Floor drains are designed to handle large volumes of water from spaces like laundry rooms or basements, directing wastewater efficiently to prevent flooding. Shower drains, specifically engineered for bathroom use, include features like hair traps and anti-odor seals to ensure hygiene and prevent clogs. Choosing the right drain type is essential for optimal water flow management and maintenance in plumbing systems.
Table of Comparison
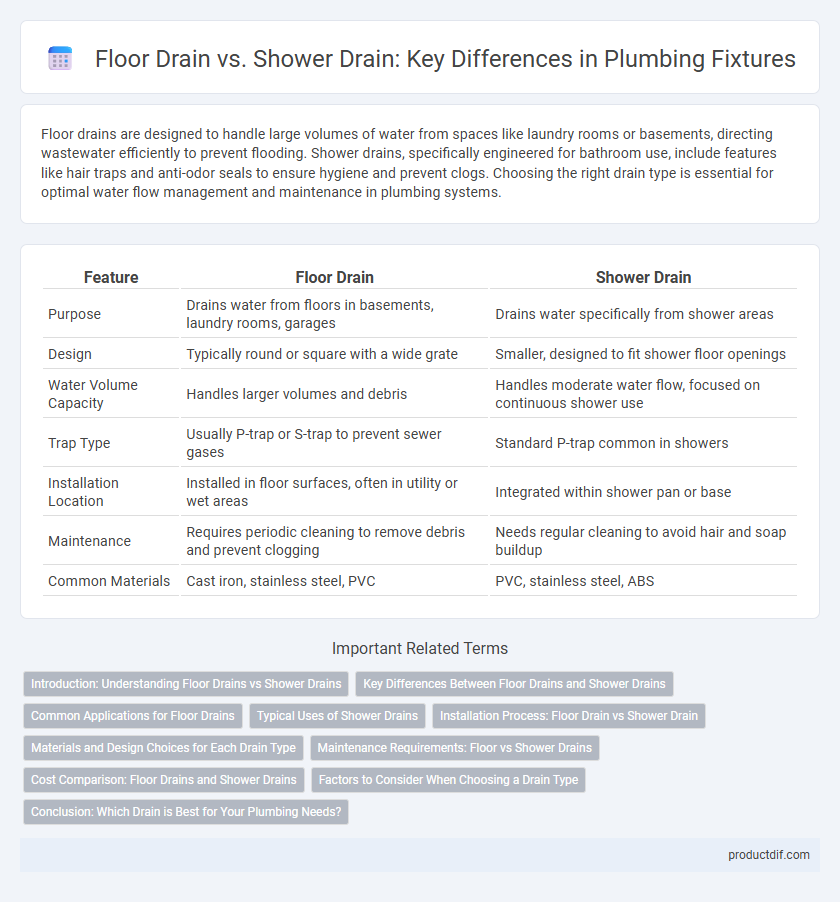
| Feature | Floor Drain | Shower Drain |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Drains water from floors in basements, laundry rooms, garages | Drains water specifically from shower areas |
| Design | Typically round or square with a wide grate | Smaller, designed to fit shower floor openings |
| Water Volume Capacity | Handles larger volumes and debris | Handles moderate water flow, focused on continuous shower use |
| Trap Type | Usually P-trap or S-trap to prevent sewer gases | Standard P-trap common in showers |
| Installation Location | Installed in floor surfaces, often in utility or wet areas | Integrated within shower pan or base |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic cleaning to remove debris and prevent clogging | Needs regular cleaning to avoid hair and soap buildup |
| Common Materials | Cast iron, stainless steel, PVC | PVC, stainless steel, ABS |
Introduction: Understanding Floor Drains vs Shower Drains
Floor drains are installed in various areas like basements, laundry rooms, and garages to direct excess water away and prevent flooding, while shower drains specifically handle water runoff within shower stalls. Floor drains typically feature a larger grate to accommodate debris and are connected to the main drainage system for effective water removal. Shower drains are designed with smaller openings to handle consistent water flow from showers, incorporating strainers to prevent clogging and maintain proper drainage.
