Enzymatic cleaners break down organic stains and residues using natural enzymes, making them highly effective for eco-friendly and sensitive surface cleaning. Chemical solvents dissolve grease, oils, and tough residues quickly but can be harsh and potentially harmful to surfaces and health. Choosing between enzymatic cleaners and chemical solvents depends on the cleaning task's specificity and environmental considerations.
Table of Comparison
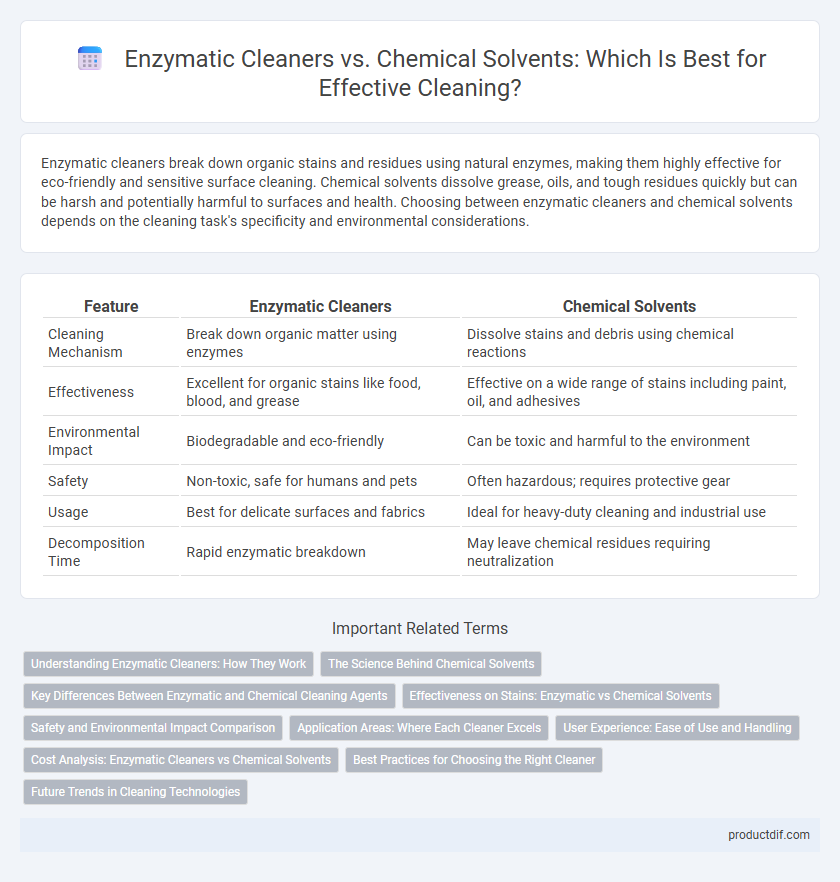
| Feature | Enzymatic Cleaners | Chemical Solvents |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning Mechanism | Break down organic matter using enzymes | Dissolve stains and debris using chemical reactions |
| Effectiveness | Excellent for organic stains like food, blood, and grease | Effective on a wide range of stains including paint, oil, and adhesives |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Can be toxic and harmful to the environment |
| Safety | Non-toxic, safe for humans and pets | Often hazardous; requires protective gear |
| Usage | Best for delicate surfaces and fabrics | Ideal for heavy-duty cleaning and industrial use |
| Decomposition Time | Rapid enzymatic breakdown | May leave chemical residues requiring neutralization |
Understanding Enzymatic Cleaners: How They Work
Enzymatic cleaners use natural enzymes to break down organic stains and soils by targeting proteins, fats, and carbohydrates at a molecular level, allowing for efficient and eco-friendly removal. These bio-catalysts accelerate the degradation process without harsh chemicals, making enzymatic cleaners safer for surfaces and the environment. Unlike chemical solvents that dissolve stains through chemical reactions, enzymatic cleaners rely on biological mechanisms that minimize residue and toxicity.
