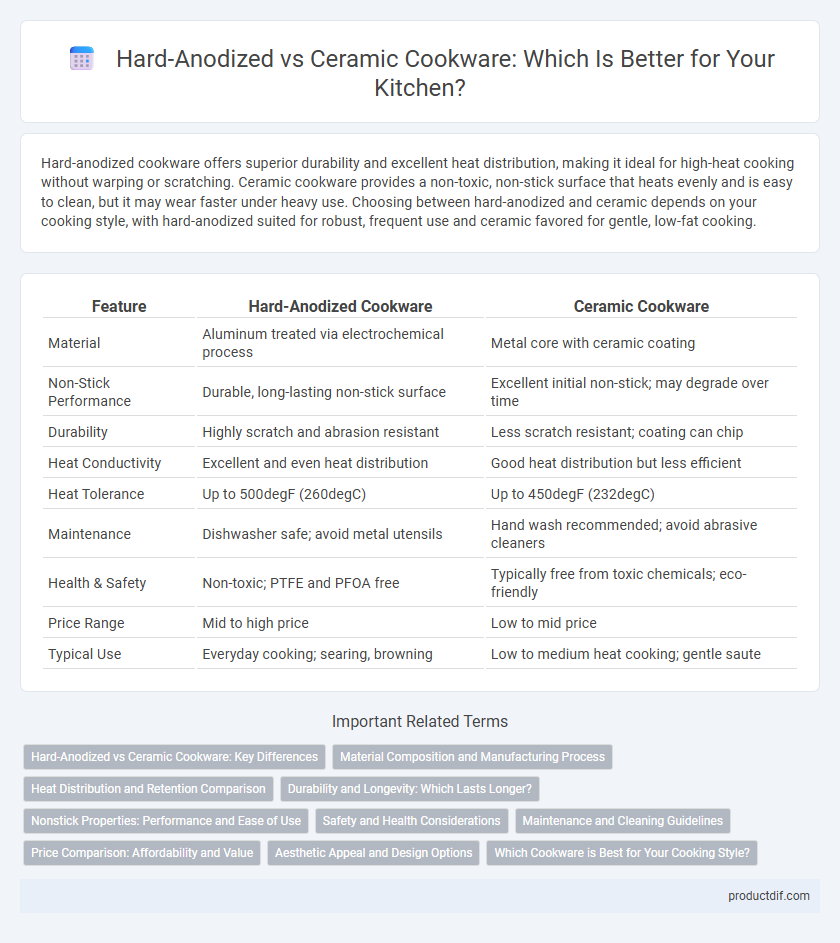
Hard-anodized cookware offers superior durability and excellent heat distribution, making it ideal for high-heat cooking without warping or scratching. Ceramic cookware provides a non-toxic, non-stick surface that heats evenly and is easy to clean, but it may wear faster under heavy use. Choosing between hard-anodized and ceramic depends on your cooking style, with hard-anodized suited for robust, frequent use and ceramic favored for gentle, low-fat cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hard-Anodized Cookware | Ceramic Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum treated via electrochemical process | Metal core with ceramic coating |
| Non-Stick Performance | Durable, long-lasting non-stick surface | Excellent initial non-stick; may degrade over time |
| Durability | Highly scratch and abrasion resistant | Less scratch resistant; coating can chip |
| Heat Conductivity | Excellent and even heat distribution | Good heat distribution but less efficient |
| Heat Tolerance | Up to 500degF (260degC) | Up to 450degF (232degC) |
| Maintenance | Dishwasher safe; avoid metal utensils | Hand wash recommended; avoid abrasive cleaners |
| Health & Safety | Non-toxic; PTFE and PFOA free | Typically free from toxic chemicals; eco-friendly |
| Price Range | Mid to high price | Low to mid price |
| Typical Use | Everyday cooking; searing, browning | Low to medium heat cooking; gentle saute |
Hard-Anodized vs Ceramic Cookware: Key Differences
Hard-anodized cookware features a durable, non-reactive surface created through an electrochemical process that makes aluminum harder and resistant to scratches and corrosion. Ceramic cookware, coated with a silica-based non-stick layer, offers excellent heat distribution but tends to be less resilient against cracking and chipping. The key differences between hard-anodized and ceramic cookware revolve around durability, heat conduction, and maintenance, with hard-anodized excelling in longevity and ceramic providing non-toxic, eco-friendly cooking options.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Hard-anodized cookware is made from aluminum that undergoes an electrochemical process, creating a dense, non-reactive oxide layer that enhances durability and corrosion resistance. Ceramic cookware features a base typically made of aluminum or aluminum alloy coated with a silica-based glaze, formed through a sol-gel process that ensures a non-stick, chemical-free surface. The manufacturing process of hard-anodized cookware results in a harder surface than stainless steel, while ceramic's sol-gel coating provides excellent heat distribution but can be more prone to chipping under heavy use.
