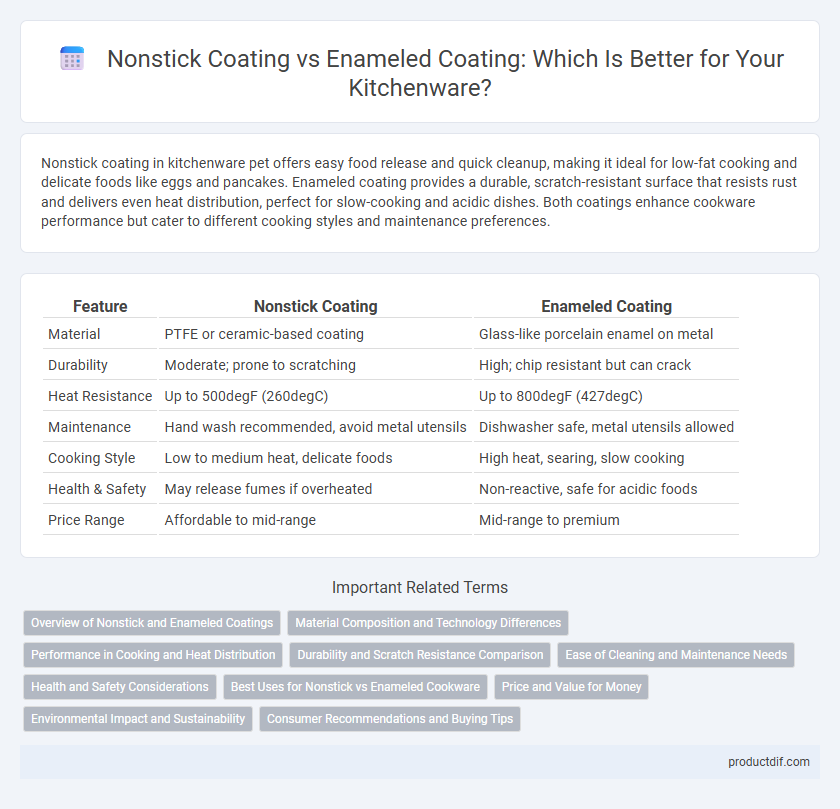
Nonstick coating in kitchenware pet offers easy food release and quick cleanup, making it ideal for low-fat cooking and delicate foods like eggs and pancakes. Enameled coating provides a durable, scratch-resistant surface that resists rust and delivers even heat distribution, perfect for slow-cooking and acidic dishes. Both coatings enhance cookware performance but cater to different cooking styles and maintenance preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nonstick Coating | Enameled Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material | PTFE or ceramic-based coating | Glass-like porcelain enamel on metal |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to scratching | High; chip resistant but can crack |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 500degF (260degC) | Up to 800degF (427degC) |
| Maintenance | Hand wash recommended, avoid metal utensils | Dishwasher safe, metal utensils allowed |
| Cooking Style | Low to medium heat, delicate foods | High heat, searing, slow cooking |
| Health & Safety | May release fumes if overheated | Non-reactive, safe for acidic foods |
| Price Range | Affordable to mid-range | Mid-range to premium |
Overview of Nonstick and Enameled Coatings
Nonstick coatings consist of polymers like PTFE that create a slick surface, preventing food from sticking and allowing for easy cleanup and low-fat cooking. Enameled coatings are made by fusing powdered glass to metal at high temperatures, providing a durable, non-reactive surface ideal for high-heat cooking and aesthetic appeal. Both coatings enhance cookware performance but differ in heat tolerance, maintenance, and cooking style compatibility.
Material Composition and Technology Differences
Nonstick coatings typically consist of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or ceramic compounds that create a slick, low-friction surface ideal for easy food release and minimal oil usage. Enameled coatings are made from layers of powdered glass fused onto metal, usually cast iron or steel, offering a durable, non-reactive, and heat-retentive finish that resists rust and corrosion. The technology behind nonstick coatings involves applying a polymer layer through spraying or dipping, while enameled coatings require a high-temperature kiln-firing process that vitrifies the glass to the cookware surface.
Performance in Cooking and Heat Distribution
Nonstick coatings provide superior food release and require less oil, enhancing cooking efficiency for delicate items like eggs and pancakes. Enameled coatings excel in even heat distribution and durability, making them ideal for slow-cooked dishes and high-temperature searing. While nonstick surfaces can degrade under high heat, enameled cookware maintains performance with resistance to scratching and thermal shock.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Nonstick coatings typically offer excellent scratch resistance but tend to degrade faster with frequent use and high heat, reducing overall durability. Enameled coatings provide superior durability due to their hard, glass-like surface that resists chipping and scratching over time even with heavy use. While nonstick surfaces enhance food release, enameled coatings maintain structural integrity longer, making them preferable for long-term kitchenware investment.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance Needs
Nonstick coatings offer superior ease of cleaning due to their smooth, slick surface that prevents food from adhering, requiring minimal scrubbing and gentle hand washing. Enameled coatings, while more durable and resistant to scratching, often need careful maintenance to avoid chipping and may require soaking or more thorough cleaning to remove stubborn residues. Regular use of non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents is recommended for both coatings to extend their lifespan and maintain performance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Nonstick coatings, typically made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), offer easy food release but may release toxic fumes when overheated above 500degF, posing health risks. Enameled coatings, composed of glass fused to metal, provide a non-reactive, chemical-free surface that withstands high temperatures without emitting harmful substances, making them safer for health-conscious cooking. Choosing enameled cookware reduces exposure to potential toxins and enhances long-term safety in daily kitchen use.
Best Uses for Nonstick vs Enameled Cookware
Nonstick cookware is ideal for cooking delicate foods such as eggs, pancakes, and fish due to its smooth, low-friction surface that prevents sticking and allows for easy cleanup. Enameled cookware excels in slow-cooking, braising, and simmering because the enamel coating provides even heat distribution and resists high temperatures without reacting to acidic ingredients. Choosing nonstick for quick, low-heat cooking and enameled pots for durable, high-heat recipes maximizes kitchen efficiency and cookware longevity.
Price and Value for Money
Nonstick coatings generally offer a lower upfront price and convenient easy-release cooking benefits, making them ideal for budget-conscious buyers seeking value in everyday use. Enameled coatings tend to have a higher initial cost but provide exceptional durability and resistance to scratches and high heat, delivering long-term value for those investing in premium cookware. Choosing between the two depends on balancing immediate affordability against extended lifespan and maintenance needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nonstick coatings often contain chemicals like PTFE and PFOA, which can release harmful toxins during manufacturing and disposal, posing environmental hazards. Enameled coatings, made from natural materials like glass fused to metal, offer a more sustainable option due to their durability and recyclability. Choosing enameled kitchenware reduces chemical pollution and supports eco-friendly waste management practices in household cookware.
Consumer Recommendations and Buying Tips
Choose nonstick coating cookware for easy food release and simple cleanup, ideal for low to medium-heat cooking and delicate foods like eggs and pancakes. Opt for enameled cookware when durability and versatility are priorities, as it resists scratching and is compatible with high heat and metal utensils. Consumers should inspect the coating for even application, verify compatibility with induction cooktops, and consider maintenance requirements to maximize longevity and performance.
Nonstick Coating vs Enameled Coating Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com