Grills provide direct heat with open flames, ideal for achieving char marks and smoky flavors on meats and vegetables. Griddles offer a flat, smooth cooking surface that evenly distributes heat, perfect for pancakes, eggs, and sandwiches. Choosing between a grill and a griddle depends on the types of food you cook and the texture or flavor you prefer.
Table of Comparison
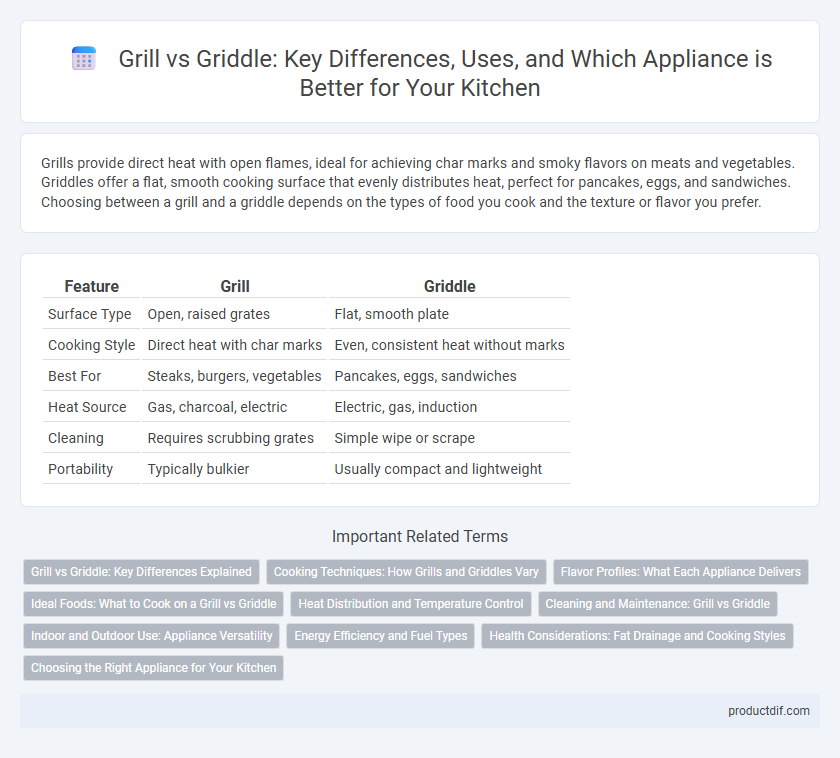
| Feature | Grill | Griddle |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Type | Open, raised grates | Flat, smooth plate |
| Cooking Style | Direct heat with char marks | Even, consistent heat without marks |
| Best For | Steaks, burgers, vegetables | Pancakes, eggs, sandwiches |
| Heat Source | Gas, charcoal, electric | Electric, gas, induction |
| Cleaning | Requires scrubbing grates | Simple wipe or scrape |
| Portability | Typically bulkier | Usually compact and lightweight |
Grill vs Griddle: Key Differences Explained
A grill uses direct heat from below, creating distinctive sear marks and allowing fat to drip away, which enhances flavor and reduces grease. A griddle provides a flat cooking surface with even heat distribution, ideal for pancakes, eggs, and delicate foods that require uniform cooking. Understanding these functional differences helps choose the right appliance for specific cooking styles and recipes.
Cooking Techniques: How Grills and Griddles Vary
Grills cook food using direct radiant heat, creating distinctive char marks and a smoky flavor ideal for meats and vegetables, while griddles provide a flat, evenly heated surface suited for cooking delicate items like pancakes and eggs. Grills use open flames or electric elements beneath grates, allowing fats to drip away, which enhances flavor through smoke. In contrast, griddles retain juices and require less oil, promoting uniform cooking and browning across the entire surface.
Flavor Profiles: What Each Appliance Delivers
Grills impart a smoky, charred flavor to foods through direct exposure to flames, enhancing the taste of meats and vegetables with crispy sear marks. Griddles provide a more even cooking surface that preserves the natural juices and tenderness of food, delivering a richer, buttery flavor ideal for pancakes, eggs, and sandwiches. Choosing between grill and griddle depends on the desired flavor profile, with grills emphasizing smoky intensity and griddles focusing on moist, well-cooked textures.
Ideal Foods: What to Cook on a Grill vs Griddle
Grills excel at cooking foods that benefit from direct, high heat and char marks, such as steaks, burgers, chicken breasts, and vegetables like bell peppers and zucchini. Griddles are ideal for evenly cooking delicate or smaller items including pancakes, eggs, bacon, and sandwiches, as well as stir-fried vegetables and seafood that require a flat, consistent surface. Choosing between a grill and griddle depends on the texture and flavor desired, with grills imparting a smoky taste and griddles providing precise temperature control for uniform cooking.
Heat Distribution and Temperature Control
Grills typically offer direct heat with open flames, enabling high-temperature searing but can create uneven heat distribution across the cooking surface. Griddles provide a flat, solid cooking area with more consistent and even heat distribution, ideal for cooking multiple items simultaneously. Temperature control on griddles is usually more precise due to integrated thermostats, while grills may rely on manual adjustments and variable flame intensity.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Grill vs Griddle
Grills typically require more intensive cleaning due to exposed grates that trap grease and food particles, often needing wire brushes and specialized cleaners to prevent buildup and rust. Griddles, with their flat, smooth cooking surfaces made of cast iron or stainless steel, offer easier maintenance through simple scraping and wiping after each use. Regular seasoning of griddles extends their lifespan and enhances non-stick properties, while grills demand more frequent deep cleaning to maintain optimal performance.
Indoor and Outdoor Use: Appliance Versatility
Grills offer high-heat cooking with open flames, ideal for outdoor use, enhancing smoky flavors in meats and vegetables. Griddles provide a flat, smooth cooking surface suitable for indoor environments, perfect for breakfast foods, sandwiches, and delicate items requiring even heat distribution. Both appliances extend versatility by adapting to different cooking styles and settings, with portable electric grills and stovetop griddles bridging indoor and outdoor culinary needs.
Energy Efficiency and Fuel Types
Grills typically use charcoal or propane gas, providing quick, high heat but often less energy efficiency due to heat loss. Griddles, powered by electric or gas sources, offer even heat distribution and generally consume less fuel, enhancing overall energy efficiency. Choosing between a grill or griddle depends on fuel availability and preferred cooking performance with energy-saving considerations.
Health Considerations: Fat Drainage and Cooking Styles
Grills allow fat to drain away from food through the grates, reducing calorie and fat intake, promoting healthier cooking of meats and vegetables. Griddles cook on a flat surface where fats remain, which can lead to higher fat absorption but provides a versatile platform for sauteing and frying. Choosing between grill and griddle appliances depends on health goals and preferred cooking styles, with grills favoring low-fat meals and griddles supporting richer, more varied dishes.
Choosing the Right Appliance for Your Kitchen
Selecting the right appliance between a grill and a griddle depends on your cooking preferences and kitchen space. Grills excel at high-heat, charred cooking ideal for steaks and vegetables, while griddles offer a flat surface perfect for pancakes, eggs, and sandwiches with even heat distribution. Consider factors like temperature control, surface area, and cleaning ease to optimize cooking efficiency and versatility in your kitchen.
Grill vs Griddle Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com