Ethical sourcing in jewelry prioritizes transparency, fair labor practices, and environmentally sustainable mining techniques to ensure that materials are obtained without exploiting workers or harming ecosystems. Conventional sourcing often relies on large-scale mining operations with less regard for social and environmental consequences, leading to issues such as child labor, habitat destruction, and conflict financing. Choosing ethically sourced jewelry supports responsible supply chains that promote social equity and environmental stewardship.
Table of Comparison
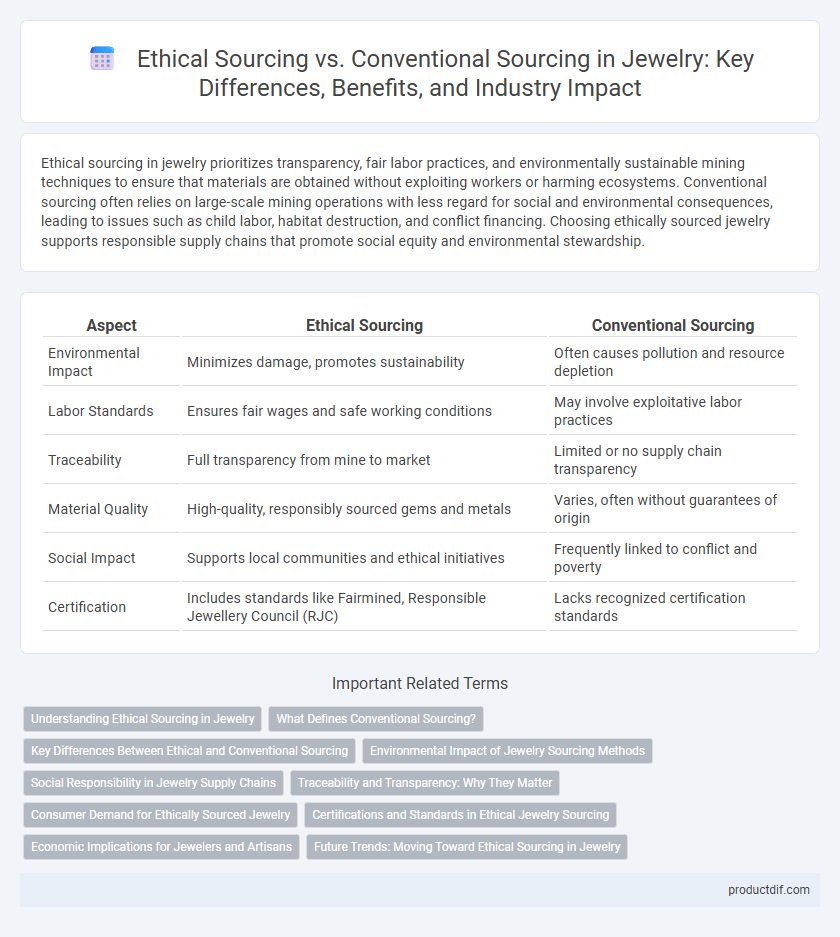
| Aspect | Ethical Sourcing | Conventional Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes damage, promotes sustainability | Often causes pollution and resource depletion |
| Labor Standards | Ensures fair wages and safe working conditions | May involve exploitative labor practices |
| Traceability | Full transparency from mine to market | Limited or no supply chain transparency |
| Material Quality | High-quality, responsibly sourced gems and metals | Varies, often without guarantees of origin |
| Social Impact | Supports local communities and ethical initiatives | Frequently linked to conflict and poverty |
| Certification | Includes standards like Fairmined, Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC) | Lacks recognized certification standards |
Understanding Ethical Sourcing in Jewelry
Ethical sourcing in jewelry emphasizes the responsible acquisition of materials, ensuring that gemstones, metals, and other components are mined and harvested without harming the environment or exploiting workers. This approach prioritizes transparency, fair labor practices, and environmental sustainability throughout the supply chain, contrasting with conventional sourcing, which often lacks these considerations. Brands committed to ethical sourcing invest in certifications like Fairtrade Gold and the Responsible Jewellery Council to validate their supply chain integrity and promote consumer trust.
What Defines Conventional Sourcing?
