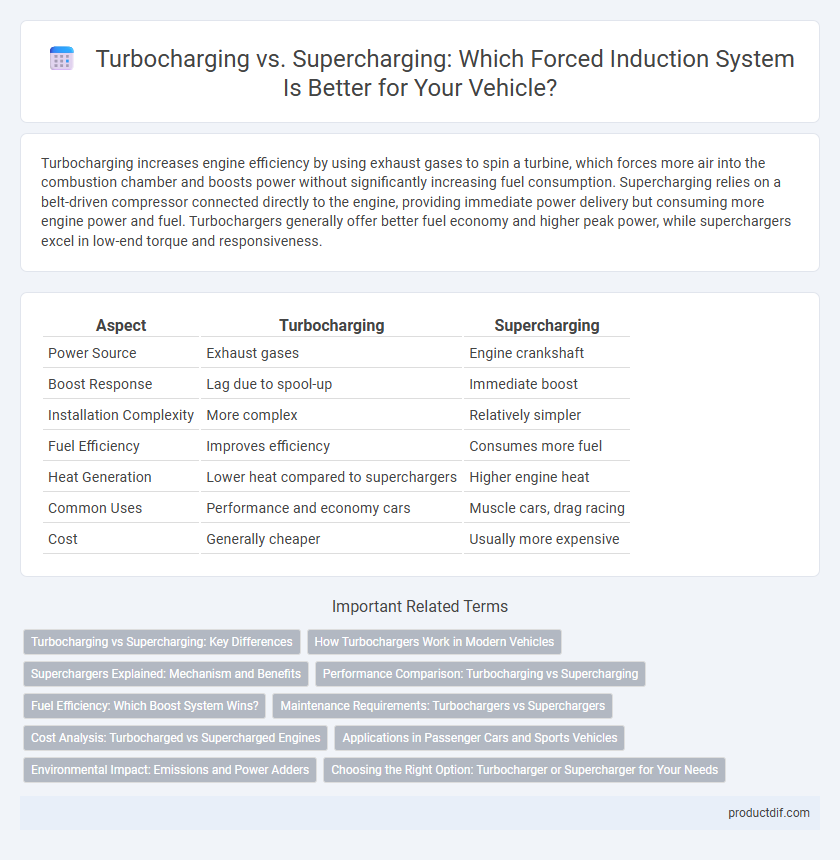
Turbocharging increases engine efficiency by using exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which forces more air into the combustion chamber and boosts power without significantly increasing fuel consumption. Supercharging relies on a belt-driven compressor connected directly to the engine, providing immediate power delivery but consuming more engine power and fuel. Turbochargers generally offer better fuel economy and higher peak power, while superchargers excel in low-end torque and responsiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Turbocharging | Supercharging |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Exhaust gases | Engine crankshaft |
| Boost Response | Lag due to spool-up | Immediate boost |
| Installation Complexity | More complex | Relatively simpler |
| Fuel Efficiency | Improves efficiency | Consumes more fuel |
| Heat Generation | Lower heat compared to superchargers | Higher engine heat |
| Common Uses | Performance and economy cars | Muscle cars, drag racing |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | Usually more expensive |
Turbocharging vs Supercharging: Key Differences
Turbocharging uses exhaust gas energy to spin a turbine, boosting engine power efficiently without drawing extra engine power, while supercharging relies on a belt-driven compressor powered directly by the engine, leading to immediate boost but higher parasitic loss. Turbochargers provide higher fuel efficiency and greater power at higher RPMs, whereas superchargers deliver instant throttle response and improved low-end torque. The choice between the two depends on desired performance characteristics, with turbocharging favoring fuel economy and top-end power, and supercharging prioritizing responsiveness and low-speed torque.
