, which retains and spreads heat more effectively. Light-gauge cookware heats up quickly but often develops hot spots that can cause uneven cooking or burning. For precise temperature control and durability, heavy-gauge pans outperform light-gauge options in delivering superior heat distribution.
Durability and Longevity: Heavy-Gauge vs Light-Gauge
Heavy-gauge cookware is crafted from thicker metal, providing superior durability and resistance to warping, making it ideal for long-term use in high-heat cooking environments. Light-gauge cookware, while easier to handle and quicker to heat, tends to wear out faster and is more prone to dents and deformation over time. Choosing heavy-gauge pots and pans ensures enhanced longevity and consistent cooking performance, especially in professional kitchens.
Cooking Performance: Impact of Gauge on Results
Heavy-gauge cookware, typically measuring 3mm or more in thickness, provides superior heat retention and even distribution, resulting in consistent cooking performance and reduced hot spots. Light-gauge cookware, usually under 2mm, heats up quickly but often suffers from uneven heat distribution, causing food to cook inconsistently. The gauge of the cookware significantly impacts the quality and precision of cooking outcomes, with heavy-gauge materials favored for professional-grade results.
Energy Efficiency: Gauge Thickness Matters
Heavy-gauge cookware, typically ranging from 3 to 5 millimeters thick, offers superior energy efficiency by distributing heat evenly and retaining it longer, reducing cooking time and energy consumption. In contrast, light-gauge cookware, often under 2 millimeters thick, heats up quickly but loses heat rapidly, leading to uneven cooking and higher energy use. Choosing heavy-gauge materials like stainless steel or cast iron enhances thermal conductivity, making them ideal for energy-conscious cooking.
Weight and Handling: Ease of Use Compared
Heavy-gauge cookware, typically made from thicker metals such as stainless steel or cast aluminum, offers superior heat retention and durability but comes with increased weight, making it more challenging to handle during cooking. Light-gauge cookware, often constructed from thinner materials like aluminum or tin, provides easier maneuverability and quicker heating but sacrifices some heat distribution and long-term resilience. Choosing between heavy-gauge and light-gauge cookware depends on balancing the importance of weight for ease of use against the benefits of even cooking and sturdiness.
Price Comparison: Investing in the Right Gauge
Heavy-gauge cookware, crafted from thicker metals like stainless steel or aluminum, typically commands a higher price due to enhanced durability and superior heat distribution, making it a long-term investment for serious cooks. Light-gauge cookware, often made from thinner materials, tends to be more affordable but may warp or wear out faster, requiring more frequent replacements. Evaluating the price difference against cooking performance and longevity helps determine the best gauge investment for your culinary needs.
Popular Heavy-Gauge and Light-Gauge Materials
Popular heavy-gauge cookware materials include stainless steel and cast iron, prized for their durability and even heat distribution, making them ideal for high-heat cooking and longevity. Light-gauge cookware often features aluminum and copper, valued for their excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight properties, which allow for quick heating and easier handling. Choosing between heavy-gauge and light-gauge depends on cooking style, as heavy-gauge materials excel in heat retention while light-gauge options offer faster temperature responsiveness.
Choosing the Best Gauge for Your Cooking Needs
Heavy-gauge cookware offers superior heat retention and durability, making it ideal for searing, slow cooking, and frequent use in professional kitchens. Light-gauge cookware heats up quickly and is lighter, providing better control for delicate tasks and easier handling during quick meals. Selecting the best gauge depends on your cooking style, with heavy-gauge suited for thorough cooking and light-gauge preferred for fast, precise heat adjustments.
Heavy-Gauge vs Light-Gauge Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com