Fair Trade beverages ensure farmers receive equitable wages and work under ethical conditions, promoting sustainable agriculture and community development. Conventional beverages often prioritize cost efficiency, which can lead to variable quality and less support for environmental and social standards. Choosing Fair Trade supports ethical production practices and contributes to a more sustainable global beverage industry.
Table of Comparison
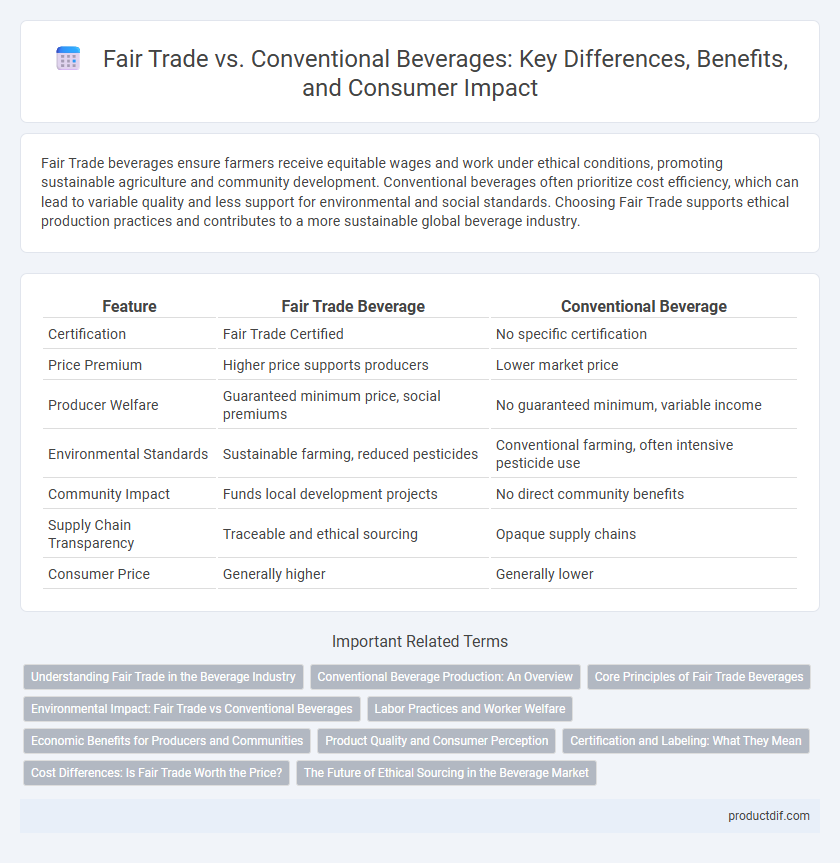
| Feature | Fair Trade Beverage | Conventional Beverage |
|---|---|---|
| Certification | Fair Trade Certified | No specific certification |
| Price Premium | Higher price supports producers | Lower market price |
| Producer Welfare | Guaranteed minimum price, social premiums | No guaranteed minimum, variable income |
| Environmental Standards | Sustainable farming, reduced pesticides | Conventional farming, often intensive pesticide use |
| Community Impact | Funds local development projects | No direct community benefits |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Traceable and ethical sourcing | Opaque supply chains |
| Consumer Price | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Understanding Fair Trade in the Beverage Industry
Fair Trade in the beverage industry ensures ethical sourcing and fair compensation for farmers, promoting sustainable agricultural practices and improved livelihoods. This certification emphasizes transparency throughout the supply chain, contrasting with conventional trade that often lacks such standards. Consumers choosing Fair Trade beverages contribute to social equity and environmental stewardship while supporting higher quality and ethically produced products.
Conventional Beverage Production: An Overview
Conventional beverage production relies heavily on large-scale monoculture farming, intensive use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and synthetic additives to maximize yield and reduce costs. This method often results in significant environmental degradation, including soil depletion, water pollution, and biodiversity loss. Despite its efficiency, conventional production processes may compromise product quality and raise concerns over worker health and safety conditions in supply chains.
Core Principles of Fair Trade Beverages
Fair Trade beverages prioritize equitable trading conditions, ensuring producers receive fair wages and work under safe, sustainable environments. Core principles include direct trade relationships, community development premiums, and environmental stewardship to promote social and economic justice. These standards contrast conventional practices that often prioritize profit over ethical sourcing and long-term sustainability.
Environmental Impact: Fair Trade vs Conventional Beverages
Fair Trade beverages significantly reduce environmental impact through sustainable farming practices such as organic cultivation, crop diversification, and reduced pesticide use compared to conventional methods. Conventional beverage production often relies on monoculture and intensive chemical inputs, leading to soil degradation, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. Fair Trade certification encourages conservation of natural resources and supports climate resilience, making it a more eco-friendly choice in the beverage industry.
Labor Practices and Worker Welfare
Fair Trade beverage production prioritizes ethical labor practices by ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and community support for farmers, contrasting with many conventional supply chains where workers often face low pay and inadequate protections. Certification systems like Fairtrade International enforce standards that promote worker welfare and prohibit exploitative labor, including child and forced labor. This emphasis creates a more sustainable and equitable environment for laborers, directly impacting the quality and social responsibility of the beverage industry.
Economic Benefits for Producers and Communities
Fair Trade beverages ensure higher and more stable incomes for producers by guaranteeing minimum prices and premiums that support community development projects. Conventional beverages often expose farmers to volatile market prices, limiting economic security and hindering sustainable growth in producer communities. By promoting Fair Trade certification, producers benefit from improved living standards, enhanced access to healthcare and education, and strengthened local economies.
Product Quality and Consumer Perception
Fair Trade beverages often exhibit superior product quality due to sustainable farming practices and rigorous quality standards, enhancing flavor profiles and freshness. Consumers perceive Fair Trade products as ethically produced and environmentally friendly, increasing brand loyalty and willingness to pay a premium. Conventional beverages may lack this ethical appeal, leading to a perception of lower quality and less transparency in sourcing.
Certification and Labeling: What They Mean
Fair Trade certification ensures that beverages meet strict social, economic, and environmental standards, guaranteeing fair wages for farmers and sustainable farming practices. Conventional beverage labeling typically does not provide assurances related to ethical sourcing or environmental impact, focusing instead on regulatory compliance and product information. Understanding certification labels like Fair Trade or organic on beverage products helps consumers make informed choices that support ethical and sustainable trade practices.
Cost Differences: Is Fair Trade Worth the Price?
Fair Trade beverages typically cost 10-30% more than conventional options due to ethical sourcing, higher labor standards, and environmental practices. Consumers often pay this premium to support sustainable farming, fair wages, and community development in producing regions. Evaluating whether Fair Trade is worth the price depends on prioritizing social responsibility and quality over immediate cost savings.
The Future of Ethical Sourcing in the Beverage Market
Fair Trade sourcing in the beverage market prioritizes sustainable farming practices and fair wages, shaping the future of ethical consumption. Increasing consumer demand for transparency and environmental responsibility drives brands to adopt Fair Trade certifications over conventional methods. This shift fosters long-term supply chain resilience and promotes social equity within coffee, tea, and cocoa production worldwide.
Fair Trade vs Conventional Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com