How Turbochargers Work in Modern Vehicles
Turbochargers in modern vehicles harness exhaust gas energy to spin a turbine connected to a compressor, forcing more air into the engine's combustion chamber for increased power and efficiency. By boosting air intake pressure, turbochargers improve fuel combustion, resulting in enhanced horsepower and reduced emissions. Advanced materials and electronic control systems optimize turbocharger responsiveness and minimize turbo lag, enhancing overall engine performance.
Superchargers Explained: Mechanism and Benefits
Superchargers operate by mechanically driving a compressor through a belt connected to the engine's crankshaft, forcing more air into the combustion chamber for increased power output. Unlike turbochargers, superchargers deliver immediate boost without lag, enhancing throttle response and acceleration. The main benefits include improved engine efficiency at low RPMs and consistent power delivery, making them ideal for performance and muscle cars.
Performance Comparison: Turbocharging vs Supercharging
Turbocharging enhances engine efficiency by utilizing exhaust gases to spin a turbine, delivering increased horsepower and torque with improved fuel economy. Supercharging provides immediate power boost through a belt-driven compressor, offering consistent performance at lower RPMs without lag. Turbochargers excel in high-end power and efficiency, while superchargers are preferred for instant throttle response and low-end torque in performance vehicles.
Fuel Efficiency: Which Boost System Wins?
Turbocharging generally offers superior fuel efficiency compared to supercharging by utilizing exhaust gases to spin the turbine, reducing wasted energy and improving engine performance without additional fuel consumption. Superchargers, driven directly by the engine's crankshaft, tend to decrease fuel economy due to the extra mechanical load they impose. Optimizing fuel efficiency with forced induction often depends on driving conditions, but turbochargers consistently demonstrate better energy utilization and lower fuel consumption in most scenarios.
Maintenance Requirements: Turbochargers vs Superchargers
Turbochargers require periodic inspection of the turbo oil lines and higher quality oil changes to prevent carbon build-up and ensure longevity due to their reliance on exhaust gases for operation. Superchargers demand regular belt replacements and tension checks as they are mechanically driven by the engine, leading to more frequent wear of drive components. Maintaining optimal lubrication and cooling systems is essential for both to avoid performance degradation and costly repairs.
Cost Analysis: Turbocharged vs Supercharged Engines
Turbocharged engines generally offer better cost efficiency due to their ability to utilize exhaust gases for increased power, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Supercharged engines, while providing immediate boost and simpler installation, often incur higher fuel costs and maintenance expenses due to their mechanical drive systems. Initial vehicle cost and long-term operational expenses favor turbocharging in performance and economy-focused applications.
Applications in Passenger Cars and Sports Vehicles
Turbocharging enhances passenger cars and sports vehicles by utilizing exhaust gases to increase engine efficiency and power output, making it ideal for fuel economy and high-performance applications. Supercharging provides immediate boost and consistent power delivery, favored in sports vehicles requiring rapid throttle response and enhanced acceleration. Both systems improve engine performance, with turbocharging preferred in modern passenger cars for fuel savings, while supercharging remains popular in high-performance sports vehicles for instant power.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Power Adders
Turbocharging enhances engine efficiency by using exhaust gases to compress intake air, reducing fuel consumption and lowering CO2 emissions compared to naturally aspirated engines. Supercharging, driven mechanically by the engine, tends to increase power output but often results in higher fuel consumption and increased emissions due to its less efficient energy transfer. In terms of environmental impact, turbochargers provide a more sustainable power adder option by optimizing energy use and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.
Choosing the Right Option: Turbocharger or Supercharger for Your Needs
Choosing between a turbocharger and a supercharger depends on your vehicle's performance goals and driving conditions. Turbochargers use exhaust gas to increase engine efficiency and power, offering better fuel economy and higher boost at high RPMs, ideal for highway driving and fuel-conscious users. Superchargers deliver instant power through a belt-driven system, providing rapid throttle response and consistent boost across all RPM ranges, making them better suited for aggressive acceleration and off-the-line performance.
Turbocharging vs Supercharging Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com