Key Differences Between Floor Drains and Shower Drains
Floor drains are designed to handle large volumes of water from various sources like washing machines or sump pumps, featuring a flat grate and wider pipe diameter for quick drainage. Shower drains typically have a smaller grate and are integrated with waterproofing systems to effectively manage water flow and prevent leaks in shower enclosures. The primary difference lies in their intended use, installation location, and drainage capacity, impacting maintenance and functionality.
Common Applications for Floor Drains
Floor drains are commonly installed in basements, laundry rooms, commercial kitchens, and garage floors to prevent flooding and facilitate water drainage in areas prone to excess moisture. Unlike shower drains, which are specifically designed for water removal within shower stalls, floor drains manage larger volumes of water from various sources, including spillages and cleaning processes. Their robust design and strategic placement make them essential for maintaining hygiene and safety in both residential and industrial settings.
Typical Uses of Shower Drains
Shower drains are specifically designed to handle the high volume of water generated during daily showers, efficiently preventing water accumulation and ensuring proper drainage in wet areas. They typically feature a grated cover to block hair and debris, reducing the risk of clogs and maintaining hygiene within residential and commercial bathrooms. Unlike floor drains, shower drains are optimized for smaller, confined spaces and often connect to a P-trap to prevent sewer gases from entering living areas.
Installation Process: Floor Drain vs Shower Drain
Floor drain installation requires precise leveling to ensure effective water flow and prevent pooling, often involving connection to a building's main drainage system. Shower drain installation demands careful sealing and waterproofing to avoid leaks, typically positioned centrally to accommodate water runoff from the shower base. Both drains require proper venting and trap placement to maintain hygiene and prevent sewer gas ingress.
Materials and Design Choices for Each Drain Type
Floor drains commonly use durable materials such as cast iron, stainless steel, or PVC to withstand heavy foot traffic and potential chemical exposure, featuring grates designed for maximum debris filtration and water flow. Shower drains often utilize corrosion-resistant materials like brass or ABS plastic, with design choices emphasizing sleek profiles and efficient water drainage to prevent pooling and promote hygiene. Each drain type incorporates specialized features tailored to its environment, balancing durability, aesthetic appeal, and functionality.
Maintenance Requirements: Floor vs Shower Drains
Floor drains require regular cleaning to prevent debris buildup and odors, often involving removal of grates and siphon trap inspections. Shower drains demand frequent hair and soap scum removal to avoid clogs and slow drainage, with occasional use of enzyme cleaners to maintain pipe flow. Both drains benefit from periodic professional inspection to address hidden blockages and ensure optimal function.
Cost Comparison: Floor Drains and Shower Drains
Floor drains typically cost between $50 and $150, depending on materials and installation complexity, while shower drains range from $20 to $100 with simpler installation requirements. Installation expenses for floor drains can be higher due to the need for specialized piping and waterproofing, compared to shower drains that usually integrate directly into bathroom plumbing. Maintenance costs for floor drains might also be greater due to potential debris accumulation and the necessity for periodic cleaning to prevent clogs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Drain Type
Selecting between a floor drain and a shower drain depends on factors such as location, drainage capacity, and intended water flow. Floor drains require a higher flow rate and broader coverage for areas like laundry rooms or basements, while shower drains are designed for localized, high-volume water disposal in bathrooms. Material durability, ease of maintenance, and compatibility with existing plumbing systems also influence the optimal drain choice.
Conclusion: Which Drain is Best for Your Plumbing Needs?
Choosing between a floor drain and a shower drain depends on the specific plumbing requirements of your space, as floor drains effectively manage water from general areas like basements and laundry rooms, while shower drains are designed to handle the concentrated flow and higher volume of water in shower stalls. For optimal performance and to prevent water damage, it is essential to select the appropriate drain type that matches the location's water drainage needs, material compatibility, and installation specifications. Consulting plumbing codes and considering factors such as drainage capacity, trap design, and maintenance accessibility will help determine the best drain for your plumbing system.
Floor Drain vs Shower Drain Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com