Conventional sourcing in jewelry involves the extraction and acquisition of precious metals and gemstones through traditional mining processes that often prioritize cost efficiency over environmental or social responsibility. This method frequently lacks transparency and may be associated with exploitative labor practices, environmental degradation, and insufficient supply chain accountability. Conventional sourcing contrasts with ethical sourcing by emphasizing volume and profit without mandated adherence to sustainability standards or fair trade principles.
Key Differences Between Ethical and Conventional Sourcing
Ethical sourcing in jewelry prioritizes transparency, fair labor practices, and environmental sustainability, ensuring materials come from conflict-free mines and responsibly managed resources. Conventional sourcing often overlooks these aspects, focusing primarily on cost and supply chain efficiency, which can lead to unethical labor conditions and environmental degradation. Key differences include the commitment to traceability, respect for human rights, and reduced ecological impact inherent in ethical sourcing compared to the often opaque and less regulated conventional methods.
Environmental Impact of Jewelry Sourcing Methods
Ethical sourcing in jewelry prioritizes sustainable mining practices that reduce habitat destruction, limit toxic waste, and promote biodiversity conservation compared to conventional sourcing, which often involves extensive environmental degradation and pollution. By using recycled metals and conflict-free gemstones, ethical sourcing minimizes carbon footprints and prevents harmful exploitation of natural resources. Conventional sourcing typically exploits ecosystems through open-pit mining and chemical leaching, resulting in soil erosion, water contamination, and loss of wildlife habitats.
Social Responsibility in Jewelry Supply Chains
Ethical sourcing in jewelry prioritizes fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and community empowerment throughout the supply chain, contrasting sharply with conventional sourcing often linked to exploitative labor and environmental harm. Certified organizations like the Responsible Jewellery Council set standards to ensure transparency and social responsibility, fostering trust and accountability. Consumers increasingly demand ethically sourced gemstones and metals, driving brands to adopt sustainable practices that uphold human rights and reduce social inequalities.
Traceability and Transparency: Why They Matter
Ethical sourcing in jewelry emphasizes traceability and transparency, ensuring materials are responsibly mined and conflict-free. Unlike conventional sourcing, which often lacks clear supply chain visibility, ethical practices enable consumers to verify the origin and environmental impact of gemstones and metals. This accountability fosters trust, supports sustainable mining communities, and minimizes exploitation in the global jewelry market.
Consumer Demand for Ethically Sourced Jewelry
Consumer demand for ethically sourced jewelry has surged as buyers increasingly prioritize sustainability and transparency in their purchases. Ethical sourcing involves using conflict-free gemstones and recycled metals, ensuring fair labor practices and minimizing environmental impact. Brands embracing ethical sourcing gain competitive advantage by aligning with growing market trends favoring responsible and socially conscious luxury goods.
Certifications and Standards in Ethical Jewelry Sourcing
Ethical jewelry sourcing prioritizes certifications such as Fairtrade, Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC), and Kimberley Process to ensure conflict-free materials and environmental responsibility. These standards verify supply chain transparency, promote fair labor practices, and minimize ecological impact, contrasting with conventional sourcing that often lacks stringent oversight. Consumers increasingly demand certified ethical jewelry to support sustainability and social accountability in the industry.
Economic Implications for Jewelers and Artisans
Ethical sourcing in jewelry prioritizes fair wages, sustainable materials, and transparent supply chains, often resulting in higher production costs but enhanced brand reputation and consumer trust. Conventional sourcing may lower immediate expenses but risks supply chain disruptions, reputational damage, and long-term economic instability for jewelers and artisans. Investing in ethical sourcing supports market differentiation, stabilizes artisan livelihoods, and aligns with growing consumer demand for socially responsible products.
Future Trends: Moving Toward Ethical Sourcing in Jewelry
Future trends in the jewelry industry increasingly emphasize ethical sourcing, driven by consumer demand for transparency and sustainability. Innovations in blockchain technology enhance traceability of minerals and gemstones, while certifications like the Responsible Jewellery Council gain prominence in ensuring conflict-free supply chains. Brands prioritizing ethical sourcing differentiate themselves by aligning with environmental and social governance standards, reflecting a broader shift towards responsible luxury.
Ethical Sourcing vs Conventional Sourcing Infographic
 productdif.com
productdif.com