The Science Behind Chemical Solvents
Chemical solvents break down grease, oils, and stains by dissolving their molecular structure, using compounds like alcohols, ketones, and hydrocarbons. These solvents interact with nonpolar substances, effectively loosening and removing tough dirt that water and detergents cannot dissolve. Their volatility also allows for rapid evaporation, leaving surfaces clean without residue.
Key Differences Between Enzymatic and Chemical Cleaning Agents
Enzymatic cleaners use natural enzymes to break down organic stains and soils at a molecular level, making them highly effective for protein, fat, and carbohydrate-based debris. Chemical solvents rely on synthetic compounds that dissolve or emulsify a broad range of contaminants quickly, often providing faster surface cleaning but with potential environmental and health concerns. Enzymatic cleaners offer biodegradable, eco-friendly advantages, while chemical solvents excel in industrial-strength cleaning where rapid results are critical.
Effectiveness on Stains: Enzymatic vs Chemical Solvents
Enzymatic cleaners target specific stain molecules by breaking down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, making them highly effective on organic stains such as blood, grease, and food residues. Chemical solvents dissolve stains through chemical reactions, excelling in removing ink, paint, and oil-based substances by breaking down their molecular structures. Enzymatic cleaners often provide a safer and more eco-friendly alternative for organic stains, while chemical solvents offer quick results on stubborn synthetic stains.
Safety and Environmental Impact Comparison
Enzymatic cleaners break down organic stains using natural enzymes, making them biodegradable and safer for both users and the environment compared to harsh chemical solvents. Chemical solvents often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that pose health risks such as respiratory irritation and contribute to air pollution. Enzymatic formulations typically have lower toxicity, reduced flammability, and minimize environmental damage through quicker degradation in water systems.
Application Areas: Where Each Cleaner Excels
Enzymatic cleaners excel in organic stain removal and are ideal for applications in healthcare, food processing, and laundry where breaking down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates is essential. Chemical solvents are more effective in industrial and automotive sectors for dissolving oil, grease, and synthetic materials on hard surfaces and machinery components. Selecting based on specific residues and surface types ensures optimal cleaning efficiency and safety.
User Experience: Ease of Use and Handling
Enzymatic cleaners offer a user-friendly experience with gentle, non-toxic ingredients that reduce skin irritation and minimize the need for protective gear. Chemical solvents often require careful handling, gloves, and proper ventilation due to their strong odors and potential hazards. Enzymatic solutions typically come in ready-to-use forms, enhancing convenience, while chemical solvents may demand dilution or precise measurement for effective application.
Cost Analysis: Enzymatic Cleaners vs Chemical Solvents
Enzymatic cleaners generally have a higher upfront cost compared to chemical solvents but offer long-term savings through reduced waste disposal fees and lower environmental compliance expenses. Chemical solvents may appear cheaper initially but often incur hidden costs related to health risks, hazardous waste handling, and potential regulatory fines. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals enzymatic cleaners as a more cost-effective and sustainable choice for industrial and household cleaning applications.
Best Practices for Choosing the Right Cleaner
Enzymatic cleaners excel at breaking down organic stains like food, grease, and blood by using natural enzymes, making them ideal for sensitive surfaces and eco-friendly cleaning. Chemical solvents offer powerful degreasing and stain removal on tough inorganic residues, yet require careful handling and proper ventilation due to their toxicity and fumes. Selecting the best cleaner involves identifying the surface type, stain composition, and safety requirements to balance effectiveness with health and environmental impact.
Future Trends in Cleaning Technologies
Enzymatic cleaners leverage biological catalysts to break down organic stains effectively while minimizing environmental impact, making them a key focus in sustainable cleaning technology development. Chemical solvents often deliver rapid and powerful cleaning results but face increasing regulatory restrictions due to toxicity and volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Future trends in cleaning technologies emphasize hybrid formulations combining enzymatic action with biodegradable solvents, enhanced by nanotechnology and biotechnology advancements to achieve superior performance and eco-friendly standards.
Enzymatic cleaners vs Chemical solvents Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com