Baking steel offers superior heat conduction compared to pizza stones, resulting in faster and more even cooking for perfectly crispy pizza crusts. Unlike pizza stones, which absorb heat and may crack over time, baking steels are highly durable and resistant to thermal shock. The steel's ability to maintain consistent high temperatures helps achieve professional-quality pizza right in your home kitchen.
Table of Comparison
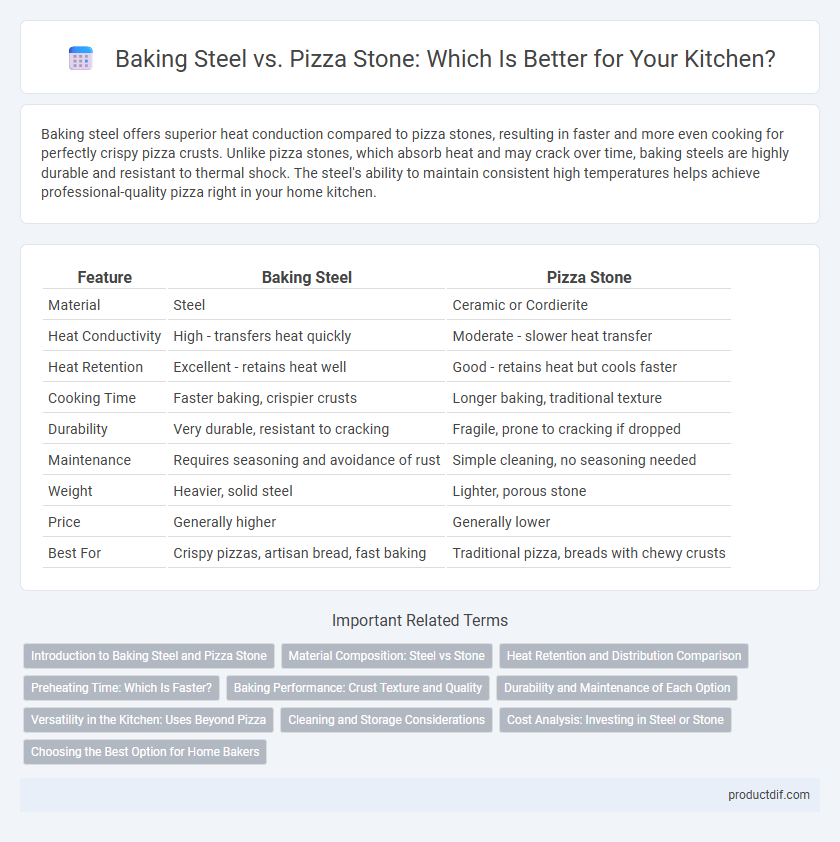
| Feature | Baking Steel | Pizza Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel | Ceramic or Cordierite |
| Heat Conductivity | High - transfers heat quickly | Moderate - slower heat transfer |
| Heat Retention | Excellent - retains heat well | Good - retains heat but cools faster |
| Cooking Time | Faster baking, crispier crusts | Longer baking, traditional texture |
| Durability | Very durable, resistant to cracking | Fragile, prone to cracking if dropped |
| Maintenance | Requires seasoning and avoidance of rust | Simple cleaning, no seasoning needed |
| Weight | Heavier, solid steel | Lighter, porous stone |
| Price | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Best For | Crispy pizzas, artisan bread, fast baking | Traditional pizza, breads with chewy crusts |
Introduction to Baking Steel and Pizza Stone
Baking steel is a flat, highly conductive steel plate that heats up quickly and provides superior heat retention, resulting in evenly cooked, crispy pizza crusts. Pizza stones, made from ceramic or cordierite, absorb moisture and distribute heat evenly to create a traditional, rustic texture while preventing sogginess. Both tools enhance home pizza baking but differ in heat conduction and durability, making baking steels ideal for faster cooking and pizza stones better for moisture absorption.
Material Composition: Steel vs Stone
Baking steel is composed of highly conductive carbon steel or stainless steel, allowing rapid and even heat transfer for crispier crusts. Pizza stone is typically made from ceramic, cordierite, or clay, which absorbs moisture and provides steady heat but heats up and cools down more slowly than steel. Steel's dense metal structure delivers superior thermal conductivity compared to the porous and heat-retentive nature of stone materials.
Heat Retention and Distribution Comparison
Baking steel offers superior heat retention and more even heat distribution compared to pizza stones, due to its higher thermal conductivity and thicker material. This ensures pizzas cook faster with a crispier crust while maintaining consistent oven temperatures. Pizza stones, made from ceramic or cordierite, heat more slowly and lose heat faster, which can result in longer cook times and less efficient heat transfer.
Preheating Time: Which Is Faster?
Baking steel heats up significantly faster than a pizza stone due to its higher thermal conductivity, reducing preheating time to around 30 minutes compared to 45-60 minutes for stone. The steel reaches optimal baking temperature quickly, ensuring a crispier crust in less time. Pizza stones retain heat well but require longer preheating to avoid uneven cooking.
Baking Performance: Crust Texture and Quality
Baking steel offers superior heat conductivity, resulting in a crispier, evenly browned crust that rivals professional pizza ovens. Pizza stones retain heat well but heat up more slowly, producing a slightly softer crust with more moisture. The steel's rapid heat transfer significantly enhances crust texture and overall baking quality, making it ideal for achieving a perfect balance of crunch and chewiness.
Durability and Maintenance of Each Option
Baking steel offers superior durability compared to pizza stones, as it resists cracking and chipping under high heat and frequent use. Pizza stones require careful handling and thorough drying after cleaning to prevent cracks and mold growth, making maintenance more labor-intensive. Steel plates also have the advantage of quick heating and easy cleaning, but they may be heavier and prone to rust without proper seasoning or storage.
Versatility in the Kitchen: Uses Beyond Pizza
Baking steel offers superior thermal conductivity, enabling faster, more even baking not only for pizza but also for bread, cookies, and roasted vegetables. Unlike pizza stones, the durable steel plate resists cracking and can double as a griddle for searing meats or making flatbreads. Its versatility makes baking steel an essential multi-purpose tool for diverse culinary applications beyond traditional pizza baking.
Cleaning and Storage Considerations
Baking steel requires minimal maintenance, as it is non-porous and resists cracking, making cleaning straightforward with just a scraper and warm water. Pizza stones absorb moisture and oils, necessitating gentle scrubbing without soap to prevent damage, and can be prone to cracking if exposed to thermal shock. For storage, baking steels are compact and durable, stacking easily in cabinets, while pizza stones need careful handling to avoid chipping or breaking during placement or removal.
Cost Analysis: Investing in Steel or Stone
Baking steel generally costs more upfront than pizza stones due to its durable steel composition, which offers superior heat conductivity and longevity. Pizza stones are more budget-friendly initially but may require replacement over time due to cracking or wear from repeated heating cycles. Considering long-term value, baking steel provides a cost-effective investment by enhancing cooking efficiency and reducing the need for frequent replacement.
Choosing the Best Option for Home Bakers
Baking steel offers superior heat conductivity and faster preheating compared to pizza stones, making it ideal for achieving crispy crusts in home baking. Pizza stones provide excellent heat retention and even distribution, which enhances moisture absorption for a perfectly baked crust. Home bakers should consider baking steel for durability and quick cooking, while pizza stones are preferable for traditional baking and ease of maintenance.
Baking steel vs pizza stone Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com