Heat Distribution and Retention Comparison
Hard-anodized cookware offers superior heat distribution due to its dense, non-porous surface, ensuring even cooking and minimizing hot spots. Ceramic cookware excels in heat retention, maintaining consistent temperatures over longer periods thanks to its insulating properties. Choosing between the two depends on whether rapid, even heating or prolonged heat maintenance is prioritized in your cooking needs.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Hard-anodized cookware features a dense, non-porous surface created through an electrochemical process, offering superior resistance to scratches, warping, and corrosion compared to ceramic cookware. Ceramic cookware, while non-reactive and environmentally friendly, tends to be more prone to chipping and wear over time due to its brittle nature. Consequently, hard-anodized cookware generally outperforms ceramic in durability and longevity, making it a better investment for frequent cooking use.
Nonstick Properties: Performance and Ease of Use
Hard-anodized cookware offers superior nonstick properties due to its durable, scratch-resistant surface that withstands high temperatures and metal utensils, ensuring long-lasting performance. Ceramic cookware provides excellent nonstick capabilities with a naturally smooth surface free from harmful chemicals, but its coating can wear down faster and requires careful maintenance to preserve ease of use. Both options deliver effective food release, but hard-anodized pans generally offer better durability and easier cleaning over time.
Safety and Health Considerations
Hard-anodized cookware offers a durable, non-reactive surface that resists scratching and reduces the risk of harmful metal leaching, making it a safe choice for daily cooking. Ceramic cookware, made from natural materials and free from PTFE and PFOA chemicals, provides a non-toxic, non-stick surface ideal for low to medium heat cooking with minimal oil. Both options promote health-conscious cooking, but ceramic pans cool quickly and require careful temperature management to prevent chipping or cracking.
Maintenance and Cleaning Guidelines
Hard-anodized cookware requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents to preserve its durable oxide layer and prevent scratches. Ceramic cookware demands careful maintenance by avoiding metal utensils and dishwasher cleaning to maintain its non-stick surface and prevent chipping. Both types benefit from handwashing and thorough drying to extend their lifespan and maintain optimal performance.
Price Comparison: Affordability and Value
Hard-anodized cookware typically costs more upfront, reflecting its durable, non-reactive surface and superior heat distribution. Ceramic cookware offers a more affordable price point, appealing to budget-conscious buyers while providing non-toxic, eco-friendly cooking surfaces. Evaluating value involves considering longevity and performance, where hard-anodized pans often justify higher costs through extended use and scratch resistance.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Hard-anodized cookware features a sleek, matte finish in dark gray or black tones, offering a modern and professional kitchen look that resists scratches and discoloration. Ceramic cookware stands out with vibrant, glossy colors and a variety of patterns, adding a bright, decorative element to kitchen aesthetics. While hard-anodized pieces emphasize durability and understated elegance, ceramic options provide diverse design choices that complement both contemporary and traditional kitchen styles.
Which Cookware is Best for Your Cooking Style?
Hard-anodized cookware offers superior durability and excellent heat conductivity, making it ideal for high-heat cooking and frequent use. Ceramic cookware provides a non-toxic, non-stick surface perfect for low to medium-heat cooking and easy cleanup, favored by those seeking chemical-free cookware. Choosing between the two depends on your cooking style: opt for hard-anodized if you need toughness and heat resilience, or ceramic for gentle, health-conscious cooking.
Hard-Anodized vs Ceramic Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com